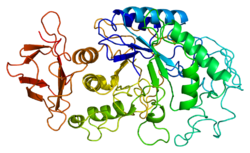
1b2y: STRUCTURE OF HUMAN PANCREATIC ALPHA-AMYLASE IN COMPLEX WITH THE CARBOHYDRATE INHIBITOR ACARBOSE
1bsi: HUMAN PANCREATIC ALPHA-AMYLASE FROM PICHIA PASTORIS, GLYCOSYLATED PROTEIN
1c8q: STRUCTURE SOLUTION AND REFINEMENT OF THE RECOMBINANT HUMAN SALIVARY AMYLASE
1cpu: SUBSITE MAPPING OF THE ACTIVE SITE OF HUMAN PANCREATIC ALPHA-AMYLASE USING SUBSTRATES, THE PHARMACOLOGICAL INHIBITOR ACARBOSE, AND AN ACTIVE SITE VARIANT
1hny: The structure of human pancreatic alpha-amylase at 1.8 angstroms resolution and comparisons with related enzymes
1jxj: Role of mobile loop in the mechanism of human salivary amylase
1jxk: Role of the mobile loop in the mechanism of human salivary amylase
1kb3: Three Dimensional Structure Analysis of the R195A Variant of Human Pancreatic Alpha Amylase
1kbb: Mechanistic Analyses of Catalysis in Human Pancreatic alpha-Amylase: Detailed Kinetic and Structural Studies of Mutants of Three Conserved Carboxylic Acids
1kbk: Mechanistic Analyses of Catalysis in Human Pancreatic Alpha-Amylase: Detailed Kinetic and Structural Studies of Mutants of Three Conserved Carboxylic Acids
1kgu: THREE DIMENSIONAL STRUCTURE ANALYSIS OF THE R337A VARIANT OF HUMAN PANCREATIC ALPHA-AMYLASE
1kgw: THREE DIMENSIONAL STRUCTURE ANALYSIS OF THE R337Q VARIANT OF HUMAN PANCREATIC ALPHA-MYLASE
1kgx: Three Dimensional Structure Analysis of the R195Q Variant of Human Pancreatic Alpha Amylase
1mfu: Probing the role of a mobile loop in human salivary amylase: Structural studies on the loop-deleted mutant
1mfv: Probing the role of a mobile loop in human slaivary amylase: Structural studies on the loop-deleted enzyme
1nm9: Crystal structure of recombinant human salivary amylase mutant W58A
1q4n: Structural studies of Phe256Trp of human salivary alpha-amylase: implications for the role of a conserved water molecule and its associated chain in enzyme activity
1smd: HUMAN SALIVARY AMYLASE
1u2y: In situ extension as an approach for identifying novel alpha-amylase inhibitors, structure containing D-gluconhydroximo-1,5-lactam
1u30: In situ extension as an approach for identifying novel alpha-amylase inhibitors, structure containing maltosyl-alpha (1,4)-D-gluconhydroximo-1,5-lactam
1u33: In situ extension as an approach for identifying novel alpha-amylase inhibitors
1xcw: Acarbose Rearrangement Mechanism Implied by the Kinetic and Structural Analysis of Human Pancreatic alpha-Amylase in Complex with Analogues and Their Elongated Counterparts
1xcx: Acarbose Rearrangement Mechanism Implied by the Kinetic and Structural Analysis of Human Pancreatic alpha-Amylase in Complex with Analogues and Their Elongated Counterparts
1xd0: Acarbose Rearrangement Mechanism Implied by the Kinetic and Structural Analysis of Human Pancreatic alpha-Amylase in Complex with Analogues and Their Elongated Counterparts
1xd1: Acarbose Rearrangement Mechanism Implied by the Kinetic and Structural Analysis of Human Pancreatic alpha-Amylase in Complex with Analogues and Their Elongated Counterparts
1xgz: Structure of the N298S variant of human pancreatic alpha-amylase
1xh0: Structure of the N298S variant of human pancreatic alpha-amylase complexed with acarbose
1xh1: Structure of the N298S variant of human pancreatic alpha-amylase complexed with chloride
1xh2: Structure of the N298S variant of human pancreatic alpha-amylase complexed with chloride and acarbose
1xv8: Crystal Structure of Human Salivary Alpha-Amylase Dimer
1z32: Structure-function relationships in human salivary alpha-amylase: Role of aromatic residues
2cpu: SUBSITE MAPPING OF THE ACTIVE SITE OF HUMAN PANCREATIC ALPHA-AMYLASE USING SUBSTRATES, THE PHARMACOLOGICAL INHIBITOR ACARBOSE, AND AN ACTIVE SITE VARIANT
3cpu: SUBSITE MAPPING OF THE ACTIVE SITE OF HUMAN PANCREATIC ALPHA-AMYLASE USING SUBSTRATES, THE PHARMACOLOGICAL INHIBITOR ACARBOSE, AND AN ACTIVE SITE VARIANT