Addu Kandu, Dv. for "Addu Channel", is the traditional name of the broad channel between Huvadhu Atoll and Addu Atoll in the south of Maldives.
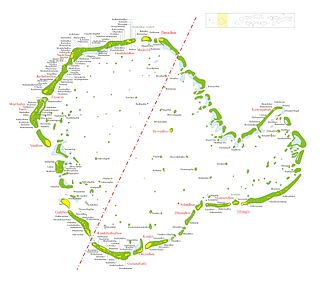
Huvadhu is a large atoll located south of the Suvadiva Channel the Republic of Maldives. With a total area of 3152 km², of which 38.5 km² is dry land, it is the second largest geographical atoll in the country, after Boduthiladhunmathi

Addu Atoll, also known as Seenu Atoll, is the southernmost atoll of the Maldives. Addu Atoll, together with Fuvahmulah, located 40 km north of Addu Atoll, extend the Maldives into the Southern Hemisphere. Addu Atoll is located 540 km south of Malé, the country's capital. Administratively, Addu Atoll is the location of Addu City, one of the two cities of the Maldives. Addu City consists of the inhabited areas of Addu Atoll, namely the natural islands of Hulhudhoo, Meedhoo, Maradhoo, Feydhoo, and Hithadhoo.. In addition to the areas that are included as a part of Addu City, Addu Atoll has a number of other inhabited and uninhabited islands, including the island of Gan, where Gan International Airport is located.

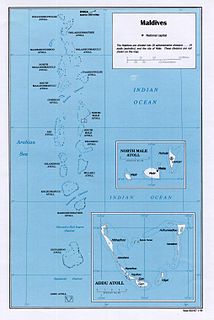
The Maldives, officially the Republic of Maldives, is an Asian country, located in the Indian Ocean, situated in the Arabian Sea. It lies southwest of Sri Lanka and India, about 1,000 kilometres (620 mi) from the Asian continent. The chain of 26 atolls stretches from Ihavandhippolhu Atoll in the north to the Addu City in the south. Comprising a territory spanning roughly 298 square kilometres (115 sq mi), the Maldives is one of the world's most geographically dispersed sovereign states as well as the smallest Asian country by land area and population, with around 427,756 inhabitants. Malé is the capital and a populated city, traditionally called the "King's Island" for its central location.
In the British Admiralty charts it is called Equatorial Channel because the Equator passes through its midst.

An equator of a rotating spheroid is its zeroth circle of latitude (parallel). It is the imaginary line on the spheroid's surface, equidistant from its poles, dividing it into northern and southern hemispheres. In other words, it is the intersection of the spheroid's surface with the plane perpendicular to its axis of rotation and midway between its geographical poles.
Within Addu Kandu the Equatorial Channel divides to form another important channel named Mulah Kandu. Geographically a part of Addu Kandu, it is located north-east of Addu Atoll, between the eastern end of this atoll and Fuvahmulah at a lat of 0° 17' S, southwards from the centre of the main channel.
Mulah Kandu, Dv. for "Mulah Channel", is the channel between Fuvahmulah and Addu Atoll.

Fuvahmulah City is an island (atoll) in the Maldives. It is under Maldives administrative divisions of Gnaviyani Atoll or Nyaviyani Atoll. The inhabitants speak a distinctive form of the Dhivehi language, known as "dhivehi bas".
This channel appeared in old French maps with the name Courant de Addoue.