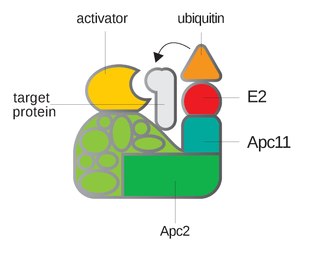
Anaphase-promoting complex is an E3 ubiquitin ligase that marks target cell cycle proteins for degradation by the 26S proteasome. The APC/C is a large complex of 11–13 subunit proteins, including a cullin (Apc2) and RING (Apc11) subunit much like SCF. Other parts of the APC/C have unknown functions but are highly conserved.

The spindle checkpoint, also known as the metaphase-to-anaphase transition, the spindle assembly checkpoint (SAC), the metaphase checkpoint, or the mitotic checkpoint, is a cell cycle checkpoint during mitosis or meiosis that prevents the separation of the duplicated chromosomes (anaphase) until each chromosome is properly attached to the spindle. To achieve proper segregation, the two kinetochores on the sister chromatids must be attached to opposite spindle poles. Only this pattern of attachment will ensure that each daughter cell receives one copy of the chromosome. The defining biochemical feature of this checkpoint is the stimulation of the anaphase-promoting complex by M-phase cyclin-CDK complexes, which in turn causes the proteolytic destruction of cyclins and proteins that hold the sister chromatids together.

Separase, also known as separin, is a cysteine protease responsible for triggering anaphase by hydrolysing cohesin, which is the protein responsible for binding sister chromatids during the early stage of anaphase. In humans, separin is encoded by the ESPL1 gene.

The cell division cycle protein 20 homolog is an essential regulator of cell division that is encoded by the CDC20 gene in humans. To the best of current knowledge its most important function is to activate the anaphase promoting complex (APC/C), a large 11-13 subunit complex that initiates chromatid separation and entrance into anaphase. The APC/CCdc20 protein complex has two main downstream targets. Firstly, it targets securin for destruction, enabling the eventual destruction of cohesin and thus sister chromatid separation. It also targets S and M-phase (S/M) cyclins for destruction, which inactivates S/M cyclin-dependent kinases (Cdks) and allows the cell to exit from mitosis. A closely related protein, Cdc20homologue-1 (Cdh1) plays a complementary role in the cell cycle.

Mitotic spindle assembly checkpoint protein MAD2A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MAD2L1 gene.

Cell division cycle protein 27 homolog is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CDC27 gene.

F-box only protein 5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FBXO5 gene.

Fizzy-related protein homolog, also known as hCDH1, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FZR1 gene.

Cell division cycle protein 16 homolog is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CDC16 gene.

Cell division cycle 23 homolog , also known as CDC23, is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the CDC23 gene.

Anaphase-promoting complex subunit 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ANAPC1 gene.

Anaphase-promoting complex subunit 2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ANAPC2 gene.

Cohesin subunit SA-2 (SA2) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the STAG2 gene. SA2 is a subunit of the Cohesin complex which mediates sister chromatid cohesion, homologous recombination and DNA looping. In somatic cells cohesin is formed of SMC3, SMC1, RAD21 and either SA1 or SA2 whereas in meiosis, cohesin is formed of SMC3, SMC1B, REC8 and SA3.

Anaphase-promoting complex subunit 5 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ANAPC5 gene.

Anaphase-promoting complex subunit 7 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ANAPC7 gene. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene.

Anaphase-promoting complex subunit 4 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ANAPC4 gene.

Sister chromatid cohesion protein PDS5 homolog A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PDS5A gene.

Anaphase-promoting complex subunit 11 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ANAPC11 gene.

Cullins are a family of hydrophobic scaffold proteins which provide support for ubiquitin ligases (E3). All eukaryotes appear to have cullins. They combine with RING proteins to form Cullin-RING ubiquitin ligases (CRLs) that are highly diverse and play a role in myriad cellular processes, most notably protein degradation by ubiquitination.

Cdh1 is one of the substrate adaptor protein of the anaphase-promoting complex (APC) in the budding yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Functioning as an activator of the APC/C, Cdh1 regulates the activity and substrate specificity of this ubiquitin E3-ligase. The human homolog is encoded by the FZR1 gene, which is not to be confused with the CDH1 gene.