Related Research Articles

New Mexico is a state in the Southwestern United States. It is one of the Mountain States of the southern Rocky Mountains, sharing the Four Corners region of the western U.S. with Utah, Colorado, and Arizona, and bordering Texas to the east and southeast, Oklahoma to the northeast, and the Mexican states of Chihuahua and Sonora to the south. The state capital is Santa Fe, which is the oldest capital in the U.S., founded in 1610 as the government seat of Nuevo México in New Spain; the largest city is Albuquerque.

The Santa Fe Trail was a 19th-century route through central North America that connected Franklin, Missouri, with Santa Fe, New Mexico. Pioneered in 1821 by William Becknell, who departed from the Boonslick region along the Missouri River, the trail served as a vital commercial highway until 1880, when the railroad arrived in Santa Fe. Santa Fe was near the end of El Camino Real de Tierra Adentro, which carried trade from Mexico City.

The New Mexico Rail Runner Express is a commuter rail system serving the metropolitan areas of Albuquerque and Santa Fe, New Mexico. It is administered by the New Mexico Department of Transportation (NMDOT) and the Rio Metro Regional Transit District, a regional transportation agency, while Herzog Transit Services currently holds the contract for the operation and maintenance of the line & equipment. Phase I of the system, operating on an existing right-of-way from Belen to Bernalillo that NMDOT purchased from BNSF Railway, opened in July 2006. Phase II, the extension of the line to Santa Fe, opened in December 2008. Daily ridership, as of February 2019, was 2,200 trips per day.

Santa Fe 2926 is a former Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway (ATSF) class 2900 4-8-4 type steam locomotive, built by Baldwin in 1944. It was used to pull passenger and fast freight trains, mostly throughout New Mexico, until its fire was dropped on Christmas Eve of 1953, and it was retired three years later. It was subsequently donated to a park in Albuquerque for static display. In 1999, it was purchased by the New Mexico Steam Locomotive and Railroad Historical Society to be rebuilt for operational purposes. After over twenty years of work, No. 2926 steamed up again on July 24, 2021, and it will be used for mainline excursion service.
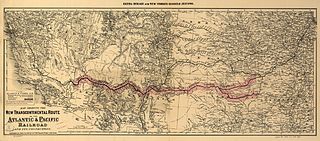
The Atlantic and Pacific Railroad was a U.S. railroad that owned or operated two disjointed segments, one connecting St. Louis, Missouri with Tulsa, Oklahoma, and the other connecting Albuquerque, New Mexico with Southern California. It was incorporated by the U.S. Congress in 1866 as a transcontinental railroad connecting Springfield, Missouri and Van Buren, Arkansas with California. The central portion was never constructed, and the two halves later became parts of the St. Louis-San Francisco Railway and Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway systems, now both merged into the BNSF Railway.

The Santa Fe, Prescott and Phoenix Railway (SFP&P) was a common carrier railroad that later became an operating subsidiary of the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway in Arizona. At Ash Fork, Arizona, the SFP&P connected with Santa Fe's operating subsidiary, the Atlantic & Pacific Railroad mainline, that ran from California to Chicago. The SFP&P's 195-mile (314 km) line extended the Santa Fe Railway south into Phoenix. The SFP&P extended another 100 miles (160 km) to the east from Phoenix to Florence and Winkelman via the Phoenix and Eastern Railroad. The SFP&P also served several mines in the Prescott area through its various subsidiary railroads.

The historic U.S. Route 66 ran east–west across the central part of the state of New Mexico, along the path now taken by Interstate 40 (I-40). However, until 1937, it took a longer route via Los Lunas, Albuquerque, and Santa Fe, now roughly New Mexico State Road 6 (NM 6), I-25, and US 84. Large portions of the old road parallel to I-40 have been designated NM 117, NM 118, NM 122, NM 124, NM 333, three separate loops of I-40 Business, and state-maintained frontage roads.

The California Southern Railroad was a subsidiary railroad of the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway in Southern California. It was organized July 10, 1880, and chartered on October 23, 1880, to build a rail connection between what has become the city of Barstow and San Diego, California.

The Gulf, Colorado and Santa Fe Railway was a subsidiary of the Atchison, Topeka & Santa Fe Railway. From its starting point in Galveston, Texas, the railroad eventually extended northwestwards across the state to Sweetwater and northwards via Fort Worth to Purcell, Oklahoma.

Tijeras Canyon is a prominent canyon in the central part of the U.S. state of New Mexico. It separates the Sandia Mountains subrange to the north from the Manzano Mountains subrange to the south. These subranges are part of the larger Sandia–Manzano Mountains; Tijeras Canyon forms a pass through this range. Elevations along the bottom of the canyon range from 5,600 feet (1,700 m) to 7,000 feet (2,100 m) above sea level. The canyon drains to the west, into a large dry wash known as Tijeras Arroyo, which runs through Kirtland Air Force Base, passes just south of the Albuquerque International Airport, and then joins the Rio Grande. The arroyo heads at the historically important pass, and this pass and the entire canyon are traversed by Interstate 40, following the path of historic U.S. Route 66.
Interstate 40 (I-40), a major east–west route of the Interstate Highway System, runs east–west through Albuquerque in the U.S. state of New Mexico. It is the direct replacement for the historic U.S. Highway 66 (US 66).

The Southern Transcon is a main line of BNSF Railway comprising 11 subdivisions between Southern California and Chicago, Illinois. Completed in its current alignment in 1908 by the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway, when it opened the Belen Cutoff in New Mexico and bypassed the steep grades of Raton Pass, it now serves as a mostly double-tracked intermodal corridor.
The Chili Line, officially known as the Santa Fe Branch, was a 3 ft narrow-gauge branch of the Denver and Rio Grande Western Railroad (D&RGW). It ran 125.6 miles (202.1 km) from Antonito, Colorado, to Santa Fe, New Mexico. The Denver and Rio Grande Railway (D&RG) began construction of the line in 1880 and completed the line from Antonito to Española, New Mexico, but could not build any further because of an agreement with the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railroad (AT&SF). The Texas, Santa Fe and Northern Railroad was incorporated to complete the line, and the line between Española and Santa Fe opened in 1886 and was transferred to the Denver and Rio Grande shortly thereafter. The D&RGW closed the Chili Line in 1941 because of competition from road transportation, and the line was abandoned shortly thereafter.

Isleta Station was a railway station on the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway in Isleta, New Mexico. Located twelve miles south of Albuquerque, Isleta was a junction station, located at the point where two lines split. One line went to El Paso, Texas while the other was the main line to Los Angeles. The Southwest Chief passenger train now passes by on the L.A. line.

Elias Sleeper Stover was an American businessman, politician, and university president.

Nutt is an unincorporated community in Luna County, southern New Mexico, in the American Southwest. It is located nineteen miles southwest of Hatch on NM 26 at the intersection with NM 27.
Edward Alfred Harrison, known as E. A. Harrison, was an American architect who worked as a staff architect for the Atchison, Topeka & Santa Fe Railway, with offices in Topeka, Kansas, and later in Chicago, Illinois.

Barton is a census-designated place (CDP) in Bernalillo and Santa Fe counties, New Mexico, United States. It was first listed as a CDP prior to the 2020 census.
The New Mexico Central Railroad was formed in 1908 from the consolidation of the Santa Fe Central Railway and the Albuquerque Eastern Railway Co., to operate the 116 miles of track between Torrance and Santa Fe, New Mexico. That line, reorganized in 1918 as the New Mexico Central Railway, was sold to the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railroad in 1926. The New Mexico Central remained the nominal owner of the Santa Fe-leased line while the Santa Fe proceeded to abandon operation of the trackage in pieces, ending in 1972 with abandonment from Willard to Calvert (Moriarty), New Mexico.
Originally chartered December 7, 1900, as the Santa Fe, Albuquerque and Pacific Railway Company, this line became the Santa Fe Central Railway in July of 1901. Its 116-mile route was completed in 1903 between a rail junction at Torrance, New Mexico and Santa Fe, New Mexico. The Governor of the New Mexico Territory called it “(o)ne of the most important railway projects for New Mexico in recent years….” The principals behind the line also intended a branch called the Albuquerque Eastern Railway running 43 miles west from Moriarty, New Mexico through the Tijeras Pass to Albuquerque. However, construction on that line was halted in 1905 after only the first 8 miles of track out of Moriarty had been built, due to the Comptroller of the Currency closing the doors of the bank financing these railroad construction projects.
References
- ↑ Governor, New Mexico (1903). "The Santa Fe Central Railway, Report of the Governor of New Mexico to the Secretary of the Interior, 1903" . Retrieved September 25, 2021.
- ↑ "History of New Mexico: Its Resources and People, Volume II". 1907. Retrieved September 25, 2021.
- 1 2 "Receivership of the New Mexico Central Railroad Co., Extension of Tenure of Government Control of Railroads, Volume 3". 1919. Retrieved September 25, 2021.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Myrick, David F. (1990). New Mexico's Railroads: A Historical Survey. ISBN 9780826311856 . Retrieved September 22, 2021.
- ↑ Sherman, James E.; Sherman, Barbara H. (January 1975). Hagan and Coyote. ISBN 9780806111063 . Retrieved September 23, 2021.