Francis Gary Powers was an American pilot whose Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) Lockheed U-2 spy plane was shot down while flying a reconnaissance mission in Soviet Union airspace, causing the 1960 U-2 incident.

The economy of Malawi is $7.522 billion by gross domestic product as of 2019, and is predominantly agricultural, with about 80% of the population living in rural areas. The landlocked country in south central Africa ranks among the world's least developed countries. In 2017, agriculture accounted for about one-third of GDP and about 80% of export revenue. The economy depends on substantial inflows of economic assistance from the IMF, the World Bank, and individual donor nations. The government faces strong challenges: to spur exports, to improve educational and health facilities, to face up to environmental problems of deforestation and erosion, and to deal with the problem of HIV/AIDS in Africa. Malawi is a least developed country according to United Nations.
Communications in Malawi includes the country's postal, telephone, television, radio and internet services.

Project MKUltra was the code name of a quasi-legal human experimentation program designed and undertaken by the U.S. Central Intelligence Agency (CIA). The experiments were intended to develop procedures and identify drugs such as LSD that could be used in interrogations to weaken individuals and force confessions through brainwashing and psychological torture. MKUltra used numerous methods to manipulate its subjects' mental states and brain functions, such as the covert administration of high doses of psychoactive drugs and other chemicals, electroshocks, hypnosis, sensory deprivation, isolation, and verbal and sexual abuse, in addition to other forms of torture.

Central Africa is a subregion of the African continent comprising various countries according to different definitions. Angola, Burundi, Cameroon, the Central African Republic, Chad, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, the Republic of the Congo, Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, Rwanda, and São Tomé and Príncipe are members of the Economic Community of Central African States (ECCAS). Six of those states are also members of the Economic and Monetary Community of Central Africa (CEMAC) and share a common currency, the Central African CFA franc.
Operation Mockingbird is an alleged large-scale program of the United States Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) that began in the early years of the Cold War and attempted to manipulate news media for propaganda purposes. According to author Deborah Davis, Operation Mockingbird recruited leading American journalists into a propaganda network and influenced the operations of front groups. CIA support of front groups was exposed when an April 1967 Ramparts article reported that the National Student Association received funding from the CIA. In 1975, Church Committee Congressional investigations revealed Agency connections with journalists and civic groups.

The Freedom of Information Act (FOIA), 5 U.S.C. § 552, is a federal freedom of information law that requires the full or partial disclosure of previously unreleased information and documents controlled by the United States government upon request. The act defines agency records subject to disclosure, outlines mandatory disclosure procedures, and includes nine exemptions that define categories of information not subject to disclosure. The act was intended to make U.S. government agencies' functions more transparent so that the American public could more easily identify problems in government functioning and put pressure on Congress, agency officials, and the president to address them. The FOIA has been changed repeatedly by both the legislative and executive branches.
Religion in Africa is multifaceted and has been a major influence on art, culture and philosophy. Today, the continent's various populations and individuals are mostly adherents of Christianity, Islam, and to a lesser extent several traditional African religions. In Christian or Islamic communities, religious beliefs are also sometimes characterized with syncretism with the beliefs and practices of traditional religions.
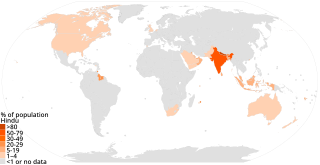
Hinduism has approximately 1.2 billion adherents worldwide. Hinduism is the third largest religion in the world behind Christianity (31.5%) and Islam (23.3%).
In United States law, the term Glomar response, also known as Glomarization or Glomar denial, refers to a response to a request for information that will "neither confirm nor deny" (NCND) the existence of the information sought. For example, in response to a request for police reports relating to a certain individual, the police agency may respond with the following: "We can neither confirm nor deny that our agency has any records matching your request."
Operation Midnight Climax was an operation carried out by the CIA as a sub-project of Project MKUltra, the mind-control research program that began in the 1950s. It was initially established in 1954 by Sidney Gottlieb and placed under the direction of the Federal Bureau of Narcotics in Boston, Massachusetts with the "Federal Narcotics Agent and CIA consultant" George Hunter White under the pseudonym of Morgan Hall. Dr. Sidney Gottlieb was a chemist who was chief of the Chemical Division of the Technical Services Staff of the CIA. Under the Cold War and fears of the Soviet Union and China, Gottlieb felt inspired to investigate methods of mind control. Gottlieb based his plan for Project MKUltra and Operation Midnight Climax off of interrogation method research under Project Artichoke. Unlike Project Artichoke, Operation Midnight Climax gave Gottlieb permission to test drugs on unknowing citizens, which made way for the legacy of this operation. Hundreds of federal agents, field operatives, and scientists worked on these programs before they were shut down in the 1960s.
There is a long history of close cooperation between the United States and the United Kingdom intelligence services; see Clandestine HUMINT and Covert Action for World War II and subsequent relationships. There are permanent liaison officers of each country in major intelligence agencies of the other, such as the Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) and the Secret Intelligence Service ("MI6"), FBI and the Security Service (MI5), and National Security Agency (NSA) and Government Communications Headquarters (GCHQ). From 1943 to 2017, the Open Source Enterprise, a division of the CIA, was run out of Caversham Park in Reading, Berkshire. American officials worked closely with their British counterparts to monitor foreign TV and radio broadcasts, as well as online information.

The Ministry of Defense is a cabinet-level office in charge of defense-related matters of Ethiopia. It oversees the Ethiopian National Defense Force and Ethiopian Defense Industry. The current minister is Abraham Belay.

The CIA Tibetan program was a nearly two decades long anti-Chinese covert operation focused on Tibet which consisted of "political action, propaganda, paramilitary and intelligence operations" based on U.S. Government arrangements made with brothers of the 14th Dalai Lama, who was not initially aware of them. The goal of the program was "to keep the political concept of an autonomous Tibet alive within Tibet and among several foreign nations".

Adherents of Islam constitute the world's second largest religious group. According to a estimation in 2020, Islam has 1.9 billion adherents, making up about 24.7% of the world population. Most Muslims are either of two denominations: Sunni or Shia. Islam is the majority religion in several subregions: Central Asia, West Asia, North Africa, the Sahel, and the Middle East. The diverse Asia-Pacific region contains the highest number of Muslims in the world, easily surpassing the combined Middle East and North Africa.
Adelaide Hawkins was a cryptologist at the Office of Strategic Services (OSS) during World War II.

Everett Francis Drumright was an American diplomat who served in a variety of posts, including as U.S. Ambassador to the Republic of China (Taiwan).
Hella Hammid was a German-American photographer whose career included teaching at UCLA. Her freelance photographs appeared in diverse publications including Life, Ebony, The Sun and The New York Times. Her softly backlit picture of two young Italian girls dancing, watched by other children in front of the abutments of a stone building, was chosen by Edward Steichen for his 1955 world-touring MoMA exhibition The Family of Man, which was seen by 9 million visitors.

Jang Do-young was a South Korean general, politician and professor who, as the Army Chief of Staff, played a decisive role in the May 16 coup and was the first chairman of the interim Supreme Council for National Reconstruction for a short time until his imprisonment.