Related Research Articles

Eilleen Regina "Shania" Twain is a Canadian singer-songwriter and actress. She has sold over 100 million records, making her the best-selling female artist in country music history and one of the best-selling music artists of all time. Her success garnered her several titles including the "Queen of Country Pop". Billboard named her as the leader of the '90s country-pop crossover stars.

Samuel Langhorne Clemens, known by his pen name Mark Twain, was an American writer, humorist, entrepreneur, publisher, and lecturer. He was praised as the "greatest humorist the United States has produced", and William Faulkner called him "the father of American literature". His novels include The Adventures of Tom Sawyer (1876) and its sequel, Adventures of Huckleberry Finn (1884), the latter of which has often been called the "Great American Novel". Twain also wrote A Connecticut Yankee in King Arthur's Court (1889) and Pudd'nhead Wilson (1894), and co-wrote The Gilded Age: A Tale of Today (1873) with Charles Dudley Warner.
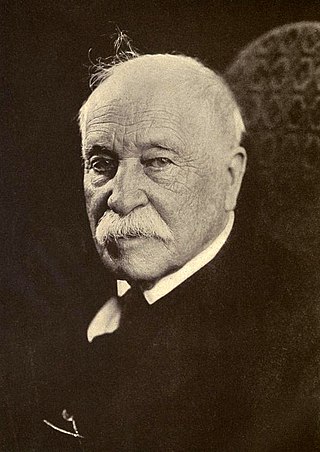
William Dean Howells was an American realist novelist, literary critic, and playwright, nicknamed "The Dean of American Letters". He was particularly known for his tenure as editor of The Atlantic Monthly, as well as for his own prolific writings, including the Christmas story "Christmas Every Day" and the novels The Rise of Silas Lapham and A Traveler from Altruria.

Carol Creighton Burnett is an American actress, comedian, singer, and writer. Her groundbreaking comedy variety show The Carol Burnett Show, which originally aired on CBS, was one of the first of its kind to be hosted by a woman. She has performed on stage, television and film in varying genres including dramatic and comedic roles. She has received numerous accolades including six Primetime Emmy Awards, a Tony Award, a Grammy Award, and seven Golden Globe Awards. Burnett was awarded Presidential Medal of Freedom in 2005, the Mark Twain Prize for American Humor in 2013 and the Screen Actors Guild Life Achievement Award in 2015.

"The Celebrated Jumping Frog of Calaveras County" is an 1865 short story by Mark Twain. It was his first great success as a writer and brought him national attention. The story has also been published as "Jim Smiley and His Jumping Frog" and "The Notorious Jumping Frog of Calaveras County". In it, the narrator retells a story he heard from a bartender, Simon Wheeler, at the Angels Hotel in Angels Camp, California, about the gambler Jim Smiley. The narrator describes him: "If he even seen a straddle bug start to go anywheres, he would bet you how long it would take him to get to wherever he going to, and if you took him up, he would foller that straddle bug to Mexico but what he would find out where he was bound for and how long he was on the road."

Letters from the Earth is a posthumously published work of American author Mark Twain (1835–1910) collated by Bernard DeVoto. It comprises essays written during a difficult time in Twain's life (1904–1909), when he was deeply in debt and had recently lost his wife and one of his daughters. The content concerns morality and religion and strikes a tone that is sarcastic—Twain's own term throughout the book. Initially, Twain's sole surviving child, Clara Clemens, objected to its publication in March 1939, probably because of its controversial and iconoclastic views on religion, claiming it presented a "distorted" view of her father. Henry Nash Smith helped change her position in 1960. Clara explained her change of heart in 1962 saying that "Mark Twain belonged to the world" and that public opinion had become more tolerant. She was also influenced to release the papers by her annoyance with Soviet reports that her father's ideas were being suppressed in the United States. The papers were selected, edited and sequenced for the book in 1939 by Bernard DeVoto.

A Tramp Abroad is a work of travel literature, including a mixture of autobiography and fictional events, by American author Mark Twain, published in 1880. The book details a journey by the author, with his friend Harris, through central and southern Europe. While the stated goal of the journey is to walk most of the way, the men find themselves using other forms of transport as they traverse the continent. The book is the fourth of Mark Twain's six travel books published during his lifetime and is often thought to be an unofficial sequel to the first one, The Innocents Abroad (1869).

Janet Hamilton was a nineteenth-century Scottish poet.
"On the Decay of the Art of Lying" is a short essay written by Mark Twain in 1880 for a meeting of the Historical and Antiquarian Club of Hartford, Connecticut. Twain published the text in The Stolen White Elephant Etc. (1882).

Galaxy Magazine, or The Galaxy, was an American monthly magazine founded by William Conant Church and his brother Francis P. Church in 1866. In 1868, Sheldon and Company gained financial control of the magazine and it was eventually absorbed by The Atlantic Monthly in 1878. Notable contributors to the magazine include Mark Twain, Walt Whitman, Ion Hanford Perdicaris and Henry James.

Edmund Falconer, born Edmund O'Rourke, was an Irish poet, actor, theatre manager, songwriter and playwright, known for his keen wit and outstanding acting skills.

An Essay on the Art of Ingeniously Tormenting was a conduct book written by Jane Collier and published in 1753. The Essay was Collier's first work, and operates as a satirical advice book on how to nag. It was modelled after Jonathan Swift's satirical essays, and is intended to "teach" a reader the various methods for "teasing and mortifying" one's acquaintances. It is divided into two sections that are organised for "advice" to specific groups, and it is followed by "General Rules" for all people to follow.
The Twain–Ament indemnities controversy was a major cause célèbre in the United States of America in 1901 as a consequence of the published reactions of American humorist Mark Twain to reports of Rev. William Scott Ament and other missionaries collecting indemnities from Chinese people in the aftermath of the Boxer Uprising.
"The Awful German Language" is an 1880 essay by Mark Twain published as Appendix D in A Tramp Abroad. The essay is a humorous exploration of the frustrations a native speaker of English has with learning German as a second language.

The $30,000 Bequest and Other Stories (1906) is a collection of thirty comic short stories by the American humorist and writer Mark Twain. The stories contained span the course of his career, from "Advice to Young Girls" in 1865 to the titular tale in 1904. Although Twain had ample time to refine his short stories between their original publication date and this collection, there is little evidence to suggest he took an active interest in doing so. "A Burlesque Biography" contains only a few minor technical revisions which make it different from the 1871 version found in Mark Twain's "(Burlesque) Autobiography and First Romance". "Advice to Little Girls" shows slight revision from its earlier publication in The Celebrated Jumping Frog of Calaveras County.

Samuel Langhorne Clemens , well known by his pen name Mark Twain, was an American author and humorist. Twain is noted for his novels Adventures of Huckleberry Finn (1884), which has been called the "Great American Novel," and The Adventures of Tom Sawyer (1876). He also wrote poetry, short stories, essays, and non-fiction. His big break was "The Celebrated Jumping Frog of Calaveras County" (1867).
"Advice to Youth" is a satirical essay written by Mark Twain in 1882. In his own words, Twain was asked by persons unspecified to write something "to [the] youth." While the exact audience of his speech is uncertain, it is most probably American; in his posthumous collected works, editor's notes have conjecturally assigned the address to the Boston Saturday Morning Club. In the essay, Twain speaks primarily of advice which can be broken into six specific topics. These include: selective obedience towards parents, respecting superiors, the wisdom of going to bed early and waking up early, lying, firearm etiquette, and the importance of good books.

The use of the pen name of Mark Twain first occurred in Samuel Clemens's writing while in the Nevada Territory which he had journeyed to with his brother. Clemens/Twain lived in Nevada from 1861 to 1864, and visited the area twice after leaving. Historians such as Peter Messent see Clemens's time in Nevada as "the third major formative period of Mark Twain's career" due to his encounters with "writers and humorists who would both shape and put the finishing touches on his literary art." The Routledge Encyclopedia of Mark Twain states that despite the few "disagreeable experiences" he had there, Twain "thrived in Nevada." Among those things he learned was "how far he could push a joke", a lesson learned from some "disagreeable experiences" he brought upon himself.

Mary Ann Harris Gay was an American writer and poet from Decatur, Georgia, known for her Civil War memoir Life in Dixie During the War (1897). This described events in Atlanta during the war. Author Margaret Mitchell said this memoir inspired some of her passages in her novel Gone with the Wind (1936). Gay also published a book of poetry (1858), which she republished after the war to raise money to help support her mother and sister.

"Giddy Up!" is a song by Canadian singer Shania Twain. It was released on January 5, 2023 by Republic Records as the second single from her sixth studio album Queen of Me (2023). The song was written by Twain, Romans, Jessica Agombar, and David Stewart and produced by the latter.
References
- 1 2 LeMaster, J. R.; Wilson, James D., eds. (6 December 2012). The Routledge Encyclopedia of Mark Twain. Taylor & Francis. pp. 15–16. ISBN 9781135881351 . Retrieved 27 March 2023.
- ↑ Branch, Edgar Marquess; Smith, Harriet E.; Hirst, Robert, eds. (27 July 1981). Early Tales & Sketches, Vol. 2. University of California Press. ISBN 9780520906778.
- ↑ Hersher, Becky. "NPR's Book Concierge: Our Guide To 2013's Great Reads". NPR. Retrieved 27 March 2023.
- ↑ Lulin, David L. (11 March 2013). "Mark Twain's 'Advice to Little Girls'". Los Angeles Times. Retrieved 27 March 2023.