| Other centuries |
| 1st century | 2nd century | 3rd century |
Events from the 2nd century in Roman Britain .
| Other centuries |
| 1st century | 2nd century | 3rd century |
Events from the 2nd century in Roman Britain .

Roman Britain was the territory that became the Roman province of Britannia after the Roman conquest of Britain, consisting of a large part of the island of Great Britain. The occupation lasted from AD 43 to AD 410.

Lucius Septimius Severus was a Roman politician who served as emperor from 193 to 211. He was born in Leptis Magna in the Roman province of Africa. As a young man he advanced through the customary succession of offices under the reigns of Marcus Aurelius and Commodus. Severus was the final contender to seize power after the death of the emperor Pertinax in 193 during the Year of the Five Emperors.

The 2nd century is the period from AD 101 through AD 200 (CC) in accordance with the Julian calendar. It is considered part of the Classical era, epoch, or historical period.
The 180s decade ran from January 1, 180, to December 31, 189.
The 190s decade ran from January 1, 190, to December 31, 199.

Year 193 (CXCIII) was a common year starting on Monday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Sosius and Ericius. The denomination 193 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Decimus Clodius Albinus was a Roman imperial pretender between 193 and 197. He was proclaimed emperor by the legions in Britain and Hispania after the murder of Pertinax in 193. Initially Albinus cooperated with another contender for the throne, Septimius Severus, but the two turned on each other in 196 and commenced a civil war. Albinus died in battle the following year.

Legio VI Victrix was a legion of the Imperial Roman army founded in 41 BC by the general Octavian. It was the twin legion of VI Ferrata and perhaps held veterans of that legion, and some soldiers kept to the traditions of the Caesarian legion.

The Caledonians or the Caledonian Confederacy were a Brittonic-speaking (Celtic) tribal confederacy in what is now Scotland during the Iron Age and Roman eras. The Greek form of the tribal name gave rise to the name Caledonia for their territory. The Caledonians were considered to be a group of Britons, but later, after the Roman conquest of the southern half of Britain, the northern inhabitants were distinguished as Picts, thought to be a related people who would have also spoken a Brittonic language. The Caledonian Britons were thus enemies of the Roman Empire, which was the state then administering most of Great Britain as the Roman province of Britannia.

Britannia Superior was a province of Roman Britain created after the civil war between Septimius Severus and Clodius Albinus. Although Herodian credits Severus with dividing Roman Britain into the Northern territory of Britannia Inferior and the Southern territory of Britannia Superior, modern scholarship argues that it is more likely that Caracella was the person who made the split sometime in the early 3rd century CE. The previous British capital Londinium remained the centre of Britannia Superior while Eboracum, or modern York was the capital of Britannia Inferior. Epigraphical evidence shows that Upper Britain encompassed approximately what is now Wales, southern England and East Anglia. However, the official boundary between Britannia Superior and Inferior is still unclear.
Ulpius Marcellus was a Roman consular governor of Britannia who returned there as general of the later 2nd century.
Virius Lupus was a Roman soldier and politician of the late 2nd and early 3rd century.

The Battle of Lugdunum, also called the Battle of Lyon, was fought on 19 February 197 at Lugdunum, between the armies of the Roman emperor Septimius Severus and of the Roman usurper Clodius Albinus. Severus' victory finally established him as the sole emperor of the Roman Empire following the Year of the Five Emperors and immediate aftermath.
Cohors secunda Gallorum veterana equitata was a mixed infantry and cavalry regiment of the Auxilia corps of the Imperial Roman army. It was stationed, in the 2nd and 3rd centuries, in a fort near Hadrian's Wall in Britain.
Events from the 3rd century in Roman Britain.
Events from the 1st century in Roman Britain.
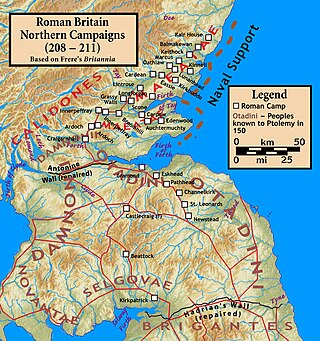
The Roman invasion of Caledonia was launched in 208 by the Roman emperor Septimius Severus. The invasion lasted until late 210, when the emperor became ill and died at Eboracum (York) on 4 February 211. The war started well for the Romans with Severus managing to quickly reach the Antonine Wall, but when Severus pushed north into the highlands he became bogged down in a guerrilla war and he was never able to fully subjugate Caledonia. He reoccupied many forts built by Agricola over 100 years earlier, following the Battle of Mons Graupius, and crippled the ability of the Caledonians to raid Roman Britain.
Cohors PrimÆ Ælia Dacorvm was an infantry regiment of the Auxilia corps of the Imperial Roman army. It was first raised by the Roman emperor Hadrian in the Roman province of Dacia not later than AD 125 and its last surviving record dates c. 400. It was deployed, for virtually its entire history, in forts on Hadrian's Wall on the northern frontier of Britannia province.