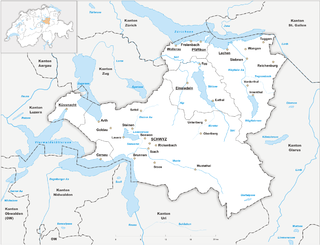
The canton of Schwyz is a canton in central Switzerland between the Alps in the south, Lake Lucerne to the west and Lake Zürich in the north, centred on and named after the town of Schwyz.

The Battle of Morgarten took place on 15 November 1315, when troops of Schwyz, supported by their allies of Uri and Unterwalden, ambushed an Austrian army under the command of Leopold I, Duke of Austria on the shores of Lake Ägeri, in the territory of Schwyz.

Schwyz is a town and the capital of the canton of Schwyz in Switzerland.

Eidgenossenschaft is a German word specific to the political history of Switzerland. It means "oath commonwealth" or "oath alliance", in reference to the "eternal pacts" formed between the Eight Cantons of the Old Swiss Confederacy of the late medieval period. In Swiss historiography, this relates most notably to the Rütlischwur between the three founding cantons Uri, Schwyz and Unterwalden, which traditionally dates to 1307. In modern usage, Eidgenossenschaft is the German term used as an equivalent to "Confederation" in the official name of Switzerland, Schweizerische Eidgenossenschaft. Its corresponding adjective, eidgenössisch—officially translated as "Swiss federal"—is used in the name of organisations such as the Eidgenössische Technische Hochschule, or Swiss Federal Institute of Technology. The term Eidgenosse refers to individual members of the Eidgenossenschaft. It is attested as early as 1315 in the Pact of Brunnen, referring to the cantons of Uri, Schwyz and Unterwalden. The abstract noun Eidgenossenschaft is attested in the 15th century. In modern usage, Eidgenosse is sometimes used in archaic or ironic usage for "Swiss citizen", especially for those citizens of purely Swiss origin and not from immigration.

Nicholas of Flüe was a Swiss hermit and ascetic who is the patron saint of Switzerland. He is sometimes invoked as Brother Klaus. A farmer, military leader, member of the assembly, councillor, judge and mystic, he was respected as a man of complete moral integrity. He is known for having fasted for over twenty years. Brother Klaus's counsel to the Diet of Stans (1481) helped prevent war between the Swiss cantons.

Einsiedeln is a municipality and district in the canton of Schwyz in Switzerland known for its monastery, the Benedictine Einsiedeln Abbey, established in the 10th century.

Waldstätte is a term which has been used since the early thirteenth century to refer to the Stätte, or later Ort or Stand of the early confederate allies of Uri, Schwyz and Unterwalden in today's Central Switzerland.

The Treaty of Basel of 22 September 1499 was an armistice following the Battle of Dornach, concluding the Swabian War, fought between the Swabian League and the Old Swiss Confederacy.
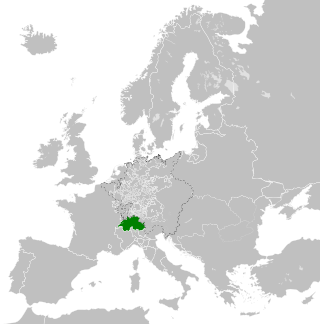
The Old Swiss Confederacy, also known as Switzerland or the Swiss Confederacy, was a loose confederation of independent small states, initially within the Holy Roman Empire. It is the precursor of the modern state of Switzerland.

The Battle of Crevola was fought in the spring of 1487, between a marauding Swiss army from the Valais and Lucerne and troops from the Duchy of Milan, for the supremacy of the Val d'Ossola (Eschental).

The English name of Switzerland is a compound containing Switzer, an obsolete term for the Swiss, which was in use during the 16th to 19th centuries. The English adjective Swiss is a loan from French Suisse, also in use since the 16th century.

The historiography of Switzerland is the study of the history of Switzerland.

The Zunfthaus zur Meisen is the guild house of the Zunft zur Meisen. It is one of the many historically valuable buildings in the Lindenhof quarter in Zürich, Switzerland, and also housed the porcelain and faience collection of the Swiss National Museum by April 2018. It is situated at the Münsterhof and the Münsterbrücke, a bridge over the river Limmat, opposite the upper Limmatquai with the Constaffel, Zimmerleuten, Kämbel and Saffran guild houses.

Rüti Monastery was a former Premonstratensian monastery, founded in 1206 and suppressed in 1525 on occasion of the Reformation in Zürich, situated in the municipality of Rüti in the canton of Zürich, Switzerland. The monastery's church was the final resting place of the Counts of Toggenburg, among them Count Friedrich VII and 13 other members of the Toggenburg family, and other noble families. Between 1206 and 1525, the monastery comprised 14 incorporated churches and the owner of extensive lands and estates at 185 localities.
In legend and in the early historiography of Switzerland there is an account of a migration of a population of Swedes and Frisians settling in the Swiss Alps, specifically in Schwyz and in Hasli (Schwedensage).

The House of Rapperswil respectively Counts of Rapperswil ruled the upper Zürichsee and Seedamm region around Rapperswil and parts of, as of today, Swiss cantons of St. Gallen, Glarus, Zürich and Graubünden when their influence was most extensive around the 1200s until the 1290s. They acted also as Vogt of the most influential Einsiedeln Abbey in the 12th and 13th century, and at least three abbots of Einsiedeln were members of Rapperswil family.

Roger Sablonier was a Swiss historian and writer of non-fiction publications, and Emeritus of the faculty of the University of Zürich.

The noble family von Sax or Saxe was a medieval noble family in eastern Switzerland. They owned estates and castles on both sides of the Alps in the modern cantons of St. Gallen, Graubünden and Ticino. The origin of the family is unknown, but they probably stem from Churrätien nobility and were related to the da Torre family. The family divided into two main lines; the Grafen (counts) von Sax-Misox and the Freiherren (barons) von Hohensax.
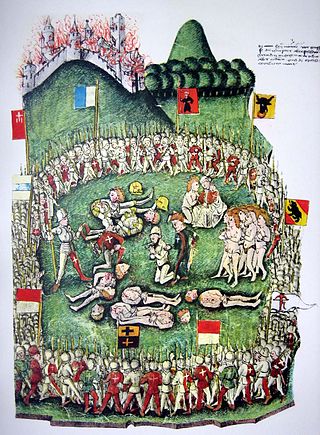
Ital Reding the Elder was Landammann of Schwyz and the leader of the forces of Schwyz during the Old Zürich War (1440–1450).

Gerold Meyer von Knonau was a Swiss geographer and historian whose most enduring contribution to scholarship may well have been his pioneering work between 1837 and 1858 as cantonal archivist for Zürich and the surrounding region.