
Tortoises are reptile species of the family Testudinidae of the order Testudines. They are particularly distinguished from turtles by being land-dwelling, while many turtle species are at least partly aquatic. However, like turtles, tortoises have a shell to protect from predation and other threats. The shell in tortoises is generally hard, and like other members of the suborder Cryptodira, they retract their necks and heads directly backwards into the shell to protect them.
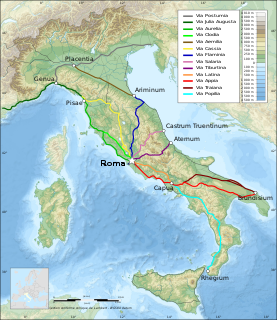
The Via Aemilia was a trunk Roman road in the north Italian plain, running from Ariminum (Rimini), on the Adriatic coast, to Placentia (Piacenza) on the river Padus (Po). It was completed in 187 BC. The Via Aemilia connected at Rimini with the Via Flaminia to Rome, which had been completed 33 years earlier.
Aemilia is a large main-belt asteroid. Aemilia was discovered by the French brothers Paul Henry and Prosper Henry on January 26, 1876. The credit for this discovery was given to Paul. It is probably named after the Via Aemilia, a Roman road in Italy that runs from Piacenza to Rimini.

The marginated tortoise is a species of tortoise in the family Testudinidae. The species is endemic to Greece, Italy, and the Balkans in Southern Europe. It is the largest European tortoise. The marginated tortoise is herbivorous, and hibernates for the winter.

The Greek tortoise, also known commonly as the spur-thighed tortoise, is a species of tortoise in the family Testudinidae. Testudo graeca is one of five species of Mediterranean tortoises. The other four species are Hermann's tortoise, the Egyptian tortoise, the marginated tortoise, and the Russian tortoise. The Greek tortoise is a very long-lived animal, achieving a lifespan of upwards of 125 years, with some unverified reports of up to 200 years.

Hermann's tortoise is one of five tortoise species traditionally placed in the genus Testudo, the others being the marginated tortoise, Greek tortoise, Russian tortoise, and Kleinmann's tortoise. Two subspecies are known: the western Hermann's tortoise and the eastern Hermann's tortoise. Sometimes mentioned as a subspecies, T. h. peleponnesica is not yet confirmed to be genetically different from T. h. boettgeri.
Aemilia Lepida is the name of several ancient Roman women belonging to the gens Aemilia. The name was given to daughters of men belonging to the Lepidus branch of the Aemilius family. The first Aemilia Lepida to be mentioned by Roman historians was the former fiancée of the younger Cato. Subsequent Aemiliae are known because of their marriages.

In Ancient Roman warfare, the testudo or tortoise formation was a type of shield wall formation commonly used by the Roman Legions during battles, particularly sieges

Testudo is a genus of tortoises found in North Africa, western Asia, and Europe. Several species are under threat in the wild, mainly from habitat destruction.

The Via Aemilia Scauri was an ancient Roman road built by the consul Marcus Aemilius Scaurus during his term as Censor in 109 BC.

Aldabrachelys is the recognised genus for the Seychelles and Madagascan radiations of giant tortoises, including the Aldabra giant tortoise.

The Galápagos tortoise complex or Galápagos giant tortoise complex are the largest living species of tortoise. Modern Galápagos tortoises can weigh up to 417 kg (919 lb). Today, giant tortoises exist on only two remote archipelagos: the Galápagos Islands 1000 km due west of mainland Ecuador; and Aldabrachelys gigantea of Aldabra in the Indian Ocean, 700 km east of Tanzania.
Emilia is a historic region of northern Italy, which approximately corresponds to the western and north-eastern portions of the modern region Emilia-Romagna, with the area of Romagna forming the remainder of the modern region.
Aemilia is a genus of tiger moths in the family Erebidae. It was initially named Ameles, but this name properly refers to a praying mantis genus.

Hesperotestudo is an extinct genus of tortoise that lived from the Miocene to the Pleistocene. Its remains are known from North America, Central America and Bermuda. Further specimens identifiable only to genus have been found in El Salvador.

Pseudohemihyalea is a genus of arctiine tussock moths in the Erebidae family. While the caterpillars of most species of Pseudohemihyalea feed on broad-leaved trees, the P. ambigua group has larvae that feed on conifers. Their forewing coloration has accordingly evolved to light-and-dark lengthwise striping, giving better camouflage among the slim needles of the host plants. In this, they seem to be convergent to certain geometer moths, such as Caripeta piniata or Sabulodes niveostriata.

Astrochelys is a genus of tortoises in the family Testudinidae. The two species are both found in Madagascar, and both classified as critically endangered on the IUCN Red List.

Porticus Aemilia was a portico in ancient Rome. It was one of the largest commercial structures of its time and functioned as a storehouse and distribution center for goods entering the city via the Tiber river.

The Chevrolet Testudo is a concept car built by Bertone on a modified Chevrolet Corvair Monza platform. The name comes from the Latin word for "Turtle". The car debuted at the 1963 Geneva Motor Show.















