
Hanover Stadtbahn is a light urban rail transport system in the city of Hanover, the capital of Lower Saxony, Germany. It opened on 29 September 1975, gradually replacing the city's tramway network over the course of the subsequent 25 years. As of 2024, the Hanover Stadtbahn system has 12 main lines, one weekend express night line, and two supplemental lines, serving 201 stations, operating on 121 kilometres (75 mi) of route. The system is run by üstra, which was originally an abbreviation for Überlandwerke und Straßenbahnen Hannover AG. In 2007 Hanover Stadtbahn transported 125 million passengers per year.

Kröpcke is the central square of the city of Hanover in Germany. The square is situated at the five-way crossroads of Georgstraße, and Karmarschstraße, Bahnhofstraße and Rathenaustraße. It is named after Wilhelm Kröpcke who started working at Café Robby, that had relocated to the then-nameless square in 1869, as a waiter in 1878, before leasing the café in 1885, changing its name to Café Kröpcke in 1895, and operating it until his death in 1919. Eventually, the square adopted the name from the café and in 1947 was officially named Kröpcke by the city of Hanover.

Hannoversche Allgemeine Zeitung is a German newspaper with a circulation of 158,000 and a widespread resonance all over Germany. It is distributed in Hanover and in all Lower Saxony.

The Red Thread is a 4.2-kilometre (2.6 mi) urban walking trail in Hanover, Germany, to 36 significant points of interest about architecture and the history of the city centre.
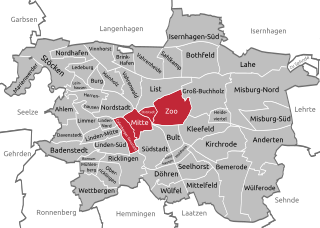
Mitte is the first borough of Hanover, the state capital of Lower Saxony. As of 2020, it has 36,645 inhabitants and consists of the quarters Mitte, Calenberger Neustadt, Oststadt and Zoo. The district mayor is Cornelia Kupsch (CDU).

The Garden Cemetery is a cemetery in Hanover, Germany. It was created in 1741 and is located by the Garden Church built in 1749. The cemetery and the church are both named after the garden parish outside the former parish city walls in front of Aegidien Gate. The cemetery, which contains a number of classicising grave markers from the first half of the nineteenth century, was closed in 1864 with the establishment of the Stadtfriedhof Engesohde. Today it forms a park in the middle of inner city Hanover. The graves of Charlotte Buff, the astronomer Caroline Herschel and the painter Johann Heinrich Ramberg are located here. The Gartenfriedhof lies on Marienstraße between Warmbüchenstraße and Arnswaldtstraße.

Warmbüchenviertel is an area in the quarter and borough of Mitte in Hanover. The quarter is characterised by insurance companies and other office buildings, but is also an inner city residential area. The name derives from two major streets: Warmbüchenstraße und Warmbüchenkamp.
The following is a timeline of the history of the city of Hanover, Germany.

The RedaktionsNetzwerk Deutschland (RND) is the Hanover-based joint corporate newsroom of German Madsack Media Group. The biggest limited partner of Madsack is the Deutsche Druck- und Verlagsgesellschaft, which is fully owned by the Social Democratic Party of Germany (SPD).

Hanover Drama is a theatre company in Hanover, the state capital of Lower Saxony, Germany. The company is resident at the Hanover Playhouse situated approximately 200 metres (660 ft) east of Hanover Opera House, and the Ballyard situated approximately 530 metres (1,740 ft) west-southwest of the opera house in the old town. Collectively these venues have five stages:
Friedhelm Erich Haak is a German newspaper publisher, media entrepreneur and consultant. He was Chairman of the Supervisory Board of Verlagsgesellschaft Madsack from 2006 to 2013.

Hugo Thielen is a German freelance author and editor, who is focused on the history of Hanover, the capital of Lower Saxony, in a lexicon of the city, another one especially of its art and culture, and a third of biographies. He co-authored a book about Jewish personalities in Hanover's history.
Heinrich Sievers was a German musicologist, music critic, university lecturer, and conductor. He was regarded as an authority on the history of music in Hanover and Lower Saxony, and wrote music-historical monographs in English and Finnish publications.

Hanover Historical Museum is an historical museum situated in Hanover, the capital of Lower Saxony, Germany. The museum was founded in 1903 as the Homeland Museum of the City of Hanover. Its collections are related to the history of the city, the history of the House of Guelf, and of the state of Lower Saxony.

The Theater am Aegi is an event venue on Aegidientorplatz square in Hannover, the capital of Lower Saxony, Germany. Like the square, it is often referred to as Aegi. The building was opened in 1953 mainly as a cinema, with a versatile stage also for other performances. It has been a Gastspieltheater for local and touring companies, without its own personnel. After a fire, it was rebuilt as a theatre only, opened in 1967, and then mainly as a venue for drama performances of the state-run Staatstheater Hannover. After a new theatre was built for that company in 1992, Theater am Aegi returned to its traditional role of a venue for various events, including congress, private functions and representation of the city.
Gerd Otto Lichtenhahn was a German architect and member of the Association of German Architects (BDA).
Hans Klüppelberg was a German architect.
Adolf Falke was a German architect, draughtsman, designer, stage designer and municipal politician.

The Otto Werner clothing store opened in 1932 in Hanover, the capital of Lower Saxony, Germany. By 1985, the store had expanded to several branches throughout the state. After the original store closed in 1999, the enterprise ceased operating in 2001.

Elsbach & Frank was a textile retail business founded in the 19th century in Hanover, the capital of Lower Saxony, Germany. The department store built by the business on the corner of Osterstraße and Große Packhofstraße, called Zum Stern, is the only building in the city centre that survived the air raids on Hanover during the Second World War without major damage. Today, the building houses a branch of the Spanish fashion chain Zara.


![The location of Aegidien Gate in the civic fortifications of Hanover [de ] is marked in red. Aegidientor Karte Hannover.jpg](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/5/55/Aegidientor_Karte_Hannover.jpg/220px-Aegidientor_Karte_Hannover.jpg)



























