
Alcohol abuse encompasses a spectrum of unhealthy alcohol drinking behaviors, ranging from binge drinking to alcohol dependence, in extreme cases resulting in health problems for individuals and large scale social problems such as alcohol-related crimes.

Kombucha is a fermented, lightly effervescent, sweetened black tea drink commonly consumed for its purported health benefits. Sometimes the beverage is called kombucha tea to distinguish it from the culture of bacteria and yeast. Juice, spices, fruit or other flavorings are often added.
Drug rehabilitation is the process of medical or psychotherapeutic treatment for dependency on psychoactive substances such as alcohol, prescription drugs, and street drugs such as cannabis, cocaine, heroin or amphetamines. The general intent is to enable the patient to confront substance dependence, if present, and stop substance misuse to avoid the psychological, legal, financial, social, and physical consequences that can be caused.

Permethrin is a medication and an insecticide. As a medication, it is used to treat scabies and lice. It is applied to the skin as a cream or lotion. As an insecticide, it can be sprayed onto clothing or mosquito nets to kill the insects that touch them.
1-Triacontanol (n-triacontanol) is a fatty alcohol of the general formula C30H62O, also known as melissyl alcohol or myricyl alcohol. It is found in plant cuticle waxes and in beeswax. Triacontanol is a growth stimulant for many plants, most notably roses, in which it rapidly increases the number of basal breaks. 1-Triacontanol is a natural plant growth regulator. It has been widely used to enhance the yield of various crops around the world, mainly in Asia. Triacontanol has been reported to increase the growth of plants by enhancing the rates of photosynthesis, protein biosynthesis, the transport of nutrients in a plant and enzyme activity, reducing complex carbohydrates among many other purposes. The fatty alcohol appears to increase the physiological efficiency of plant cells and boost the potential of the cells responsible for the growth and maturity of a plant.

A breathalyzer or breathalyser is a device for estimating blood alcohol content (BAC), or to detect viruses or diseases from a breath sample.

Micrognathism is a condition where the jaw is undersized. It is also sometimes called mandibular hypoplasia. It is common in infants, but is usually self-corrected during growth, due to the jaws' increasing in size. It may be a cause of abnormal tooth alignment and in severe cases can hamper feeding. It can also, both in adults and children, make intubation difficult, either during anesthesia or in emergency situations.

The Journal of Studies on Alcohol and Drugs (JSAD) is a peer-reviewed scientific journal that publishes original research articles on various aspects of the use and misuse of alcohol and other drugs. Topics covered include the biological, medical, epidemiological, social, psychological, and legal aspects of alcohol and other drug use, abuse, and dependence. The journal was established in 1940 as the Quarterly Journal of Studies on Alcohol, changed its name in 1975 to Journal of Studies on Alcohol, before obtaining its current name in 2007. The journal appears bimonthly and publishes supplements at irregular intervals. The Journal of Studies on Alcohol and Drugs is a not-for-profit journal based in the Center of Alcohol Studies at Rutgers University.
Genes, Brain and Behavior is a peer-reviewed online-only scientific journal covering research in the fields of behavioral, neural, and psychiatric genetics. It is published by Wiley-Blackwell on behalf of the International Behavioural and Neural Genetics Society. The journal was established in 2002 as a quarterly and is currently published monthly. G2B is a hybrid open access journal, but two years after publication all content is available for free online.
Addiction is a monthly peer-reviewed scientific journal established in 1903 by the Society for the Study of Addiction to Alcohol and other Drugs as the British Journal of Inebriety. It was renamed British Journal of Addiction to Alcohol & Other Drugs in 1947, then renamed to British Journal of Addiction in 1980, before finally obtaining its current name in 1993. It covers research relating to the abuse of alcohol, illicit drugs, and tobacco, as well as behavioural addictions. The editor-in-chief is John Marsden.
Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research is a scientific journal covering research concerning alcohol abuse and its treatment. It is published by Wiley-Blackwell on behalf of the Research Society on Alcoholism and the International Society for Biomedical Research on Alcoholism.

Addiction Biology is a quarterly peer-reviewed scientific journal covering research on substance abuse. It is one of two journals published on behalf of the Society for the Study of Addiction to Alcohol and other Drugs. The major focus of Addiction Biology is on neuroscience contributions from animal experimentation and clinical point of views. The editor-in-chief is Rainer Spanagel . According to the Journal Citation Reports, the journal has a 2020 impact factor of 4.280.
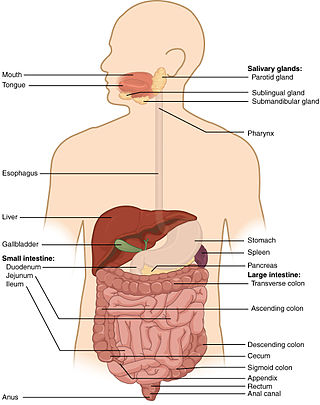
Auto-brewery syndrome(ABS) (also known as gut fermentation syndrome, endogenous ethanol fermentation or drunkenness disease) is a condition characterized by the fermentation of ingested carbohydrates in the gastrointestinal tract of the body caused by bacteria or fungi. ABS is a rare medical condition in which intoxicating quantities of ethanol are produced through endogenous fermentation within the digestive system. The organisms responsible for ABS include various yeasts and bacteria, including Saccharomyces cerevisiae, S. boulardii, Candida albicans, C. tropicalis, C. krusei, C. glabrata, C. kefyr, C. parapsilosis, Klebsiella pneumoniae, and Enterococcus faecium. These organisms use lactic acid fermentation or mixed acid fermentation pathways to produce an ethanol end product. The ethanol generated from these pathways is absorbed in the small intestine, causing an increase in blood alcohol concentrations that produce the effects of intoxication without the consumption of alcohol.

Alcohol, sometimes referred to by the chemical name ethanol, is a depressant drug that is the active ingredient in drinks such as beer, wine, and distilled spirits. It is one of the oldest and most commonly consumed recreational drugs, causing the characteristic effects of alcohol intoxication ("drunkenness"). Among other effects, alcohol produces happiness and euphoria, decreased anxiety, increased sociability, sedation, impairment of cognitive, memory, motor, and sensory function, and generalized depression of central nervous system (CNS) function. Ethanol is only one of several types of alcohol, but it is the only type of alcohol that is found in alcoholic beverages or commonly used for recreational purposes; other alcohols such as methanol and isopropyl alcohol are significantly more toxic. A mild, brief exposure to isopropanol, being only moderately more toxic than ethanol, is unlikely to cause any serious harm. Methanol, being profoundly more toxic than ethanol, is lethal in quantities as small as 10–15 milliliters.
The American Journal of Drug and Alcohol Abuse is a bimonthly peer-reviewed medical journal covering all aspects of addiction. It was established in 1974 and is published by Taylor & Francis.
Drug and Alcohol Review is a peer-reviewed medical journal covering research related to alcohol and drug-related problems. It is the official journal of the Australasian Professional Society on Alcohol and other Drugs. It publishes seven issues annually.
Traffic Injury Prevention is a bimonthly peer-reviewed academic journal covering the prevention of injuries resulting from traffic accidents. It was established in 1999 as the Journal of Crash Prevention and Injury Control, obtaining its current name in 2002. It is the official journal of the Association for the Advancement of Automotive Medicine, the International Traffic Medicine Association, the International Research Council on the Biomechanics of Impact, and the International Council on Alcohol Drugs and Traffic Safety. The editor-in-chief is David C. Viano. According to the Journal Citation Reports, the journal has a 2014 impact factor of 1.413, ranking it 95th out of 162 journals in the category "Public, Environmental & Occupational Health".
Alcohol and Alcoholism is a bimonthly peer-reviewed medical journal covering alcoholism and other health effects of alcohol. It was established in 1963 as the Bulletin on Alcoholism, with H.D. Chalke as the founding editor. In 1968, it was renamed the Journal of Alcoholism, and in 1977, it was again renamed, this time to British Journal on Alcohol and Alcoholism. In 1983, it obtained its current name. It is co-owned and co-published by the Medical Council on Alcohol (MCA) along with Oxford University Press, which bought a 50% stake in the journal in 2011. It is the official journal of both the MCA and the European Society for Biomedical Research on Alcoholism. The editors-in-chief are Jonathan D. Chick and Lorenzo Leggio. According to the Journal Citation Reports, the journal has a 2020 impact factor of 2.826.
Nordic Studies on Alcohol and Drugs is a bimonthly peer-reviewed open access medical journal covering research on the health effects of alcohol and other drugs. It was established in 1984 as Alkoholpolitik – Tidskrift för nordisk alkoholforskning. It was originally published as part of a partnership between the Nordic Council for Alcohol and Drug Research and the Finnish alcohol company Alko. It was previously published by Walter de Gruyter until being acquired by its current publisher, SAGE Publications, in 2017. The editor-in-chief is Matilda Hellman. According to the Journal Citation Reports, the journal has a 2020 impact factor of 1.600.








