| Other centuries |
| Prehistory | 1st century | 2nd century |
Events from the 1st century in Roman Britain .
| Other centuries |
| Prehistory | 1st century | 2nd century |
Events from the 1st century in Roman Britain .

Boudica or Boudicca was a queen of the ancient British Iceni tribe, who led a failed uprising against the conquering forces of the Roman Empire in AD 60 or 61. She is considered a British national heroine and a symbol of the struggle for justice and independence.
AD 43 (XLIII) was a common year starting on Tuesday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Caesar and Vitellius. The denomination AD 43 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

The 60s decade ran from January 1, AD 60, to December 31, AD 69.

AD 60 (LX) was a leap year starting on Tuesday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Nero and Lentulus. The denomination AD 60 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
AD 61 (LXI) was a common year starting on Thursday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Turpilianus and Caesennius. The denomination AD 61 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

The Roman conquest of Britain was the Roman Empire's conquest of most of the island of Britain, which was inhabited by the Celtic Britons. It began in earnest in AD 43 under Emperor Claudius, and was largely completed in the southern half of Britain by AD 87, when the Stanegate was established. The conquered territory became the Roman province of Britannia. Attempts to conquer northern Britain (Caledonia) in the following centuries were not successful.

Caratacus was a 1st-century AD British chieftain of the Catuvellauni tribe, who resisted the Roman conquest of Britain.

Cartimandua or Cartismandua was a 1st-century queen of the Brigantes, a Celtic people living in what is now northern England. She came to power around the time of the Roman conquest of Britain, and formed a large tribal agglomeration that became loyal to Rome. The only account of her is by the Roman historian Tacitus, through which she appears to have been widely influential in early Roman Britain.

Gaius Suetonius Paulinus was a Roman general best known as the commander who defeated Boudica and her army during the Boudican revolt.

Aulus Plautius was a Roman politician and general of the mid-1st century. He began the Roman conquest of Britain in 43, and became the first governor of the new province, serving from 43 to 46.

The Iceni or Eceni were an ancient tribe of eastern Britain during the Iron Age and early Roman era. Their territory included present-day Norfolk and parts of Suffolk and Cambridgeshire, and bordered the area of the Corieltauvi to the west, and the Catuvellauni and Trinovantes to the south. In the Roman period, their capital was Venta Icenorum at modern-day Caistor St Edmund.
Quintus Petillius Cerialis Caesius Rufus, otherwise known as Quintus Petillius Cerialis, was a Roman general and administrator who served in Britain during Boudica's rebellion and went on to participate in the civil wars after the death of Nero. He later crushed the rebellion of Julius Civilis and returned to Britain as its governor.

Venutius was a 1st-century king of the Brigantes in northern Britain at the time of the Roman conquest. Some have suggested he may have belonged to the Carvetii, a tribe that probably formed part of the Brigantes confederation.
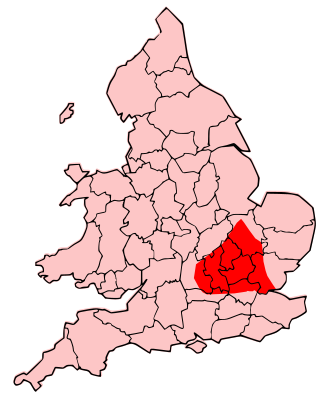
The Catuvellauni were a Celtic tribe or state of southeastern Britain before the Roman conquest, attested by inscriptions into the 4th century.

Cunobeline or Cunobelin, also known by his name's Latin form Cunobelinus, was a king in pre-Roman Britain from about AD 9 to about AD 40. He is mentioned in passing by the classical historians Suetonius and Dio Cassius, and many coins bearing his inscription have been found. He controlled a substantial portion of south-eastern Britain, including the territories of the Catuvellauni and the Trinovantes, and is called "King of the Britons" by Suetonius. Cunobeline may have been a client king of Rome, based on the images and legends appearing on his coins. Cunobeline appears in British legend as Cynfelyn (Welsh), Kymbelinus or Cymbeline, as in the play by William Shakespeare.
Togodumnus was king of the British Catuvellauni tribe, whose capital was at St. Albans, at the time of the Roman conquest. He can probably be identified with the legendary British king Guiderius. He is usually thought to have led the fight against the Romans alongside his brother, but to have been killed early in the campaign. However, some authorities now argue that he sided with the Romans and is one and the same person as the client-king Tiberius Claudius Cogidubnus, whose original name may have been Togidubnus or Togodumnus.

The Brigantes were Ancient Britons who in pre-Roman times controlled the largest section of what would become Northern England. Their territory, often referred to as Brigantia, was centred in what was later known as Yorkshire. The Greek geographer Ptolemy named the Brigantes as a people in Ireland also, where they could be found around what is now Wexford, Kilkenny and Waterford, while another people named Brigantii is mentioned by Strabo as a sub-tribe of the Vindelici in the region of the Alps.

Publius Ostorius Scapula was a Roman statesman and general who governed Britain from 47 until his death, and was responsible for the defeat and capture of Caratacus.
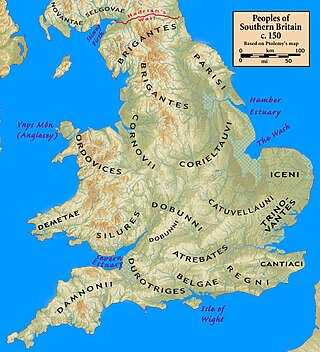
The Roman client kingdoms in Britain were native tribes which chose to align themselves with the Roman Empire because they saw it as the best option for self-preservation or for protection from other hostile tribes. Alternatively, the Romans created some client kingdoms when they felt influence without direct rule was desirable. Client kingdoms were ruled by client kings. In Latin these kings were referred to as rex sociusque et amicus, which translates to "king, ally, and friend". The type of relationships between client kingdoms and Rome was reliant on the individual circumstances in each kingdom.

The Boudican revolt was an armed uprising by native Celtic Britons against the Roman Empire during the Roman conquest of Britain. It took place circa AD 60–61 in the Roman province of Britain, and was led by Boudica, the Queen of the Iceni tribe. The uprising was motivated by the Romans' failure to honour an agreement they had made with Boudica's husband, Prasutagus, regarding the succession of his kingdom upon his death, and by the brutal mistreatment of Boudica and her daughters by the occupying Romans.