In cell biology, protein kinase A (PKA) is a family of serine-threonine kinase whose activity is dependent on cellular levels of cyclic AMP (cAMP). PKA is also known as cAMP-dependent protein kinase. PKA has several functions in the cell, including regulation of glycogen, sugar, and lipid metabolism. It should not be confused with 5'-AMP-activated protein kinase.

The catalytic subunit α of protein kinase A is a key regulatory enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PRKACA gene. This enzyme is responsible for phosphorylating other proteins and substrates, changing their activity. Protein kinase A catalytic subunit is a member of the AGC kinase family, and contributes to the control of cellular processes that include glucose metabolism, cell division, and contextual memory. PKA Cα is part of a larger protein complex that is responsible for controlling when and where proteins are phosphorylated. Defective regulation of PKA holoenzyme activity has been linked to the progression of cardiovascular disease, certain endocrine disorders and cancers.

cAMP-dependent protein kinase type I-alpha regulatory subunit is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PRKAR1A gene.

cAMP-dependent protein kinase type II-alpha regulatory subunit is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PRKAR2A gene.

cAMP-dependent protein kinase type II-beta regulatory subunit is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PRKAR2B gene.

A-kinase anchor protein 13 is a protein that in humans, is encoded by the AKAP13 gene. This protein is also called AKAP-Lbc because it encodes the lymphocyte blast crisis (Lbc) oncogene, and ARHGEF13/RhoGEF13 because it contains a guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) domain for the RhoA small GTP-binding protein.

A-kinase anchor protein 5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the AKAP5 gene.

cAMP-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit beta is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PRKACB gene.

A-kinase anchor protein 12, aka AKAP250, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the AKAP12 gene.

A kinase anchor protein 1, mitochondrial is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the AKAP1 gene.

A-kinase anchor protein 8 is an enzyme that, in humans, is encoded by the AKAP8 gene.

A-kinase anchor protein 11 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the AKAP11 gene.
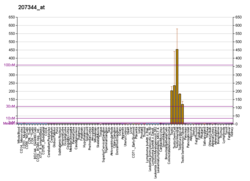
A kinase anchor protein 10, mitochondrial is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the AKAP10 gene.

A-kinase anchor protein 6 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the AKAP6 gene.

C-Myc-binding protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MYCBP gene.

A-kinase anchor protein 4 is a scaffold protein that in humans is encoded by the AKAP4 gene. It involves in the intracellular signalling of protein kinase -A. AKAP4 is called as cancer /testis antigen (CTA), it belongs to a class of tumour linked antigens categories by high expression in germ cells and cancer than normal tissues. AKAP4 is not normally expressed in mRNA and protein level in MM cell line.

Calcium-binding tyrosine phosphorylation-regulated protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CABYR gene.
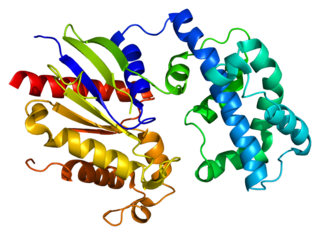
Guanine nucleotide-binding protein subunit alpha-13 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GNA13 gene.

A-kinase anchor protein 7 isoform gamma is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the AKAP7 gene.
The A-kinase anchoring proteins or A-kinase anchor proteins (AKAPs) are a group of structurally diverse proteins, which have the common function of binding to the regulatory subunit of protein kinase A (PKA) and confining the holoenzyme to discrete locations within the cell. At least 20 AKAPs have been cloned. There are at least 50 members, often named after their molecular mass.