
3C 449 is a low-redshift Fanaroff and Riley class I radio galaxy. It is thought to contain a highly warped circumnuclear disk surrounding the central active galactic nucleus (AGN). The name signifies that it was the 449th object of the Third Cambridge Catalog of Radio Sources (3C), published in 1959.

3C 305, also known as IC 1065, is a lenticular galaxy located in the constellation Draco. The galaxy is located 577 million light-years away from Earth. It has an active galactic nucleus and is classified as a Seyfert 2 galaxy. This galaxy was discovered by American astronomer Lewis Swift on April 7th, 1888.

3C 249.1 is a Seyfert galaxy located in the constellation Draco. It hosts a powerful radio source and is located at redshift 0.3115, with a peculiar radio structure. One of its radio lobes is classified as having a Fanaroff-Riley classification Type II, while the other lobe has no features nor containing hotspots.
3C 285 is a radio galaxy located in the constellation Canes Venatici. It is located about 1 bilion light years away. It is a Fanaroff-Riley 2 radio galaxy and is hosted in a disturbed spiral galaxy.

3C 438 is a Seyfert galaxy and Fanaroff and Riley class II radio galaxy located in the constellation Cygnus. The radio galaxy has two lobes and there is a radio jet leading to the south lobe, which also has a prominent double hot spot. There is age variation across the lobes.

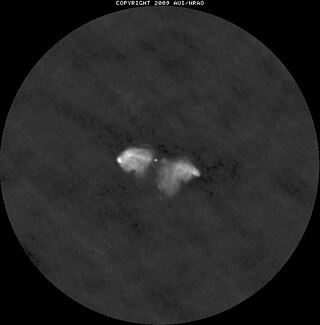
Hercules A is a bright astronomical radio source in the constellation Hercules corresponding to the galaxy 3C 348.

NGC 3862 is an elliptical galaxy located 300 million light-years away in the constellation Leo. Discovered by astronomer William Herschel on April 27, 1785, NGC 3862 is an outlying member of the Leo Cluster.

NGC 708 is an elliptical galaxy located 240 million light-years away in the constellation Andromeda and was discovered by astronomer William Herschel on September 21, 1786. It is classified as a cD galaxy and is the brightest member of Abell 262. NGC 708 is a weak FR I radio galaxy and is also classified as a type 2 Seyfert galaxy.

III Zw 2 is a Seyfert 1 galaxy located in the Pisces constellation. It has a redshift of 0.089 and is notable as the first of its kind to exhibit a superluminal jet.

An extended emission-line region (EELR) is a giant interstellar cloud ionized by the radiation of an active galactic nucleus (AGN) inside a galaxy or photons produced by the shocks associated with the radio jets. An EELR can appear as a resolved cloud in relative nearby galaxies and as narrow emission lines in more distant galaxies.

NGC 5920 is a large lenticular galaxy located in the Serpens constellation. Discovered on March 30, 1887, by American astronomer Lewis Swift, NGC 5920 is 711 million light-years distant from planet Earth. It is a narrow-line radio galaxy and about 300,000 light-years in diameter.

MRC 0406-244 also known as TN J0408-2418, is a radio galaxy producing an astrophysical jet, located in the constellation of Eridanus. At its redshift of 2.44, it is roughly ten billion light years from Earth.

4C +41.17 is a radio galaxy located in the constellation Auriga. With the redshift of 3.79, it is located nearly 11.7 billion light-years from Earth. At the time of its discovery in 1988, it was one of the most distant galaxies ever seen.

PKS 1345+125 known as PKS 1345+12 and 4C +12.50, is an ultraluminous infrared galaxy (ULIG) with an active galactic nucleus, located in the constellation Boötes. With a redshift of 0.121740, the galaxy is located 1.7 billion light-years from Earth.

3C 346 is an elliptical galaxy located in the constellation Hercules. It is located nearly 2.5 billion light years away from Earth and classified a Seyfert galaxy and a compact steep-spectrum source (CSS), although later studies confirm it as a Fanaroff-Riley class II source.

3C 459 known as IRAS 23140+0348, is a radio galaxy located in the constellation Pisces. It is located 2.74 billion light years from Earth and is classified as a Seyfert 2 and LINER galaxy.

3C 138 is a quasar located in the constellation of Taurus. It has a redshift of (z) 0.76. The radio spectrum of this source appears both compact and steep, making it a compact steep-spectrum radio quasar. It is also one of the few 3C objects showing a defined and turn-over in its electromagnetic spectrum at low frequencies.

3C 309.1 is a quasar located in the constellation of Ursa Minor. It has a redshift (z) of 0.90 and was first identified as an astronomical radio source from the Third Cambridge Catalogue of Radio Sources by in 1966. This object contains a compact steep spectrum (CSS) source, and is classified as one of the brightest and largest of its kind.

3C 196.1 is a low-excitation radio galaxy located in the constellation of Hydra. It has a redshift of 0.198 and was first discovered as an astronomical radio source in 1965. This object resides as the brightest cluster galaxy (BCG) of a cool core galaxy cluster CIZA J0815.4-0308 located at the same redshift, with its source being best described as a HyMOR.

3C 356 is a distant radio galaxy located in the constellation of Draco, hosted by a merging pair of elliptical galaxies located at redshift (z) 1.079 with two radio cores having a separation gap of 5 arcseconds. It was first discovered as an astronomical radio source by P. Veron from a 3C revised catalogue in 1966 and such, shows an alignment effect at both wavelengths. The X-ray source luminosity for this galaxy is estimated to be 2.5 x 1044 erg s-1.




















