The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three historical Metal Ages, after the Chalcolithic and Bronze Age. It has also been considered as the final age of the three-age division starting with prehistory and progressing to protohistory. In this usage, it is preceded by the Stone Age and Bronze Age. These concepts originated for describing Iron Age Europe and the Ancient Near East. The indigenous cultures of the New World did not develop an iron economy before 1500.
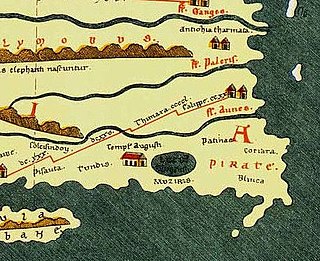
Muchiri, commonly anglicized as Muziris was an ancient harbour and an urban centre on the Malabar Coast. Muziris found mention in the Periplus of the Erythraean Sea, the bardic Tamil poems and a number of classical sources. It was the major ancient port city of Cheras. The exact location of Muziris has been a matter of dispute among historians and archaeologists. However, excavations since 2004 at Pattanam in Ernakulam district of Kerala have led some experts to suggesting the hypothesis that the city was located just there. It was an important trading port for Christian and Muslim merchants arriving from other countries.

Bronze mirrors preceded the glass mirrors of today. This type of mirror, sometimes termed a copper mirror, has been found by archaeologists among elite assemblages from various cultures, from Etruscan Italy to Japan. Typically they are round and rather small, in the West with a handle, in East Asia with a knob to hold at the back, often with a loop for a cord, or silk tassel. Some were fitted with small stands, and others had a hinged protective cover. In surviving ancient examples the surface is too corroded to be reflective, but some bronze mirrors are still made.

Pattanam is a village located in the Ernakulam District in the southern Indian state of Kerala. It is located 2 km north of North Paravur, 6 km and East of Chendamangalam 25 km north of Kochi (Cochin).

Bhattiprolu is a village in Bapatla district of the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh. It is the headquarters of Bhattiprolu mandal in Tenali revenue division. The Buddhist stupa in the village is one of the centrally protected monuments of national importance. One of the earliest evidence of Brahmi script in South India comes from Bhattiprolu. The script was written on an urn containing Buddha's relics. The script has been named Bhattiprolu script.

Tamil-Brahmi, also known as Tamili or Damili, was a variant of the Brahmi script in southern India. It was used to write inscriptions in Old Tamil. The Tamil-Brahmi script has been paleographically and stratigraphically dated between the third century BCE and the first century CE, and it constitutes the earliest known writing system evidenced in many parts of Tamil Nadu, Kerala, Andhra Pradesh and Sri Lanka. Tamil Brahmi inscriptions have been found on cave entrances, stone beds, potsherds, jar burials, coins, seals, and rings.
Korkai is a small village in the Srivaikuntam taluk of Thoothukudi district in Tamil Nadu, India. It was called Pandya-Kavada in the Kapatapuram in Kalithogai. It is situated about 3 km north of the Thamirabarani River and about 6 km from the shore of Bay of Bengal.
Sembiyankandiyur is an archaeological site in Nagapattinam district in Tamil Nadu, India.

The Bhattiprolu script is a variant of the Brahmi script which has been found in old inscriptions at Bhattiprolu, a small village in the erstwhile Guntur district of Andhra Pradesh, India. It is located in the fertile Krishna River delta and the estuary region where the river meets the Bay of Bengal.

Mathilakam is a village in Kodungallur taluk, Thrissur district in Kerala, South India. It is located around 5 miles north of Kodungallur on National Highway 66. Its nearby localities include S.N Puram and Panangad. The place also resides near to Triprayar and Irinjalakuda routes.

Keezhadi, also spelt Keeladi, is a village near the village of Silaiman, on the border between Madurai and Sivagangai districts, in Tamil Nadu, India. The Keezhadi excavation site is located in this area: excavations carried out by the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) and the Tamil Nadu Archaeology Department (TNAD) have revealed a Sangam era settlement dated to the 6th century BCE by radiocarbon dating. Claims that the results show that there was writing at that time have been challenged. It is not clear whether the potsherds containing inscriptions were found in the same archaeological layer as the 6th century samples, and University of Calcutta archaeologist Bishnupriya Basak said that "This unfortunately is not clear from the report and is very crucial", adding that the issues of "layer, period and absolute dates" needed clarity. Dravidian University archaeologist E. Harsha Vardhan said that a single report was not enough to "state scientifically that the Tamil-Brahmi script belongs to the sixth century BC".

Tamil Nadu is known for its ancient temple architecture. Nearly 33,000 ancient temples, many at least 800 to 2000 years old, are found scattered all over Tamil Nadu. As per Tamil Nadu Hindu Endowments Board, there are 38,615 temples. Most of the largest Hindu Temples are located in Tamil Nadu. Studded with complex architecture, a variety of sculptures, and rich inscriptions, the temples remain the very essence of the culture and heritage of Tamil land, with historical records dating back to at least 3,000 years.
Dr. Koluvail Vyasaraya Ramesh was an Indian epigraphist and Sanskrit scholar who served as the Chief Epigraphist and Joint Director General of the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI).
Alagankulam is a village situated on the east coast in the Ramanathapuram taluk and district in India. The village is situated on the banks of the Vaigai River and is about 3 kilometres (1.9 mi) away from the seashore. The village is located 18 kilometres (11 mi) east of Ramanathapuram. The village had a population of 15,473 at the 2011 census.

The Amaravathi Archaeological Museum is a museum located in, a village in of the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh. It features an impressive collection of relics that span thousands of years, primarily reflecting the region's history from the 3rd century B.C. It houses sculptures from the Mahachaitya, providing insights into ancient Buddhist art and culture. It includes a model of the reconstructed Mahachaitya in its courtyard. Visitors can explore various galleries that showcase significant artifacts, including life-size Buddha statues and intricate carvings, representing the rich artistic traditions of Amaravathi.

Keezhadi, or Keeladi, is a Sangam period settlement site, where excavation are carried out by the Archaeological Survey of India and the Tamil Nadu State Department of Archaeology. This site is located near the town of Keezhadi in Sivaganga district, Tamil Nadu, about 12 km southeast of Madurai. The settlement lies on the bank of the Vaigai River and it reflects the ancient culture of Tamil Nadu. Epigraphist V. Vedachalam, who served as a domain expert for the excavation, dated the excavated remains between 6th century BCE and 3rd century BCE.

This is a list of archaeological artefacts and epigraphs which have Tamil inscriptions. Of the approximately 100,000 inscriptions found by the Archaeological Survey of India in India, about 60,000 were in Tamil Nadu
K. Amarnath Ramakrishna is an Indian archaeologist. He is noted for his research into the Keeladi excavation site, a Sangam period settlement in Tamil Nadu. Ramakrishna also worked in Kondapur and Nagarjunakonda museums.
Archaeology in Tamil Nadu is mainly done under the supervision of Archaeological Survey of India and Tamil Nadu State Department of Archaeology. As of 2023, excavations have been done at 40 sites and 36 reports have been issued.
Perumbalai is a village in Tamil Nadu, India. It is located within Dharmapuri district.














