
Io, or Jupiter I, is the innermost and second-smallest of the four Galilean moons of the planet Jupiter. Slightly larger than Earth's moon, Io is the fourth-largest moon in the Solar System, has the highest density of any moon, the strongest surface gravity of any moon, and the lowest amount of water by atomic ratio of any known astronomical object in the Solar System. It was discovered in 1610 by Galileo Galilei and was named after the mythological character Io, a priestess of Hera who became one of Zeus's lovers.

Volcanism on Io, a moon of Jupiter, is represented by the presence of volcanoes, volcanic pits and lava flows on the surface. Io's volcanic activity was discovered in 1979 by Linda Morabito, an imaging scientist working on Voyager 1. Observations of Io by passing spacecraft and Earth-based astronomers have revealed more than 150 active volcanoes. As of 2024, up to 400 such volcanoes are predicted to exist based on these observations. Io's volcanism makes the satellite one of only four known currently volcanically or cryovolcanically active worlds in the Solar System

Reiden Patera is a volcanic feature on Jupiter's moon Io. It was first detected by the Galileo SSI Team during the spacecraft Galileo's first orbit around Jupiter, initially detected as a hotspot. It was once thought that the activity there had stopped or waned below the limits of the spacecraft's Solid State Imager or Near-Infrared Mapping Spectrometer. However, it was noticed in 2002 that Reiden Patera has darkened considerably since the 24th orbit of Galileo. It has been spouting bright red pyroclastic deposits of its own. It is located at 13.4°S 235.45°W and is 70 kilometers in diameter. It is named after a Japanese thunder god. Asha Patera can be found to the east, and Kami-Nari Patera can be found to the north.
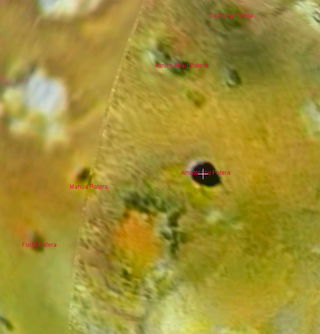
Amaterasu Patera is a patera, a complex crater with scalloped edges, on Jupiter's moon Io. It is one of the darkest features on Io, and the measurement of its thermal spectrum helped to support an anticorrelation between albedo and temperature for Ionian hotspots. The feature has darkened further since the first orbit around Jupiter by the Galileo spacecraft. It is 100 kilometers in diameter and located at 38.1°N 306.5°W. It was named after the Japanese sun goddess Amaterasu. To the north are Kinich Ahau Patera and Dazhbog Patera, and to the west are Manua Patera and Fuchi Patera.

Asha Patera is a patera, or a complex crater with scalloped edges, on Jupiter's moon Io. It is approximately 108 kilometers in diameter and located at 8.84°S 225.69°W. It is named after asha, the Zoroastrian principle of Truth. Its name was adopted by the International Astronomical Union in 1979. Reiden Patera and Kami-Nari Patera can both be found to the west.

Monan Patera is a patera, or a complex crater with scalloped edges, on Jupiter's moon Io. It is about 137 kilometers in diameter and is located at 19.82°N 104.81°W. It is named after Monan, a god in Brazilian mythology that destroyed the world with fire and floods. Its name was adopted by the International Astronomical Union in 1997.

Gish Bar Patera is a patera, or a complex crater with scalloped edges, on Jupiter's moon Io. It is 106.3 by 115.0 kilometers and 9,600 km2 in area. It is located at 16.18°N 90.26°W. It is named after the Babylonian sun god Gish Bar. Its name was approved by the International Astronomical Union in 1997. It is located at the southern base of Gish Bar Mons, an 11-kilometer-high mountain. To the northeast is Skythia Mons, and to the east is Monan Mons, at the north and south ends of which are Monan Patera and Ah Peku Patera.

Estan Patera is a patera, or a complex crater with scalloped edges, on Jupiter's moon Io. It is 95 kilometers in diameter and located at 21.53°N 87.59°W. It is named after the Hittite sun god Estan. Its name was adopted by the International Astronomical Union in 2006. It is located at the northern base of the 11-kilometer mountain Gish Bar Mons. Located west-northwest is Skythia Mons, and to the southwest is Monan Mons, at the northern and southern ends of which are Monan Patera and Ah Peku Patera.

Shango Patera is a patera, or a complex crater with scalloped edges, on Jupiter's moon Io. It is about 90 kilometers in diameter and is located at 32.35°N 100.52°W. It is named after the Yoruba thunder god Shango. Its name was approved by the International Astronomical Union in 2000. It is located north of Skythia Mons. To the southwest is the eruptive center Amirani, and to the southeast are Gish Bar Patera, Gish Bar Mons, and Estan Patera.

Maui Patera is a patera, or a complex crater with scalloped edges, on Jupiter's moon Io. It is about 38 kilometers in diameter and is located at 16.61°N 124.23°W. It is named after Māui, a Hawaiian demigod that sought fire from Mafuike. Its name was approved by the International Astronomical Union in 1979. It is located southwest of the eruptive center Maui, south of Euxine Mons, and southwest of the volcano Amirani. Due east are Monan Patera, Monan Mons, and Ah Peku Patera.

Babbar Patera is a patera, or a complex crater with scalloped edges, on Jupiter's moon Io. It is about 86 kilometers in diameter and is located at 39.8°S 272°W. It is named after a Sumerian sun god, and its name was approved by the International Astronomical Union in 1979. Some scarps near Babbar Patera may represent faults. Immediately south of Babbar Patera is the plateau Lyrcea Planum, and further south is Svarog Patera. To the east is the mountain Egypt Mons.

Svarog Patera is a patera, or a complex crater with scalloped edges, on Jupiter's moon Io. It is 124 kilometers in diameter and is located at 48.66°S 265.74°W. It is named after the Russian smith god Svarog. Its name was approved by the International Astronomical Union in 1979. Svarog Patera is a Voyager spacecraft-detected hot spot. North of Svarog Patera is Lyrcea Planum, north of which is Babbar Patera. To the south is Silpium Mons, and to the east is Hermes Mensa. To the southeast are Pyerun Patera and Epaphus Mensa.

Pyerun Patera is a patera, or a complex crater with scalloped edges, on Jupiter's moon Io. It is about 57 kilometers in diameter and is located at 55.65°S 251.06°W. It is named after the Slavonic god of thunder, Pyerun. The name was adopted by the International Astronomical Union in 1985. West of Pyerun Patera is Mithra Patera, and to the east is the mesa Epaphus Mensa. To the northeast is Epaphus Mensa, and to the northwest are the mountain Silpium Mons and Svarog Patera.

Viracocha Patera is a patera, or a complex crater with scalloped edges, on Jupiter's moon Io. It is about 61 kilometers in diameter and is located at 61.75°S 280.07°W. It is named after the Quechua creator god Viracocha. The name was adopted by the International Astronomical Union in 1979. Viracocha Patera is a Voyager spacecraft-detected hot spot. To Viracocha Patera's east-northeast is Mithra Patera, and to the northeast is the mountain Silpium Mons.

Egypt Mons is a mountain on Jupiter's moon Io. It is 10 kilometers in height, making it the 11th tallest mountain on Io, and taller than Mount Everest. Although the U.S. Geological Survey gives a diameter of 193.7 kilometers, the Io Mountain Database gives a length of 133.8 kilometers and a width of 146.0 kilometers. It is a Flatiron Massif mountain, meaning it has a rugged, irregular appearance and complex surface morphology. It is 9792 km2 in area and its center located at 41.49°S 257.6°W. It has a steep, north-facing scarp. Egypt Mons is named for Egypt, because that is the place where Io ended her wanderings in the mythology. Its name was adopted by the International Astronomical Union in 1997. To the northwest is Babbar Patera, and southeast is Hermes Mensa. Svarog Patera can be found to the southwest.

Tohil Mons is a mountain on Io, one of Jupiter's moons. It stands at 5400 m and is located in the Culann–Tohil region of Io's antijovian hemisphere. It was named after the Mayan weather god Tohil.

Amirani is an active volcano on Jupiter's moon Io, the inner-most of the Galilean Moons. It is located on Io's leading hemisphere at 24.46°N 114.68°W. The volcano is responsible for the largest active lava flow in the entire Solar System, with recent flows dwarfing those of even other volcanos on Io.

The Chaac-Camaxtli region is a volcanic region on Jupiter's moon Io, located from approximately 5 to 20°N and 130 to 160°W in its anti-Jovian hemisphere. It consists mainly of the hummocky bright plains that occupy the surface. This area is defined on the west by Chaac Patera, and on the east by Camaxtli Patera. At least 10 distinct volcanic centers are located in the region, making it a volcanically active region on Io's surface. Most of the volcanism here is expressed as paterae, which range in size from circular to elliptical. A patera is defined by the International Astronomical Union as "irregular or complex craters with scalloped edges." The largest volcanic structure here is the Chaac Patera. The paterae found in the Chaac-Camaxtli region are Chaac, Balder Patera, Grannos, Ababinili, Ruaumoko, Steropes, Camaxtli, Tien Mu, Utu, and Mentu.

PateraPAT-ər-ə is an irregular crater, or a complex crater with scalloped edges on a celestial body. Paterae can have any origin, although the majority of them were created by volcanism. The term comes from Latin, where it refers to a shallow bowl used in antique cultures.















