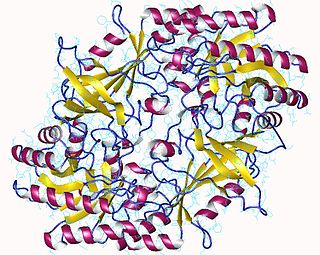
The enzyme ornithine decarboxylase catalyzes the decarboxylation of ornithine to form putrescine. This reaction is the committed step in polyamine synthesis. In humans, this protein has 461 amino acids and forms a homodimer.

Arginase (EC 3.5.3.1, arginine amidinase, canavanase, L-arginase, arginine transamidinase) is a manganese-containing enzyme. The reaction catalyzed by this enzyme is: arginine + H2O → ornithine + urea. It is the final enzyme of the urea cycle. It is ubiquitous to all domains of life.
Spermine is a polyamine involved in cellular metabolism that is found in all eukaryotic cells. The precursor for synthesis of spermine is the amino acid ornithine. It is an essential growth factor in some bacteria as well. It is found as a polycation at physiological pH. Spermine is associated with nucleic acids and is thought to stabilize helical structure, particularly in viruses.
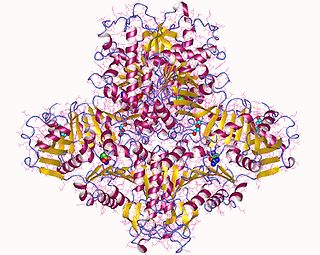
N-Acetylglutamate synthase (NAGS) is an enzyme that catalyses the production of N-acetylglutamate (NAG) from glutamate and acetyl-CoA.

Complement component 1s is a protein involved in the complement system. C1s is part of the C1 complex. In humans, it is encoded by the C1S gene.
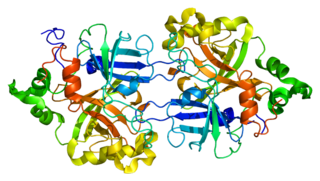
Complement factor B is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CFB gene.

Malonyl-CoA decarboxylase, is found in bacteria and humans and has important roles in regulating fatty acid metabolism and food intake, and it is an attractive target for drug discovery. It is an enzyme associated with Malonyl-CoA decarboxylase deficiency. In humans, it is encoded by the MLYCD gene.

In molecular biology, Ornithine decarboxylase antizyme (ODC-AZ) is an ornithine decarboxylase inhibitor. It binds to, and destabilises, ornithine decarboxylase (ODC), a key enzyme in polyamine synthesis. ODC is then rapidly degraded. It was first characterized in 1981. The expression of ODC-AZ requires programmed, ribosomal frameshifting which is modulated according to the cellular concentration of polyamines. High levels of polyamines induce a +1 ribosomal frameshift in the translation of mRNA for the antizyme leading to the expression of a full-length protein. At least two forms of ODC-AZ exist in mammals and the protein has been found in Drosophila as well as in Saccharomyces yeast.

Extracellular superoxide dismutase [Cu-Zn] is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the SOD3 gene.

Ornithine decarboxylase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ODC1 gene.

The enzyme diaminopimelate decarboxylase (EC 4.1.1.20) catalyzes the cleavage of carbon-carbon bonds in meso 2,6 diaminoheptanedioate to produce CO2 and L-lysine, the essential amino acid. It employs the cofactor pyridoxal phosphate, also known as PLP, which participates in numerous enzymatic transamination, decarboxylation and deamination reactions.

Zinc finger protein 148 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ZNF148 gene.

Ornithine decarboxylase antizyme is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the OAZ1 gene.

Sentrin-specific protease 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the SENP1 gene.
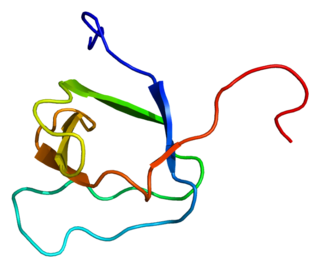
Protein arginine N-methyltransferase 2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PRMT2 gene.

Carboxypeptidase D is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CPD gene.

Disintegrin and metalloproteinase domain-containing protein 23 is a non-catalytic protein that in humans is encoded by the ADAM23 gene. It is a member of the ADAM family of extracellular matrix metalloproteinases.

Antizyme inhibitor 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the AZIN1 gene.

Ornithine decarboxylase antizyme 2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the OAZ2 gene.

Y+L amino acid transporter 2, also known as cationic amino acid transporter, y+ system, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC7A6 gene.






















