In chemistry, a pentose is a monosaccharide with five carbon atoms. The chemical formula of all pentoses is C
5H
10O
5, and their molecular weight is 150.13 g/mol.
Cubane (C8H8) is a synthetic hydrocarbon molecule that consists of eight carbon atoms arranged at the corners of a cube, with one hydrogen atom attached to each carbon atom. A solid crystalline substance, cubane is one of the Platonic hydrocarbons and a member of the prismanes. It was first synthesized in 1964 by Philip Eaton and Thomas Cole. Before this work, researchers believed that cubic carbon-based molecules would be too unstable to exist. The cubic shape requires the carbon atoms to adopt an unusually sharp 90° bonding angle, which would be highly strained as compared to the 109.45° angle of a tetrahedral carbon. Once formed, cubane is quite kinetically stable, due to a lack of readily available decomposition paths. It is the simplest hydrocarbon with octahedral symmetry.

The Grignard reaction is an organometallic chemical reaction in which alkyl, allyl, vinyl, or aryl-magnesium halides is added to a carbonyl group in an aldehyde or ketone. This reaction is important for the formation of carbon–carbon bonds. The reaction of an organic halide with magnesium is not a Grignard reaction, but provides a Grignard reagent.

Organolithium reagents are organometallic compounds that contain carbon – lithium bonds. These reagents are important in organic synthesis, and are frequently used to transfer the organic group or the lithium atom to the substrates in synthetic steps, through nucleophilic addition or simple deprotonation. Organolithium reagents are used in industry as an initiator for anionic polymerization, which leads to the production of various elastomers. They have also been applied in asymmetric synthesis in the pharmaceutical industry. Due to the large difference in electronegativity between the carbon atom and the lithium atom, the C-Li bond is highly ionic. Owing to the polar nature of the C-Li bond, organolithium reagents are good nucleophiles and strong bases. For laboratory organic synthesis, many organolithium reagents are commercially available in solution form. These reagents are highly reactive, and are sometimes pyrophoric.

Diethyl malonate, also known as DEM, is the diethyl ester of malonic acid. It occurs naturally in grapes and strawberries as a colourless liquid with an apple-like odour, and is used in perfumes. It is also used to synthesize other compounds such as barbiturates, artificial flavourings, vitamin B1, and vitamin B6.
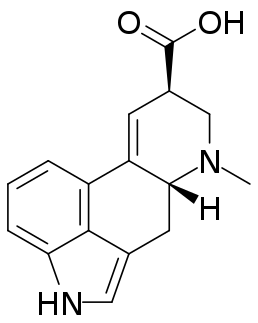
Lysergic acid, also known as D-lysergic acid and (+)-lysergic acid, is a precursor for a wide range of ergoline alkaloids that are produced by the ergot fungus and found in the seeds of Turbina corymbosa (ololiuhqui), Argyreia nervosa, and Ipomoea tricolor. Amides of lysergic acid, lysergamides, are widely used as pharmaceuticals and as psychedelic drugs (LSD). Lysergic acid received its name as it was a product of the lysis of various ergot alkaloids.

Organoborane or organoboron compounds are chemical compounds of boron and carbon that are organic derivatives of BH3, for example trialkyl boranes. Organoboron chemistry or organoborane chemistry is the chemistry of these compounds.
Organosulfur compounds are organic compounds that contain sulfur. They are often associated with foul odors, but many of the sweetest compounds known are organosulfur derivatives, e.g., saccharin. Nature abounds with organosulfur compounds—sulfur is essential for life. Of the 20 common amino acids, two are organosulfur compounds, and the antibiotics penicillin and sulfa drugs both contain sulfur. While sulfur-containing antibiotics save many lives, sulfur mustard is a deadly chemical warfare agent. Fossil fuels, coal, petroleum, and natural gas, which are derived from ancient organisms, necessarily contain organosulfur compounds, the removal of which is a major focus of oil refineries.
Okadaic acid, C44H68O13, is a toxin produced by several species of dinoflagellates, and is known to accumulate in both marine sponges and shellfish. One of the primary causes of diarrhetic shellfish poisoning, okadaic acid is a potent inhibitor of specific protein phosphatases and is known to have a variety of negative effects on cells. A polyketide, polyether derivative of a C38 fatty acid, okadaic acid and other members of its family have shined light upon many biological processes both with respect to dinoflagellete polyketide synthesis as well as the role of protein phosphatases in cell growth.

Orthocarbonic acid (methanetetrol) is the name given to a hypothetical compound with the chemical formula H4CO4 or C(OH)4. Its molecular structure consists of a single carbon atom bonded to four hydroxy groups. It would be therefore a fourfold alcohol. In theory it could lose four protons to give the hypothetical oxocarbon anion CO4−
4 (orthocarbonate), and is therefore considered an oxoacid of carbon.
Squaric acid, also called quadratic acid because its four carbon atoms approximately form a square, is a dibasic organic acid with the chemical formula C4O2(OH)2.

Meldrum's acid or 2,2-dimethyl-1,3-dioxane-4,6-dione is an organic compound with formula C
6H
8O
4. Its molecule has a heterocyclic core with four carbon and two oxygen atoms; the formula can also be written as [−O−(C
2)−O−(C=O)−(CH
2)−(C=O)−].

Equilenin, also known as 6,8-didehydroestrone, as well as estra-1,3,5(10),6,8-pentaen-3-ol-17-one, is a naturally occurring steroidal estrogen obtained from the urine of pregnant mares. It is used as one of the components in conjugated estrogens. It was the first complex natural product to be fully synthesized, in work reported by 1940 by Bachmann and Wilds.

Phenylboronic acid or benzeneboronic acid, abbreviated as PhB(OH)2 where Ph is the phenyl group C6H5-, is a boronic acid containing a phenyl substituent and two hydroxyl groups attached to boron. Phenylboronic acid is a white powder and is commonly used in organic synthesis. Boronic acids are mild Lewis acids which are generally stable and easy to handle, making them important to organic synthesis.
A homologation reaction, also known as homologization, is any chemical reaction that converts the reactant into the next member of the homologous series. A homologous series is a group of compounds that differ by a constant unit, generally a (-CH2-) group. The reactants undergo a homologation when the number of a repeated structural unit in the molecules is increased. The most common homologation reactions increase the number of methylene (-CH2-) units in saturated chain within the molecule. For example, the reaction of aldehydes or ketones with diazomethane or methoxymethylenetriphenylphosphine to give the next homologue in the series.
In enzymology, a leucine-tRNA ligase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Pyrethrin I is one of the two pyrethrins, natural organic compounds with potent insecticidal activity. It is an ester of (+)-trans-chrysanthemic acid with (S)-(Z)-pyrethrolone.
The imine Diels–Alder reaction involves the transformation of all-carbon dienes and imine dienophiles into tetrahydropyridines.
An insertion reaction is a chemical reaction where one chemical entity interposes itself into an existing bond of typically a second chemical entity e.g.:

Trifluoroperacetic acid is an organofluorine compound, the peroxy acid analog of trifluoroacetic acid, with the condensed structural formula CF
3COOOH. It is a strong oxidizing agent for organic oxidation reactions, such as in Baeyer–Villiger oxidations of ketones. It is the most reactive of the organic peroxy acids, allowing it to successfully oxidise relatively unreactive alkenes to epoxides where other peroxy acids are ineffective. It can also oxidise the chalcogens in some functional groups, such as by transforming selenoethers to selones. It is a potentially explosive material and is not commercially available, but it can be quickly prepared as needed. Its use as a laboratory reagent was pioneered and developed by William D. Emmons.











