
20°S47°E

The Sphingidae are a family of moths (Lepidoptera) called sphinx moths, also colloquially known as hawk moths, with many of their caterpillars known as “hornworms”; it includes about 1,450 species. It is best represented in the tropics, but species are found in every region. They are moderate to large in size and are distinguished among moths for their agile and sustained flying ability, similar enough to that of hummingbirds as to be reliably mistaken for them. Their narrow wings and streamlined abdomens are adaptations for rapid flight. The family was named by French zoologist Pierre André Latreille in 1802.

Buxus is a genus of about seventy species in the family Buxaceae. Common names include box or boxwood.

Dudgeonea is a small genus of moths and the only genus of its family, the Dudgeoneidae. It includes six species distributed sparsely across the Old World from Africa and Madagascar to Australia and New Guinea.

The Lymantriinae are a subfamily of moths of the family Erebidae. The taxon was erected by George Hampson in 1893.

Omphalea is a plant genus of the family Euphorbiaceae first described as a genus in 1759. It is native to tropical parts of the Americas, the West Indies, Asia, Australia, and Africa.

Chrysiridia rhipheus, the Madagascan sunset moth, is a species of day-flying moth of the family Uraniidae. It is considered one of the most impressive and appealing-looking lepidopterans. Famous worldwide, it is featured in most coffee table books on Lepidoptera and is much sought after by collectors, though many older sources misspell the species name as "ripheus". It is very colourful, though the iridescent parts of the wings do not have pigment; rather the colours originate from optical interference. Adults have a wingspan of 7–9 cm (2.8–3.5 in).

The comet moth or Madagascan moon moth is a moth native to the rain forests of Madagascar. The species was first described by Félix Édouard Guérin-Méneville in 1847. The male has a wingspan of 20 cm and a tail span of 15 cm, making it one of the world's largest silk moths. The female lays from 120 to 170 eggs, and after hatching, the larvae feed on Eugenia and Weinmannia leaves for approximately two months before pupating. The cocoon has numerous holes to keep the pupa from drowning in the daily rains of its natural habitat. The adult moth cannot feed and only lives for 4 to 5 days. Although endangered in the wild due to habitat loss, the comet moth has been bred in captivity.
Copromorphidae, the "tropical fruitworm moths", is a family of insects in the lepidopteran order. These moths have broad, rounded forewings, and well-camouflaged scale patterns. Unlike Carposinidae the mouthparts include "labial palps" with the second rather than third segment the longest. With other unusual structural characteristics of the caterpillar and adult, it could represent the sister lineage of all other extant members of this superfamily. The genus Sisyroxena from Madagascar is also notable for its unusual venation and wing scale sockets.

Galacticidae is a recently recognised and enigmatic family of insects in the lepidopteran order. These moderate sized moths are 8–17 mm in wingspan and have previously been embedded within several lepidopteran superfamilies, but Galacticidae is currently placed in its own superfamily at the base of the natural group Apoditrysia.

The Uraniinae or uraniine moths are a subfamily of moths in the family Uraniidae. It contains seven genera that occur in the tropics of the world.
Whalleyana is an enigmatic genus of moths in the lepidopteran group Obtectomera, endemic to Madagascar. The genus contains two species, whose biology are unknown. The genus had been placed in the picture-winged leaf moths, (Thyrididae), but then was placed in its own family, and later elevated to its own superfamily ; see also Fänger (2004). The genus was named after Paul E. S. Whalley, a British entomologist. Genomic studies have found them to be most closely related to Callidulidae, and it is suggested that they should be placed in Calliduloidea.

Adansonia grandidieri, sometimes known as Grandidier's baobab, is the biggest and most famous of Madagascar's six species of baobabs. This tree is endemic to the island of Madagascar, where it is an endangered species threatened by the encroachment of agricultural land.

Angraecum sesquipedale, also known as Darwin's orchid, Christmas orchid, Star of Bethlehem orchid, and king of the angraecums, is an epiphytic orchid in the genus Angraecum endemic to Madagascar. The orchid was first discovered by the French botanist Louis-Marie Aubert du Petit-Thouars in 1798, but was not described until 1822. It is noteworthy for its long spur and its association with the naturalist Charles Darwin, who surmised that the flower was pollinated by a then undiscovered moth with a proboscis whose length was unprecedented at the time. His prediction had gone unverified until 21 years after his death, when the moth was discovered and his conjecture vindicated. The story of its postulated pollinator has come to be seen as one of the celebrated predictions of the theory of evolution.

Xanthopan is a monotypic genus of sphinx moth, with Xanthopan morganii, commonly called Morgan's sphinx moth, as its sole species. It is a very large sphinx moth from Southern Africa and Madagascar. Little is known about its biology, though the adults have been found to visit orchids and are one of the main pollinators of several of the Madagascar endemic baobab (Adansonia) species, including the critically endangered Adansonia perrieri or Perrier's baobab.
Obana is a genus of moths of the family Erebidae. The genus was erected by Francis Walker in 1862.

Pericyma is a genus of moths in the family Erebidae. The genus was erected by Gottlieb August Wilhelm Herrich-Schäffer in 1851.
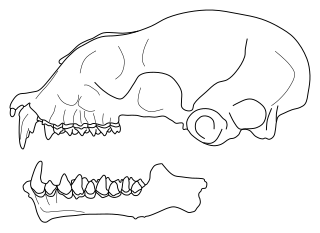
Triaenops menamena is a bat in the genus Triaenops found on Madagascar, mainly in the drier regions. It was known as Triaenops rufus until 2009, when it was discovered that that name had been incorrectly applied to the species. Triaenops rufus is a synonym of Triaenops persicus, a Middle Eastern species closely related to T. menamena— the Malagasy species had previously been placed as a subspecies of T. persicus by some authors. Triaenops menamena is mostly found in forests, but also occurs in other habitats. It often roosts in large colonies and eats insects such as butterflies and moths. Because of its wide range, common occurrence, and tolerance of habitat degradation, it is not considered to be threatened.

Borocera madagascariensis is a species of lasiocampid moth endemic to coastal Madagascar. It is one of three species of silk producing moths found on the island of Madagascar. B. madagascariensis is often confused with the similar Borocera cajani, which is distributed throughout the island and whose silk is more widely used for silk production. Many publications erroneously refer to B. cajani as B. madagascariensis. It shares the common name of landibe with B. cajani. The pupae of B. madagascariensis is consumed by the people of Madagascar, and is known in Malagasy as soherina.

Borocera cajani, also known as landibe in Malagasy, is a species of silk-producing lasiocampid moth endemic to Madagascar. It is often confused with the similar Borocera madagascariensis, which has the same Malagasy name. However, B. cajani is the species associated with silk production in highland Madagascar, while B. madagascariensis is found in the coastal portion of the island.
















