Additive may refer to:
Additive may refer to:
Additive synthesis is a sound synthesis technique that creates timbre by adding sine waves together.

A dye is a colored substance that chemically bonds to the substrate to which it is being applied. This distinguishes dyes from pigments which do not chemically bind to the material they color. Dye is generally applied in an aqueous solution and may require a mordant to improve the fastness of the dye on the fiber.

A flavoring, also known as flavor or flavorant, is a food additive used to improve the taste or smell of food. It changes the perceptual impression of food as determined primarily by the chemoreceptors of the gustatory and olfactory systems. Along with additives, other components like sugars determine the taste of food.

Food additives are substances added to food to preserve flavor or enhance taste, appearance, or other sensory qualities. Some additives have been used for centuries as part of an effort to preserve food, for example vinegar (pickling), salt (salting), smoke (smoking), sugar (crystallization), etc. This allows for longer-lasting foods such as bacon, sweets or wines. With the advent of ultra-processed foods in the second half of the twentieth century, many additives have been introduced, of both natural and artificial origin. Food additives also include substances that may be introduced to food indirectly in the manufacturing process, through packaging, or during storage or transport.

E numbers, short for Europe numbers, are codes for substances used as food additives, including those found naturally in many foods, such as vitamin C, for use within the European Union (EU) and European Free Trade Association (EFTA). Commonly found on food labels, their safety assessment and approval are the responsibility of the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). The fact that an additive has an E number implies that its use was at one time permitted in products for sale in the European Single Market; some of these additives are no longer allowed today.

Food coloring, color additive or colorant is any dye, pigment, or substance that imparts color when it is added to food or beverages. Colorants can be supplied as liquids, powders, gels, or pastes. Food coloring is commonly used in commercial products and in domestic cooking.

Physical or chemical properties of materials and systems can often be categorized as being either intensive or extensive, according to how the property changes when the size of the system changes. The terms "intensive and extensive quantities" were introduced into physics by German mathematician Georg Helm in 1898, and by American physicist and chemist Richard C. Tolman in 1917.

Motor oil, engine oil, or engine lubricant is any one of various substances used for the lubrication of internal combustion engines. They typically consist of base oils enhanced with various additives, particularly antiwear additives, detergents, dispersants, and, for multi-grade oils, viscosity index improvers. The main function of motor oil is to reduce friction and wear on moving parts and to clean the engine from sludge and varnish (detergents). It also neutralizes acids that originate from fuel and from oxidation of the lubricant (detergents), improves the sealing of piston rings, and cools the engine by carrying heat away from moving parts.
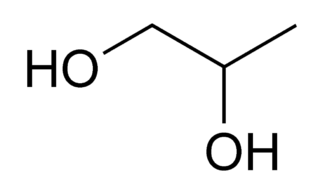
Propylene glycol (IUPAC name: propane-1,2-diol) is a viscous, colorless liquid. It is almost odorless and has a faintly sweet taste. Its chemical formula is CH3CH(OH)CH2OH. As it contains two alcohol groups, it is classified as a diol. An aliphatic diol may also be called a glycol. It is miscible with a broad range of solvents, including water, acetone, and chloroform. In general, glycols are non-irritating and have very low volatility.
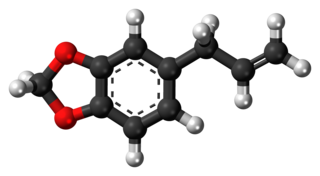
Safrole is an organic compound with the formula CH2O2C6H3CH2CH=CH2. It is a colorless oily liquid, although impure samples can appear yellow. A member of the phenylpropanoid family of natural products, it is found in sassafras plants, among others. Small amounts are found in a wide variety of plants, where it functions as a natural antifeedant. Ocotea pretiosa, which grows in Brazil, and Sassafras albidum, which grows in eastern North America, are the main natural sources of safrole. It has a characteristic "sweet-shop" aroma.

Xanthan gum is a polysaccharide with many industrial uses, including as a common food additive. It is an effective thickening agent and stabilizer that prevents ingredients from separating. It can be produced from simple sugars by fermentation and derives its name from the species of bacteria used, Xanthomonas campestris.

The Food Additives Amendment of 1958 is a 1958 amendment to the United States' Food, Drugs, and Cosmetic Act of 1938. It was a response to concerns about the safety of new food additives. The amendment established an exemption from the "food additive" definition and requirements for substances "generally recognized as safe" by scientific experts in the field, based on long history of use before 1958 or based on scientific studies. New food additives would be subject to testing including by the "Delaney clause". The Delaney clause was a provision in the amendment which said that if a substance were found to cause cancer in man or animal, then it could not be used as a food additive.
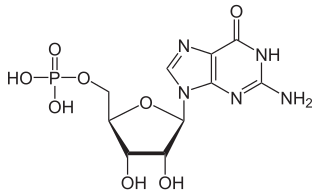
Guanosine monophosphate (GMP), also known as 5′-guanidylic acid or guanylic acid, is a nucleotide that is used as a monomer in RNA. It is an ester of phosphoric acid with the nucleoside guanosine. GMP consists of the phosphate group, the pentose sugar ribose, and the nucleobase guanine; hence it is a ribonucleotide monophosphate. Guanosine monophosphate is commercially produced by microbial fermentation.
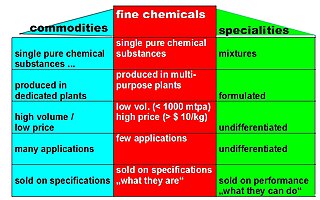
In chemistry, fine chemicals are complex, single, pure chemical substances, produced in limited quantities in multipurpose plants by multistep batch chemical or biotechnological processes. They are described by exacting specifications, used for further processing within the chemical industry and sold for more than $10/kg. The class of fine chemicals is subdivided either on the basis of the added value, or the type of business transaction, namely standard or exclusive products.
In colorimetry, the CIE 1976L*, u*, v*color space, commonly known by its abbreviation CIELUV, is a color space adopted by the International Commission on Illumination (CIE) in 1976, as a simple-to-compute transformation of the 1931 CIE XYZ color space, but which attempted perceptual uniformity. It is extensively used for applications such as computer graphics which deal with colored lights. Although additive mixtures of different colored lights will fall on a line in CIELUV's uniform chromaticity diagram, such additive mixtures will not, contrary to popular belief, fall along a line in the CIELUV color space unless the mixtures are constant in lightness.

The regulation of food and dietary supplements by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration is a process governed by various statutes enacted by the United States Congress and interpreted by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration ("FDA"). Pursuant to the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act and accompanying legislation, the FDA has authority to oversee the quality of substances sold as food in the United States, and to monitor claims made in the labeling about both the composition and the health benefits of foods.
Adulteration is a legal offense and when the food fails to meet the legal standards set by the government, it is said to have been Adulterated Food. One form of adulteration is the addition of another substance to a food item in order to increase the quantity of the food item in raw form or prepared form, which results in the loss of the actual quality of the food item. These substances may be either available food items or non-food items. Among meat and meat products some of the items used to adulterate are water or ice, carcasses, or carcasses of animals other than the animal meant to be consumed. In the case of seafood, adulteration may refer to species substitution (mislabeling), which replaces the species identified on the product label with another species, or undisclosed processing methods, in which treatments such as additives, excessive glazing, or short-weighting are not disclosed to the consumer.
A feed additive is an additive of extra nutrient or drug for livestock. Such additives include vitamins, amino acids, fatty acids, minerals, pharmaceutical, fungal products and steroidal compounds. The additives might impact feed presentation, hygiene, digestibility, or effect on intestinal health.
Specialty chemicals are particular chemical products which provide a wide variety of effects on which many other industry sectors rely. Some of the categories of speciality chemicals are adhesives, agrichemicals, cleaning materials, colors, cosmetic additives, construction chemicals, elastomers, flavors, food additives, fragrances, industrial gases, lubricants, paints, polymers, surfactants, and textile auxiliaries. Other industrial sectors such as automotive, aerospace, food, cosmetics, agriculture, manufacturing, and textiles are highly dependent on such products.

Pit additives is a commercially-produced material that aims to reduce fecal sludge build-up and control odor in pit latrines, septic tanks and wastewater treatment plants. Manufacturers claim to use effective microorganisms (EM) in their products. Current scientific evidence does not back up most claims made by manufacturers about the benefits. Removing sludge continues to be a problem in pit latrines and septic tanks.