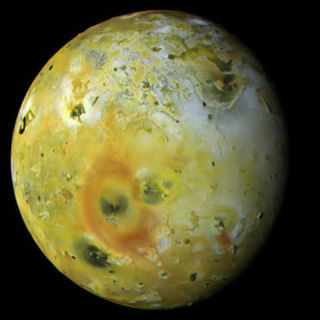
Io, or Jupiter I, is the innermost and second-smallest of the four Galilean moons of the planet Jupiter. Slightly larger than Earth's moon, Io is the fourth-largest moon in the Solar System, has the highest density of any moon, the strongest surface gravity of any moon, and the lowest amount of water by atomic ratio of any known astronomical object in the Solar System. It was discovered in 1610 by Galileo Galilei and was named after the mythological character Io, a priestess of Hera who became one of Zeus's lovers.

Alba Mons is a volcano located in the northern Tharsis region of the planet Mars. It is the biggest volcano on Mars in terms of surface area, with volcanic flow fields that extend for at least 1,350 km (840 mi) from its summit. Although the volcano has a span comparable to that of the United States, it reaches an elevation of only 6.8 km (22,000 ft) at its highest point. This is about one-third the height of Olympus Mons, the tallest volcano on the planet. The flanks of Alba Mons have very gentle slopes. The average slope along the volcano's northern flank is 0.5°, which is over five times lower than the slopes on the other large Tharsis volcanoes. In broad profile, Alba Mons resembles a vast but barely raised welt on the planet's surface. It is a unique volcanic structure with no counterpart on Earth or elsewhere on Mars.
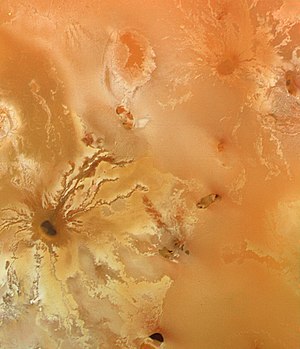
Dazhbog Patera is a patera on Jupiter's moon Io. Named after Dažbog in 1979, it has a largest size of approximately 120 km and is located 55.13°N 301.52°W. This volcano is difficult to differentiate from the other volcanoes and geological features in some images of Io. In images from the Voyager spacecraft, this caldera is quite prominent with its dark reddish floor with a darkish halo around the caldera. However, in Galileo images it is hard to tell where the volcano is. One would suspect that this would mean that it was inactive. But in July 1998, the Hubble Space Telescope using its NICMOS instrument detected a hotspot at Dazhbog.
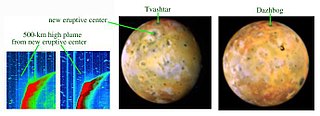
Loki Patera is the largest volcanic depression on Jupiter's moon Io, 202 kilometres (126 mi) in diameter. It contains an active lava lake, with an episodically overturning crust. The level of activity seen is similar to a superfast spreading mid-ocean ridge on Earth. It is the largest volcano on Io, producing about 10% of Io’s total thermal emission. Temperature measurements of thermal emission at Loki Patera taken by Voyager 1's Infrared Interferometer Spectrometer and Radiometer (IRIS) instrument were consistent with sulfur volcanism.
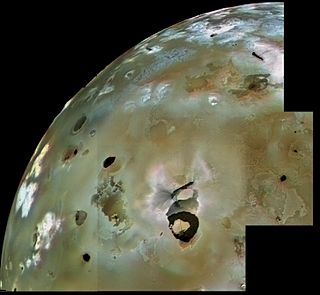
Pele is an active volcano on the surface of Jupiter's moon Io. It is located on Io's trailing hemisphere at 18.7°S 255.3°W. A large, 300-kilometer (190 mi) tall volcanic plume has been observed at Pele by various spacecraft starting with Voyager 1 in 1979, though it has not been persistent. The discovery of the Pele plume on March 8, 1979 confirmed the existence of active volcanism on Io. The plume is associated with a lava lake at the northern end of the mountain Danube Planum. Pele is also notable for a persistent, large red ring circling the volcano resulting from sulfurous fallout from the volcanic plume.

Volcanism on Io, a moon of Jupiter, is represented by the presence of volcanoes, volcanic pits and lava flows on the surface. Io's volcanic activity was discovered in 1979 by Linda Morabito, an imaging scientist working on Voyager 1. Observations of Io by passing spacecraft and Earth-based astronomers have revealed more than 150 active volcanoes. As of 2024, up to 400 such volcanoes are predicted to exist based on these observations. Io's volcanism makes the satellite one of only four known currently volcanically or cryovolcanically active worlds in the Solar System

Biblis Tholus is an extinct Martian volcano located at 2.55°N 235.62°E, one of two volcanoes near the center of the Tharsis volcanism. Along with Ulysses Tholus, it is almost midway between Olympus Mons and the Tharsis Montes. Biblis Tholus lies in the Tharsis quadrangle. It is approximately 170 kilometers (110 mi) long and 100 kilometers (62 mi) wide, rising about 3 kilometers (1.9 mi) from its surroundings.

Tohil Mons is a mountain on Io, one of Jupiter's moons. It stands at 5400 m and is located in the Culann–Tohil region of Io's antijovian hemisphere. It was named after the Mayan weather god Tohil.

Surt is an active volcano on Jupiter's moon Io. It is located on Io's Jupiter-facing hemisphere at 45.21°N 336.49°W. Surt consists of an oblong volcanic pit, 75 by 40 kilometres in diameter, surrounded by reddish sulfur and bright sulfur dioxide deposits to its south and east. The volcano was first observed in images acquired by the Voyager 1 spacecraft in March 1979. Later that year, the International Astronomical Union named this feature after Surtr, a leader of the fire giants of Norse mythology.

Prometheus is an active volcano on Jupiter's moon Io. It is located on Io's hemisphere facing away from Jupiter at 1.52°S 153.94°W.

Amirani is an active volcano on Jupiter's moon Io, the inner-most of the Galilean Moons. It is located on Io's leading hemisphere at 24.46°N 114.68°W. The volcano is responsible for the largest active lava flow in the entire Solar System, with recent flows dwarfing those of even other volcanos on Io.

Tupan Patera is an active volcano on Jupiter's moon Io. It is located on Io's anti-Jupiter hemisphere at 18.73°S 141.13°W. Tupan consists of a volcanic crater, known as a patera, 79 kilometers across and 900 meters deep. The volcano was first seen in low-resolution observations by the two Voyager spacecraft in 1979, but volcanic activity was not seen at this volcano until June 1996 during the Galileo spacecraft's first orbit. Following this first detection of near-infrared thermal emission and subsequent detections by Galileo during the next few orbits, this volcano was formally named Tupan Patera, after the thunder god of the Tupí-Guaraní indigenous peoples in Brazil, by the International Astronomical Union in 1997.

Tawhaki Patera is an active volcano on Jupiter's moon Io. It is located on Io's leading hemisphere at 3.32°N 76.18°W within the equatorial plains of western Media Regio. Tawhaki is an Ionian patera, a type of volcanic crater similar to a caldera, 49.8 kilometers (30.9 mi) wide and 550 meters (1,800 ft) deep.

The exploration of Io, Jupiter's innermost Galilean and third-largest moon, began with its discovery in 1610 and continues today with Earth-based observations and visits by spacecraft to the Jupiter system. Italian astronomer Galileo Galilei was the first to record an observation of Io on January 8, 1610, though Simon Marius may have also observed Io at around the same time. During the 17th century, observations of Io and the other Galilean satellites helped with the measurement of longitude by map makers and surveyors, with validation of Kepler's Third Law of planetary motion, and with measurement of the speed of light. Based on ephemerides produced by astronomer Giovanni Cassini and others, Pierre-Simon Laplace created a mathematical theory to explain the resonant orbits of three of Jupiter's moons, Io, Europa, and Ganymede. This resonance was later found to have a profound effect on the geologies of these moons. Improved telescope technology in the late 19th and 20th centuries allowed astronomers to resolve large-scale surface features on Io as well as to estimate its diameter and mass.

Thor is an active volcano on Jupiter's moon Io. It is located on Io's anti-Jupiter hemisphere at 39.15°N 133.14°W. A major eruption with high thermal emission and a large, volcanic plume was observed during a Galileo flyby on August 6, 2001, when the spacecraft flew through the outer portions of the plume allowing for direct sampling. The eruption continued into Galileo's next flyby in October 2001. As seen during high-resolution images taken during the eruption, Thor consists of a series of dark lava flows emanating from a set of nearby volcanic depressions. Before the eruption, the area consisted of red-brown plains, composed of irradiated sulfur, typical of Io's mid- to high-northern latitudes and a set of yellow flows, possibly consisting of sulfur or silicate flows covered by diffuse sulfur deposits. During the New Horizons encounter in February 2007, Thor was still active, with the spacecraft observing thermal emission in the near-infrared and a volcanic plume at the volcano.

Zamama is an active volcanic center on Jupiter's moon Io. This volcanic center erupted after the Voyager 1 flyby in 1979, making it one of the few planetary volcanoes known to have activated during this generation's lifetime. Further analysis and study by the Galileo spacecraft helped with the overall study of Io's volcanism. Galileo located it on Io at 21°N173°W. Zamama has a fissure-fed-type flow that is 150 km (93 mi) long with temperatures of 1,100 K, and the volcanic center site has explosive and effusive eruption characteristics. The flow appears to be emanating from the Promethean-type volcano.

The Chaac-Camaxtli region is a volcanic region on Jupiter's moon Io, located from approximately 5 to 20°N and 130 to 160°W in its anti-Jovian hemisphere. It consists mainly of the hummocky bright plains that occupy the surface. This area is defined on the west by Chaac Patera, and on the east by Camaxtli Patera. At least 10 distinct volcanic centers are located in the region, making it a volcanically active region on Io's surface. Most of the volcanism here is expressed as paterae, which range in size from circular to elliptical. A patera is defined by the International Astronomical Union as "irregular or complex craters with scalloped edges." The largest volcanic structure here is the Chaac Patera. The paterae found in the Chaac-Camaxtli region are Chaac, Balder Patera, Grannos, Ababinili, Ruaumoko, Steropes, Camaxtli, Tien Mu, Utu, and Mentu.

Leviathan Patera is a major cryovolcanic caldera on Neptune's largest moon Triton. Discovered by the Voyager 2 spacecraft in 1989, Leviathan Patera is located in Monad Regio and within Cipango Planum's western regions. Leviathan Patera is approximately 80 kilometres in diameter and may be the center of one of the largest cryovolcanic or volcanic edifices in the Solar System.