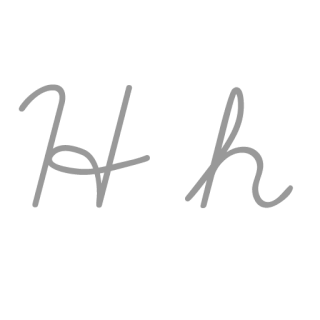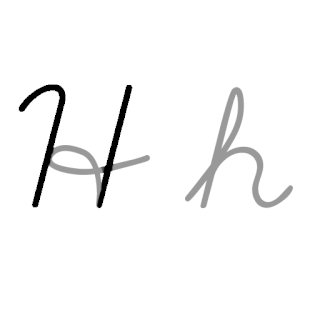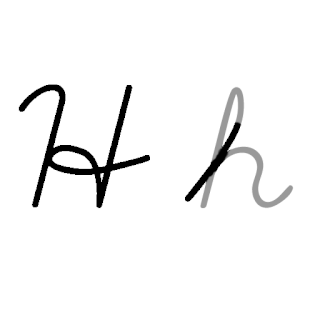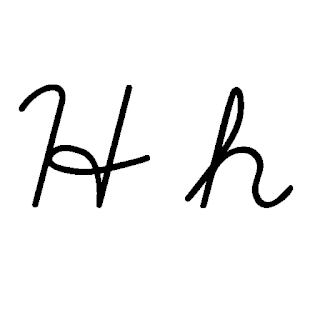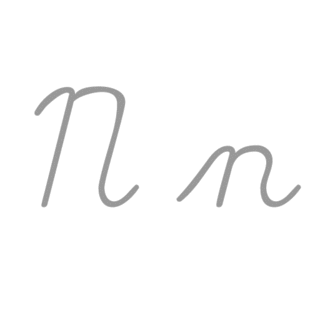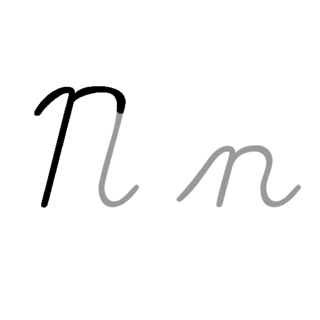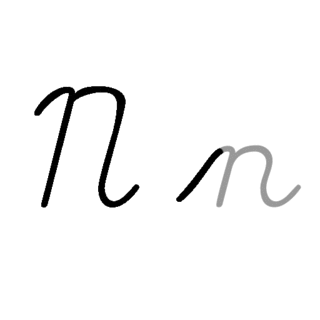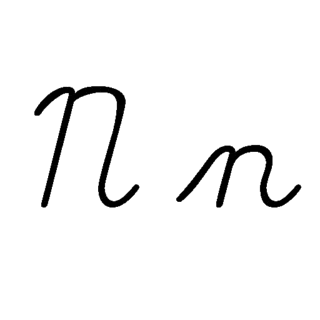A, or a, is the first letter and the first vowel of the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is a, plural aes. It is similar in shape to the Ancient Greek letter alpha, from which it derives. The uppercase version consists of the two slanting sides of a triangle, crossed in the middle by a horizontal bar. The lowercase version can be written in two forms: the double-storey a and single-storey ɑ. The latter is commonly used in handwriting and fonts based on it, especially fonts intended to be read by children, and is also found in italic type.

An alphabet is a standardized set of basic written symbols or graphemes that represent the phonemes of certain spoken languages. Not all writing systems represent language in this way; in a syllabary, each character represents a syllable, and logographic systems use characters to represent words, morphemes, or other semantic units.

A book is a medium for recording information in the form of writing or images, typically composed of many pages bound together and protected by a cover. The technical term for this physical arrangement is codex. In the history of hand-held physical supports for extended written compositions or records, the codex replaces its predecessor, the scroll. A single sheet in a codex is a leaf and each side of a leaf is a page.

A central processing unit (CPU), also called a central processor, main processor or just processor, is the electronic circuitry that executes instructions comprising a computer program. The CPU performs basic arithmetic, logic, controlling, and input/output (I/O) operations specified by the instructions in the program. This contrasts with external components such as main memory and I/O circuitry, and specialized processors such as graphics processing units (GPUs).
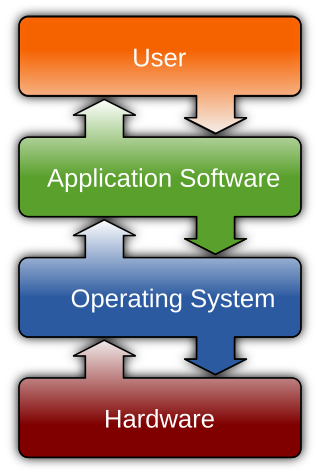
Software is a set of computer programs and associated documentation and data. This is in contrast to hardware, from which the system is built and which actually performs the work.

In physics, energy is the quantitative property that is transferred to a body or to a physical system, recognizable in the performance of work and in the form of heat and light. Energy is a conserved quantity—the law of conservation of energy states that energy can be converted in form, but not created or destroyed. The unit of measurement for energy in the International System of Units (SI) is the joule (J).

The guitar is a fretted musical instrument that typically has six strings. It is usually held flat against the player's body and played by strumming or plucking the strings with the dominant hand, while simultaneously pressing selected strings against frets with the fingers of the opposite hand. A plectrum or individual finger picks may also be used to strike the strings. The sound of the guitar is projected either acoustically, by means of a resonant chamber on the instrument, or amplified by an electronic pickup and an amplifier.
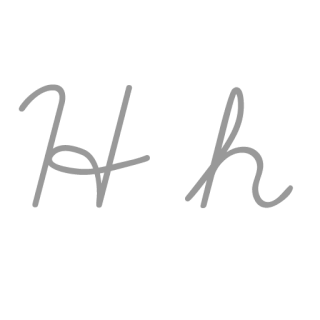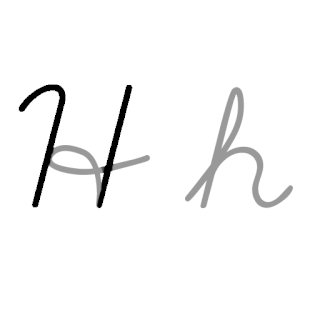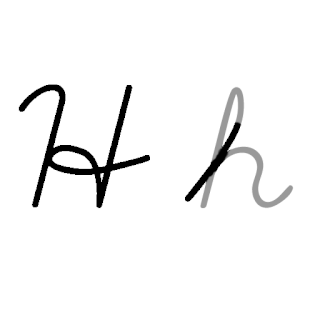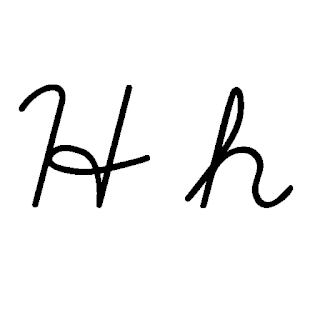
H, or h, is the eighth letter in the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is aitch, or regionally haitch.

Insurance is a means of protection from financial loss in which, in exchange for a fee, a party agrees to compensate another party in the event of a certain loss, damage, or injury. It is a form of risk management, primarily used to hedge against the risk of a contingent or uncertain loss.

Language is a structured system of communication. The structure of a language is its grammar and the free components are its vocabulary. Languages are the primary means by which humans communicate, and may be conveyed through a variety of methods, including spoken, sign, and written language. Many languages, including the most widely-spoken ones, have writing systems that enable sounds or signs to be recorded for later reactivation. Human language is highly variable between cultures and across time.
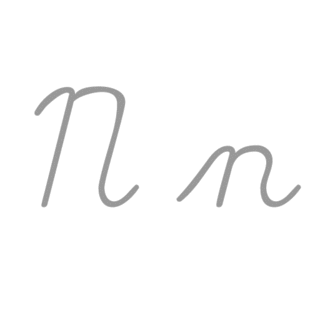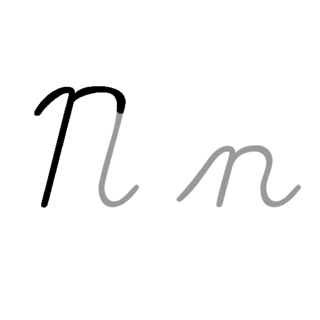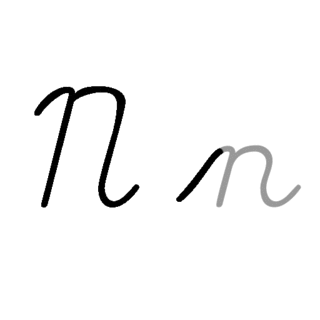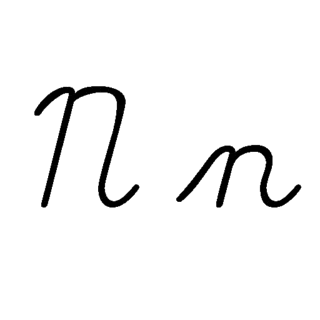
N, or n, is the fourteenth letter in the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is en, plural ens.

An operating system (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware, software resources, and provides common services for computer programs.

P, or p, is the sixteenth letter of the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is pee, plural pees.
The International System of Units, known by the international abbreviation SI in all languages and sometimes pleonastically as the SI system, is the modern form of the metric system and based on the metre as the unit of length and either the kilogram as the unit of mass or the kilogram-force as the unit of force.</ref> and the world's most widely used system of measurement. Established and maintained by the General Conference on Weights and Measures (CGPM), it is the only system of measurement with an official status in nearly every country in the world, employed in science, technology, industry, and everyday commerce.

Sex is the trait that determines whether a sexually reproducing animal or plant produces male or female gametes. Male plants and animals produce smaller mobile gametes, while females produce larger ones. Organisms that produce both types of gametes are called hermaphrodites. During sexual reproduction, male and female gametes fuse to form zygotes, which develop into offspring that inherit traits from each parent.

Zoroastrianism is an Iranian religion and one of the world's oldest organized faiths, based on the teachings of the Iranian-speaking prophet Zoroaster. It has a dualistic cosmology of good and evil within the framework of a monotheistic ontology and an eschatology which predicts the ultimate conquest of evil by good. Zoroastrianism exalts an uncreated and benevolent deity of wisdom known as Ahura Mazda as its supreme being. Historically, the unique features of Zoroastrianism, such as its monotheism, messianism, belief in free will and judgement after death, conception of heaven, hell, angels, and demons, among other concepts, may have influenced other religious and philosophical systems, including the Abrahamic religions and Gnosticism, Northern Buddhism, and Greek philosophy.

The Fox Broadcasting Company, commonly known simply as Fox and stylized in all caps as FOX, is an American commercial broadcast television network owned by Fox Corporation and headquartered in New York City, with master control operations and additional offices at the Fox Network Center in Los Angeles and the Fox Media Center in Tempe. Launched as a competitor to the Big Three television networks on October 9, 1986, Fox went on to become the most successful attempt at a fourth television network. It was the highest-rated free-to-air network in the 18–49 demographic from 2004 to 2012 and again in 2020, and was the most-watched American television network in total viewership during the 2007–08 season.
The English football league system, also known as the football pyramid, is a series of interconnected leagues for men's association football clubs in England, with five teams from Wales, one from Guernsey, one from Jersey and one from the Isle of Man also competing. The system has a hierarchical format with promotion and relegation between leagues at different levels, allowing even the smallest club the theoretical possibility of ultimately rising to the very top of the system, the Premier League. Below that are levels 2–4 organised by the English Football League, then the National League System from levels 5–10 administered by the FA, and thereafter feeder leagues run by relevant county FAs on an ad hoc basis.

Biology is the scientific study of life. It is a natural science with a broad scope but has several unifying themes that tie it together as a single, coherent field. For instance, all organisms are made up of cells that process hereditary information encoded in genes, which can be transmitted to future generations. Another major theme is evolution, which explains the unity and diversity of life. Energy processing is also important to life as it allows organisms to move, grow, and reproduce. Finally, all organisms are able to regulate their own internal environments.