
Salamanders are a group of amphibians typically characterized by their lizard-like appearance, with slender bodies, blunt snouts, short limbs projecting at right angles to the body, and the presence of a tail in both larvae and adults. All ten extant salamander families are grouped together under the order Urodela. Salamander diversity is highest in the Northern Hemisphere and most species are found in the Holarctic realm, with some species present in the Neotropical realm.
The Puerto Hondo stream salamander or Michoacan stream salamander, Ambystoma ordinarium, is a mole salamander from the Cordillera Volcánica within the Mexican state of Michoacán.

The barred tiger salamander or western tiger salamander is a species of mole salamander found from southwestern Canada in British Columbia, Alberta, Saskatchewan, and Manitoba, south through the western United States to Texas and northern Mexico.

The Japanese giant salamander is a species of salamander in the family Cryptobranchidae. This fully aquatic salamander is endemic to Japan, where it is known as Ōsanshōuo (オオサンショウウオ/大山椒魚), literally meaning "giant salamander". Other local names include Hanzaki,Hanzake, and Ankou. With a length of up to 5 feet (1.5 m), it is the third-largest salamander in the world, only being surpassed by the very similar and closely related Chinese giant salamander and South China giant salamander. There are currently only five known members of the family Cryptobranchidae: the Japanese, Chinese, and South China giant salamanders, an undescribed Andrias species from eastern China, and the hellbender in the eastern United States.

The Chinese giant salamander is one of the largest salamanders and one of the largest amphibians in the world. It is fully aquatic and is endemic to rocky mountain streams and lakes in the Yangtze river basin of central China. Either it or a close relative has been introduced to Kyoto Prefecture in Japan and to Taiwan. It is considered critically endangered in the wild due to habitat loss, pollution, and overcollection, as it is considered a delicacy and used in traditional Chinese medicine. On farms in central China, it is extensively farmed and sometimes bred, although many of the salamanders on the farms are caught in the wild. It has been listed as one of the top-10 "focal species" in 2008 by the Evolutionarily Distinct and Globally Endangered project. The Chinese giant salamander is considered to be a "living fossil". Although protected under Chinese law and CITES Appendix I, the wild population has declined by more than an estimated 80% since the 1950s. Although traditionally recognized as one of two living species of Andrias salamander in Asia, the other being the Japanese giant salamander, evidence indicates that the Chinese giant salamander may be composed of at least five cryptic species, further compounding each individual species' endangerment.

The Sardinian brook salamander or Sardinian mountain newt is a species of salamander in the family Salamandridae found only in Sardinia, Italy.
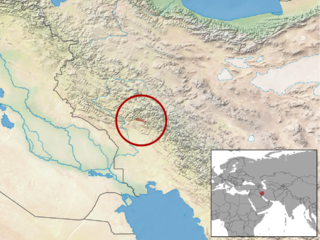
Neurergus kaiseri, the Luristan newt, Kaiser's mountain newt, Kaiser's spotted newt or emperor spotted newt, is a species of very colourful salamander in the family Salamandridae. It is endemic to the southern Zagros Mountains in Iran where it is known from just four streams. Populations of this newt have been declining and the International Union for Conservation of Nature has rated it as "vulnerable". A captive breeding programme has been established in several zoos.
Hynobius arisanensis, the Alishan salamander, is a species of salamander in the family Hynobiidae endemic to Taiwan. It occurs in the Alishan Range, the Yushan Range, and southern Central Mountain Range, where it lives at altitudes of 1,800–3,600 m (5,900–11,800 ft) above sea level. Its natural habitats are temperate forests, rivers, and freshwater springs. It is usually hiding during day time.

Desmognathus fuscus is a species of amphibian in the family Plethodontidae. The species is commonly called the dusky salamander or northern dusky salamander to distinguish it from populations in the southern United States which form a separate species, the southern dusky salamander. The northern dusky salamander is the most widespread representative of its genus in Canada. It can be found in eastern North America from extreme eastern Canada in New Brunswick south into the panhandle of Florida and west to Louisiana. The size of the species' total population is unknown, but is assumed to easily exceed 100,000. The species' habitat differs somewhat geographically; dusky salamanders in the northern part of the range prefer rocky woodland streams, seepages, and springs, while those in the south favor floodplains, sloughs, and muddy places along upland streams. They are most common where water is running or trickling. They hide under various objects, such as leaves or rocks, either in or near water. Alternatively, they may enter burrows for protection. The dusky salamander lays its eggs close to water under moss or rocks, in logs, or in stream-bank cavities. The larval stage which follows is normally aquatic.

The imitator salamander is a species of salamander in the family Plethodontidae. It is endemic to the Appalachian Mountains in the Eastern United States.
The Ocoee salamander is a species of salamander in the family Plethodontidae.
The black mountain salamander is a species of salamander in the family Plethodontidae.

The northern two-lined salamander is a species of salamander in the family Plethodontidae found in Canada and the United States. Its natural habitats are temperate forests, temperate shrubland, rivers, intermittent rivers, freshwater marshes, freshwater springs, arable land, and urban areas. It is more water-oriented than the related northern redback salamander, and can often be found in and around water such as rain puddles, streams, swamps, and damp stream beds, whereas the northern redback tends to be found in damp ground, but usually not near open water.

The Junaluska salamander is a species of lungless salamander native to the south-eastern United States. It was first described by David M. Sever, Harold M. Dundee, and Charles D. Sullivan who found the species in the range from the Cheoah River, Santeetlah Creek, and Tululah Creek in Graham County of North Carolina. Adults of this species can be found near large, rocky streams and on rainy nights on roads in the areas specified. The salamander is characterized by brownish-yellow coloration with a series of small dots along the body and a robust build compared to the other salamanders in Eurycea. The Junaluska salamander's breeding habits tend to be in large streams where the eggs are laid and attached to the bottom of rocks in the streams where they are found. According to the overall conservation listing for IUCN, this species is listed as Vulnerable. Conservation acts are important in both North Carolina and Eastern Tennessee, since the population of this species in each state is so small.

The Shenandoah salamander is a small, terrestrial salamander found exclusively in Shenandoah National Park in Virginia. The Shenandoah salamander inhabits a very small range of land on just three mountain peaks. Due to the small habitat range, interspecies competition, and climate change, the population of the Shenandoah salamander is vulnerable to extinction. Mitigating human effects on the habitat of the species will be essential in attempting to preserve and grow the population

The red salamander is a species of salamander in the family Plethodontidae endemic to the eastern United States. Its skin is orange/red with random black spots. Its habitats are temperate forests, small creeks, ponds, forests, temperate shrubland, rivers, intermittent rivers, freshwater, trees springs. Overall this species is common and widespread, but locally it has declined because of habitat loss and it is considered threatened in Indiana. Red salamanders eat insects, earthworms, spiders, small crustaceans, snails and smaller salamanders. The red salamander, as a member of the family Plethodontidae, lacks lungs and respires through its skin.

The California giant salamander is a species of salamander in the family Ambystomatidae. Dicamptodon ensatus is endemic to California, in the western United States. The species once additionally included individuals now belonging to the species D. aterrimus and D. tenebrosus, under the common name Pacific giant salamander, which now refers to the genus and family.

The southern torrent salamander is a member of the salamander family Rhyacotritonidae. This species of torrent salamander is found the farthest south in the region. It is a small salamander endemic to the Pacific Northwest from Northern California to Northern Oregon. It is one of four species of Rhyacotriton, along with R. cascadae, R. kezeri and R. olympicus. All species of Rhyacotriton are small, with their body lengths being less than 5 inches. The species reproduces annually, with an extended courtship and egg-laying period. The time it takes from oviposition to reach sexual maturity ranges from five to eight years, making the generation interval rather long. The larval stage, from hatching to metamorphosis, lasts 2.0-2.5 yr, with females requiring another 1.5–2.0 yr until they can first breed. They reach sexual maturity 1.0-1.5 yr after metamorphosis which occurs between 4.5 and 5.0 yr. This species feeds on small insects and spiders. Although it is found over a large area, it is not a migratory creature. It is preyed on by Pacific giant salamanders and garter snakes.
The mountain stream salamander or mountain stream siredon is a species of mole salamander that only lives in central México.

Paradactylodon is a genus of salamanders, known as the mountain salamanders or Middle Eastern stream salamanders, in the family Hynobiidae, endemic to Iran and Afghanistan.















