Related Research Articles

Stippling is the creation of a pattern simulating varying degrees of solidity or shading by using small dots. Such a pattern may occur in nature and these effects are frequently emulated by artists.
Keyesville is an unincorporated community in Kern County, California. It is located 2 miles (3.2 km) west of Lake Isabella and the Kern River Valley, at an elevation of 2,848 feet (868 m). Keyesville, founded in 1854 is named for Richard M. Keyes, whose discovery of gold in 1853 started the Kern River Gold Rush.

Micrococcus luteus is a Gram-positive to Gram-variable, nonmotile, tetrad-arranging, pigmented, saprotrophic coccus bacterium in the family Micrococcaceae. It is urease and catalase positive. An obligate aerobe, M. luteus is found in soil, dust, water and air, and as part of the normal microbiota of the mammalian skin. The bacterium also colonizes the human mouth, mucosae, oropharynx and upper respiratory tract.

The Sudan golden sparrow is a small species of bird in the sparrow family found in sub-Saharan Africa. It is a famous cage bird, and in aviculture, it is known as the golden song sparrow. The Arabian golden sparrow and this species are sometimes considered one species, as the "golden sparrow".

Suillus is a genus of basidiomycete fungi in the family Suillaceae and order Boletales. Species in the genus are associated with trees in the pine family (Pinaceae), and are mostly distributed in temperate locations in the Northern Hemisphere, although some species have been introduced to the Southern Hemisphere.

Micrococcus is a genus of bacteria in the Micrococcaceae family. Micrococcus occurs in a wide range of environments, including water, dust, and soil. Micrococci have Gram-positive spherical cells ranging from about 0.5 to 3 micrometers in diameter and typically appear in tetrads. They are catalase positive, oxidase positive, indole negative and citrate negative. Micrococcus has a substantial cell wall, which may comprise as much as 50% of the cell mass. The genome of Micrococcus is rich in guanine and cytosine (GC), typically exhibiting 65 to 75% GC-content. Micrococci often carry plasmids that provide the organism with useful traits.

Suillus luteus is a bolete fungus, and the type species of the genus Suillus. A common fungus native all across Eurasia from Ireland to Korea, it has been introduced widely elsewhere, including North and South America, southern Africa, Australia and New Zealand. Commonly referred to as slippery jack or sticky bun in English-speaking countries, its names refer to the brown cap, which is characteristically slimy in wet conditions. The fungus, initially described as Boletus luteus by Carl Linnaeus in 1753, is now classified in a different fungus family as well as genus. Suillus luteus is edible, though not as highly regarded as other bolete mushrooms. It is commonly prepared and eaten in soups, stews or fried dishes. The slime coating, however, may cause indigestion if not removed before eating. It is often sold as a dried mushroom.

Calochortus luteus, the yellow mariposa lily, is a mariposa lily endemic to California.
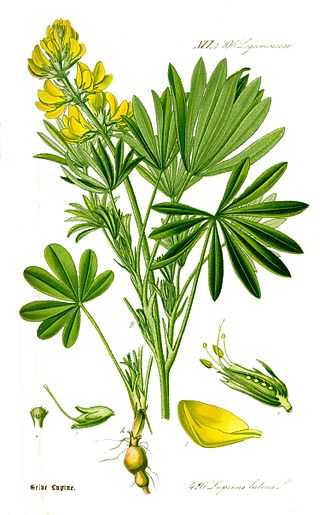
Lupinus luteus is known as annual yellow-lupin, European yellow lupin or yellow lupin. It is native to the Mediterranean region of Southern Europe.

Zapus is a genus of North American jumping mouse. It is the only genus whose members have the dental formula 1.0.1.31.0.0.3. Zapus are the only extant mammals aside from the Aye-aye with a total of 18 teeth.
The yellow steppe lemming is a species of rodent in the family Cricetidae. It is found in China, Kazakhstan, and Mongolia. Its natural habitat is temperate desert.

Eolagurus is a genus of rodent in the family Cricetidae. It contains the following species:

The canary white-eye or yellow white-eye is a species of white-eye endemic to northern Australia in subtropical or tropical mangrove forests. Its common name reflects the circle of white feathers around its eye.
Oloplotosus is a genus of eeltail catfishes endemic to the island of New Guinea.
Haplochromis luteus is a species of cichlid endemic to Lake Victoria where it is known from the western park of Speke Gulf and also from the Sengerema region, all in Tanzania. This shallow water species, 0 to 2 metres, is found along gently sloping rocky shores. This species can reach a length of 13.3 centimetres (5.2 in) SL. This species was originally described in the genus Mbipia, however not all scientists have accepted such placement. It may be placed back in Mbipia should a comprehensive review of the genus Haplochromis be conducted.

Gymnopilus luteus, known as the yellow gymnopilus, is a widely distributed mushroom-forming fungus of the Eastern United States. It contains the hallucinogens psilocybin and psilocin. It is often mistaken for G. speciosissimus and G. subspectabilis.
Arthrobacter luteus (ALU) is a species of gram-positive bacteria in the genus Arthrobacter. A. luteus is facultatively anaerobic, pleomorphic, branching, non-motile, non-sporulating, non-acid-fast, catalase-positive, and rod-shaped.
Angustibacter luteus is a bacterium from the genus of Angustibacter which has been isolated from subarctic forest soil.
Flaviaesturariibacter luteus is a Gram-negative, rod-shaped, non-spore-forming and non-motile bacterium from the genus of Flaviaesturariibacter which has been isolated from soil from an agricultural floodplain from Mashare in Namibia.
Alkalicoccus saliphilus is a Gram-positive and haloalkaliphilic bacterium from the genus of Alkalicoccus.
References
- 1 2 "Species: Alkalicoccus luteus". LPSN.DSMZ.de.
- 1 2 Subhash, Y.; Sasikala, Ch.; Ramana, Ch. V. (1 May 2014). "Bacillus luteus sp. nov., isolated from soil". International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology. 64 (Pt_5): 1580–1586. doi: 10.1099/ijs.0.053504-0 . PMID 24478212.
- 1 2 "Alkalicoccus luteus". www.uniprot.org.