| zf-AN1 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
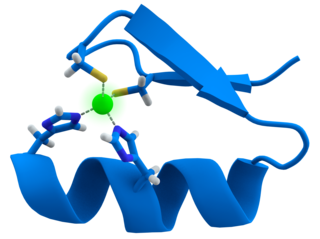
 Solution structure of the zf-an1 domain from arabiopsis thaliana f5o11.17 protein | |||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| Symbol | zf-AN1 | ||||||||
| Pfam | PF01428 | ||||||||
| InterPro | IPR000058 | ||||||||
| SMART | ZnF_AN1 | ||||||||
| |||||||||
In molecular biology, the AN1-type zinc finger domain, which has a dimetal (zinc)-bound alpha/beta fold. This domain was first identified as a zinc finger at the C terminus of AN1 SWISSPROT, a ubiquitin-like protein in Xenopus laevis. [1] The AN1-type zinc finger contains six conserved cysteines and two histidines that could potentially coordinate 2 zinc atoms.
Certain stress-associated proteins (SAP) contain AN1 domain, often in combination with A20 zinc finger domains (SAP8) or C2H2 domains (SAP16). [2] For example, the human protein Znf216 has an A20 zinc-finger at the N terminus and an AN1 zinc-finger at the C terminus, acting to negatively regulate the NFkappaB activation pathway and to interact with components of the immune response like RIP, IKKgamma and TRAF6. The interact of Znf216 with IKK-gamma and RIP is mediated by the A20 zinc-finger domain, while its interaction with TRAF6 is mediated by the AN1 zinc-finger domain; therefore, both zinc-finger domains are involved in regulating the immune response. [3] The AN1 zinc finger domain is also found in proteins containing a ubiquitin-like domain, which are involved in the ubiquitination pathway. [1] Proteins containing an AN1-type zinc finger include:
- Ascidian posterior end mark 6 (pem-6) protein . [4]
- Human AWP1 protein (associated with PRK1), which is expressed during early embryogenesis. [5]
- Human immunoglobulin mu binding protein 2 (SMUBP-2), mutations which cause muscular atrophy with respiratory distress type 1. [6]
AN1-type zinc finger domains are widely present across diverse "Euryarchaeota" and Nitrososphaerota, where they are often fused to membrane-associated peptidase domains such as the rhomboid family serine peptidase, transglutaminase-like thiol peptidases of the papain fold, and Zn-dependent metallopeptidases. Archaeal AN1 domains are also linked to transmembrane helices, and domains such as DNAJ and SCP/PR1. These fusions suggest membrane-associated roles for AN1 domain containing proteins in archaea, such as in the proteolytic processing of polypeptides and in regulating protein folding or stability. The architectural syntax is remarkably similar to that of the prokaryotic B-box zinc finger and LIM domains. [7]