
The M27 is a motorway in Hampshire, England. It is 27.9 miles (44.9 km) long and runs between Cadnam and Portsmouth. It was opened in stages between 1975 and 1983, providing the largest two urban areas in Hampshire with a direct motorway link. An extension into the county of West Sussex was planned but never constructed. A number of smaller motorways were proposed, connecting the city centres of Southampton and Portsmouth to the motorway; of these only the M271 and M275 were built. Three sections of the M27 have since been widened to four lanes each way, the first between junctions 7 and 8, the second between junctions 3 and 4, and the third begins at the slip road where junction 11 joins until mid-way to junction 12.
M27, M.27 or M-27 may refer to:

The A27 is a major road in England. It runs from its junction with the A36 at Whiteparish in the county of Wiltshire, follows the south coast of Hampshire and West Sussex, and terminates at Pevensey in East Sussex.

The A31 is a major trunk road in southern England that runs from Guildford in Surrey to Bere Regis in Dorset. Its best-known section is the Hog's Back, a ridge forming part of the North Downs between Guildford and Farnham in Surrey.

Gagra is a town in Abkhazia/Georgia, sprawling for 5 km on the northeast coast of the Black Sea, at the foot of the Caucasus Mountains. Its subtropical climate made Gagra a popular health resort in Imperial Russian and Soviet times.
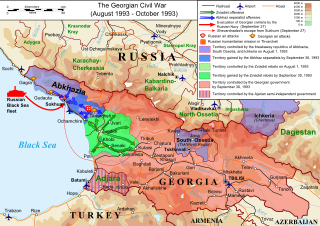
The Georgian Civil War lasted from 1991 to 1993 in the South Caucasian country of Georgia. It consisted of inter-ethnic and international conflicts in the regions of South Ossetia and Abkhazia, as well as the violent military coup d'état against the first democratically-elected President of Georgia, Zviad Gamsakhurdia, and his subsequent uprising in an attempt to regain power.

Politics in Abkhazia is dominated by its conflict with Georgia. Abkhazia became de facto independent from Georgia after the 1992–1993 war, but its de jure independence has only been recognised by a few other countries. Abkhazia is a presidential representative democratic republic with a multi-party system, wherein the President is both head of state and head of government. Executive power is exercised by the government of the Republic of Abkhazia. Legislative power is vested in both the government and the People's Assembly of Abkhazia.

The history of Abkhazia, a region in the South Caucasus, spans more than 5,000 years from its settlement by the lower-paleolithic hunter-gatherers to its present status as a partially recognized state.

Abkhazian railway is a rail operator in the partially recognised state of Abkhazia. Under a monopoly agreement, it is fully managed and partially owned by Russian Railways for a ten year contract from 2009 to 2019.

The A1025 is a significant road located in Harlow, England, serving as a vital transportation link within the region. It connects the A1169 with M11 Junction 7A, facilitating access to the motorway network for local and through traffic. Notably, an of extension to the M11 was opened to traffic on 10 June 2022, enhancing connectivity to the motorway. The road previously terminated on the A414, Before its current designation. and before that it was allocated to a different route in Norwich, which is now the A147 and A1242. In the road traffic statistics for 2020, the road accommodates 8,400 vehicles per day, while this significantly increases in between A1169 and A1019, with 28,700 vehicles per day with the A1019 and A414, indicating higher traffic volume towards the latter section.

Abkhazia, officially the Republic of Abkhazia, is a partially recognised state in the South Caucasus, on the eastern coast of the Black Sea, at the intersection of Eastern Europe and West Asia. It covers 8,665 square kilometres (3,346 sq mi) and has a population of around 245,000. Its capital and largest city is Sukhumi.

European route E 97 is an A-class European Route in Ukraine, Russia, Georgia, and Turkey. The highway runs for 1,360 kilometres (850 mi) in total. It connects the North Black Sea region with the South Black Sea region along the eastern shores of the sea.
Vesyoloye is a rural locality in Nizhneshilovsky Rural Okrug under the administrative jurisdiction of Adlersky City District of the City of Sochi. Population: 4,100.

Georgia's road network plays an important role in both domestic and international traffic with the four neighboring countries. This is expressed in the road numbering system. The country has a network of 13 internationally oriented trunk highways that connect the capital Tbilisi, home to about a third of the national population, with its four neighboring countries. This is also the backbone of a network of domestic oriented national roads connecting vital regions with each other.

The Georgian S1 route, is a "road of international importance" with a registered length of 542.7 kilometres (337.2 mi) within the Georgian classification system, which makes it the longest Georgian highway route. It runs from Tbilisi via Mtskheta, Gori, Khashuri, Zestaponi, Kutaisi, Samtredia, Senaki, Zugdidi, Sukhumi and Gagra to the border with Russia near Leselidze at the northwestern tip of the country, covering in practice 537 kilometres (334 mi). After crossing the Georgia–Russia border in breakaway Abkhazia, the highway continues to Sochi and Krasnodar as A147. It is part of European E60, E97 and E117 routes and Asian Highways AH5, AH81 and AH82, and connects with six other S-routes.

Russian-occupied territories in Georgia are areas of Georgia that have been occupied by Russia since the Russo-Georgian War in 2008. They consist of the regions of the Autonomous Republic of Abkhazia and the former South Ossetian Autonomous Region of Soviet Georgia, whose status is a matter of international dispute.

The Georgian S3 route, also known as Mtskheta-Stepantsminda-Larsi or Georgian Military Road, is a "road of international importance" within the Georgian road network and runs from Mtskheta to the border with Russia near Stepantsminda with a length of 139 kilometres (86 mi). After crossing the Georgian-Russian border the highway continues as A161 to Vladikavkaz, the capital of Russia's North Ossetia–Alania federal republic. The highway is the only open land route between Russia and Georgia (country), while routes via Georgian breakaways South Ossetia and Abkhazia are effectively closed for through traffic.
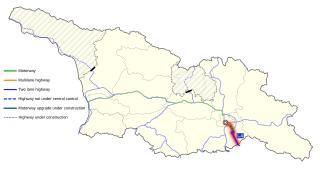
The Georgian S4 route, also known as Tbilisi–Red Bridge or Rustavi Highway, is a "road of international importance" within the Georgian road network and runs from Tbilisi via Rustavi city to the border with Azerbaijan at the Red Bridge over a distance of 57 kilometres (35 mi). After crossing the Georgian-Azerbaijan border the highway continues as M2 to Ganja and Baku.
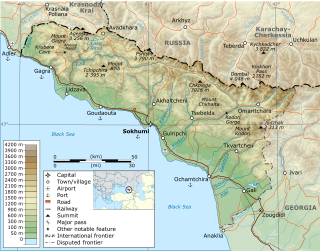
The Abkhazia–Georgia separation line is a de facto boundary set up in aftermath of the War in Abkhazia and Russo-Georgian War, which separates the self-declared Republic of Abkhazia from the territory controlled by the Government of Georgia. Republic of Abkhazia, and those states that recognise its independence, view the line as an international border separating two sovereign states, whereas the Georgian government and most other countries refer to it as an 'Administrative Border Line' within Georgian territory. The Georgian government views Abkhazia as a Russian-occupied Georgian territory and designates the de facto boundary as an occupation line in accordance with the Georgian "Law on Occupied Territories of Georgia". The Constitution of Georgia recognizes Abkhazia as autonomous within Georgia, therefore the line corresponds to the 'Administrative Border' of the Autonomous Republic of Abkhazia within Georgian territory.
Sirius is an urban locality in Krasnodar Krai, Russia. It is incorporated as a federal territory.






















