| Other centuries |
| 4th century | 5th century | 6th century |
Events from the 5th century in England . Note that many of these dates may only be approximate.
| Other centuries |
| 4th century | 5th century | 6th century |
Events from the 5th century in England . Note that many of these dates may only be approximate.

Ambrosius Aurelianus was a war leader of the Romano-British who won an important battle against the Anglo-Saxons in the 5th century, according to Gildas. He also appeared independently in the legends of the Britons, beginning with the 9th-century Historia Brittonum. Eventually, he was transformed by Geoffrey of Monmouth into the uncle of King Arthur, the brother of Arthur's father Uther Pendragon, as a ruler who precedes and predeceases them both. He also appears as a young prophet who meets the tyrant Vortigern; in this guise, he was later transformed into the wizard Merlin.
Ælle is recorded in much later medieval sources as the first king of the South Saxons, reigning in what is now called Sussex, England, from 477 to perhaps as late as 514.

Hengist and Horsa are Germanic brothers said to have led the Angles, Saxons and Jutes in their supposed invasion of Britain in the 5th century. Tradition lists Hengist as the first of the Jutish kings of Kent.
The 440s decade ran from January 1, 440, to December 31, 449.

Year 455 (CDLV) was a common year starting on Saturday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Valentinianus and Anthemius. The denomination 455 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Year 447 (CDXLVII) was a common year starting on Wednesday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Calepius and Ardabur. The denomination 447 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Vortigern, also spelled Vortiger, Vortigan, Voertigern and Vortigen, was a 5th-century warlord in Britain, known perhaps as a king of the Britons or at least connoted as such in the writings of Bede and Gildas. His existence is contested by scholars and information about him is obscure.
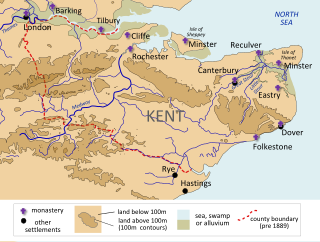
The Kingdom of the Kentish, today referred to as the Kingdom of Kent, was an early medieval kingdom in what is now South East England. It existed from either the fifth or the sixth century AD until it was fully absorbed into the Kingdom of Wessex in the late 9th century and later into the Kingdom of England in the early 10th century.
Vortimer, also known as Saint Vortimer, is a figure in British tradition, a son of the 5th-century Britonnic ruler Vortigern. He is remembered for his fierce opposition to his father's Saxon allies. In Geoffrey of Monmouth's Historia Regum Britanniae, he overthrows his father and reigns as King of Britain for a brief period before his death restores Vortigern to power.
The Treason of the Long Knives is an account of a massacre of British Celtic chieftains by Anglo-Saxon soldiers at a peace conference on Salisbury Plain in the 5th century. The story is thought to be pseudohistorical as the only surviving records mentioning it are centuries later in the semi-mythological histories of the Historia Brittonum and the Historia Regum Britanniae. Though a popular cautionary tale in medieval Europe, there is no other historical evidence for The Treason of the Long Knives. Most historians interpret the story as a purely literary construction.
Octa was an Anglo-Saxon King of Kent during the 6th century. Sources disagree on his relationship to the other kings in his line; he may have been the son of Hengist or Oisc, and may have been the father of Oisc or Eormenric. The dates of his reign are unclear, but he may have ruled from 512 to 534 or from 516 to 540. Despite his shadowy recorded history Octa made an impact on the Britons, who describe his deeds in several sources.

The Battle of Aylesford or Epsford was fought between Britons and Anglo-Saxons recorded in the Anglo-Saxon Chronicle and the Historia Brittonum. Both sources concur that it involved the Anglo-Saxon leaders Hengist and Horsa on one side and the family of Vortigern on the other, but neither says who won the battle. It was fought near Æglesthrep, presumed to be Aylesford, in Kent.
The Timeline of conflict in Anglo-Saxon Britain is concerned with the period of history from just before the departure of the Roman Army, in the 4th century, to just after the Norman Conquest in the 11th century.

Ebbsfleet is a hamlet near Ramsgate, Kent, at the head of Pegwell Bay. Historically it was a peninsula on the southern coast of the Isle of Thanet, marking the eastern end of the Wantsum Channel that separated Thanet from the Kentish mainland. It is in the civil parish of Minster-in-Thanet.

Rowena in the Matter of Britain was the daughter of the purported Anglo-Saxon chief Hengist and wife of Vortigern, "King of the Britons". Presented as a beautiful femme fatale, she won her people the Kingdom of Kent through her treacherous seduction of Vortigern. Contemporary sources are nearly non-existent, so it is impossible to know if she actually existed.
The Battle of Mercredesburne was one of three battles fought as part of the conquest of what became the Kingdom of Sussex in southern England. The battles were fought between the Saxon leader Ælle's army and the local Britons.

The white dragon is a symbol associated in Welsh mythology with the Anglo-Saxons.

The Battle of Guoloph, also known as the Battle of Wallop, took place in the 5th century. Various dates have been put forward: 440 AD by Alfred Anscombe, 437 AD according to John Morris, and 458 by Nikolai Tolstoy. It took place at what is now Nether Wallop, 15 kilometers southeast of Amesbury, in the district of Test Valley, northeastern Hampshire. The battle was an internal conflict between the rival Britonnic forces of Ambrosius Aurelianus and Vortigern (Vitalinus).
Budic I of Brittany was the king of Brittany, inheriting the title over the territory from his father, Aldroen of Brittany.