Mollicutes is a class of bacteria distinguished by the absence of a cell wall. The word "Mollicutes" is derived from the Latin mollis, and cutis. Individuals are very small, typically only 0.2–0.3 μm in size and have a very small genome size. They vary in form, although most have sterols that make the cell membrane somewhat more rigid. Many are able to move about through gliding, but members of the genus Spiroplasma are helical and move by twisting. The best-known genus in the Mollicutes is Mycoplasma. Colonies show the typical "fried-egg" appearance.
Haloarcula is a genus of extreme halophilic Archaea in the class of Halobactaria.
In taxonomy, Haloferax is a genus of the Haloferacaceae.

Lipothrixviridae is a family of viruses in the order Ligamenvirales. Thermophilic archaea in the phylum Thermoproteota serve as natural hosts. There are 11 species in this family, assigned to 4 genera. The genus

Globuloviridae is a family of hyperthermophilic archaeal viruses. Crenarchaea of the genera Pyrobaculum and Thermoproteus serve as natural hosts. There are four species in this family, assigned to a single genus, Alphaglobulovirus.

Halspiviridae is a family of viruses that consists of a single genus, Salterprovirus, which consists of a single recognised species; Salterprovirus His1. This virus was isolated from hypersaline water in Australia and was able to be cultured on the halophilic archaeon Haloarcula hispanica. Like many other archaeoviruses, His1 has an approximately limoniform (lemon-shaped) virion.

Ampullaviridae is a family of viruses that infect archaea of the genus Acidianus. Only one genus in this family has been described, Bottigliavirus, which contains three species. The name of the family and genus is derived from the Latin word for bottle, ampulla, due to the virions having the shape of a bottle. The family was first described during an investigation of the microbial flora of hot springs in Italy.

Bicaudaviridae is a family of hyperthermophilic archaeal viruses. Members of the genus Acidianus serve as natural hosts. There is only one genus (Bicaudavirus) and one species in this family: Acidianus two-tailed virus. However, Sulfolobus tengchongensis spindle-shaped viruses 1 and 2 are regarded to belong to this family also.

Haloarcula hispanica pleomorphic virus 1 (HHPV1) is a double stranded DNA virus that infects the halophilic archaeon Haloarcula hispanica. It has a number of unique features unlike any previously described virus.
Haloarcula hispanica SH1 virus is a double-stranded DNA virus that infects the archaeon Haloarcula hispanica. This virus has a number of unique features that were unlike any other known virus when it was described. However similarities have since been found with the Thermus thermophilus virus P23-77 and the Thermus aquaticus virus IN93. These viruses may form a new taxon when in the next revision of the taxonomy by the ICTV.
Yingchengvirus is a genus of double stranded DNA viruses that infect haloarchaea. The genus was previously named Betasphaerolipovirus.
Hukuchivirus is a genus of double-stranded DNA viruses that infect thermophilic bacteria. The genus was previously named Gammasphaerolipovirus.
Tristromaviridae is a family of viruses. Archaea of the genera Thermoproteus and Pyrobaculum serve as natural hosts. Tristromaviridae is the sole family in the order Primavirales. There are two genera and three species in the family.
Turriviridae is a family of viruses; it contains only one genus, Alphaturrivirus. The archaea Sulfolobus solfataricus serve as natural hosts. There are two species in the genus Alphaturrivirus.
Spiraviridae is a family of viruses that replicate in hyperthermophilic archaea of the genus Aeropyrum, specifically Aeropyrum pernix. The family contains one genus, Alphaspiravirus, which contains one species, Aeropyrum coil-shaped virus. The virions of Aeropyrum coil-shaped virus (ACV) are non-enveloped and in the shape of hollow cylinders that are formed by a coiling fiber that consists of two intertwining halves of the circular DNA strand inside a capsid. An appendage protrudes from each end of the cylindrical virion. The viral genome is positive-sense, single-stranded DNA ( ssDNA) and encodes for significantly more genes than other known ssDNA viruses. ACV is also unique in that it appears to lack its own enzymes to aid replication, instead likely using the host cell's replisomes. ACV has no known relation to any other archaea-infecting viruses, but it does share its coil-like morphology with some other archaeal viruses, suggesting that such viruses may be an ancient lineage that only infect archaea.

Varidnaviria is a realm of viruses that includes all DNA viruses that encode major capsid proteins that contain a vertical jelly roll fold. The major capsid proteins (MCP) form into pseudohexameric subunits of the viral capsid, which stores the viral deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), and are perpendicular, or vertical, to the surface of the capsid. Apart from this, viruses in the realm also share many other characteristics, such as minor capsid proteins (mCP) with the vertical jelly roll fold, an ATPase that packages viral DNA into the capsid, and a DNA polymerase that replicates the viral genome.
Portogloboviridae is a family of DNA viruses that infect archaea. It is a proposed family of the realm Varidnaviria. Viruses in the family are related to Halopanivirales. The capsid proteins of these viruses and their characteristics are of evolutionary importance for the origin of the other Varidnaviria viruses since they seem to retain primordial characters.
Thaspiviridae is a family of spindle-shaped viruses that is not assigned to any higher taxonomic ranks. The family contains a single genus, Nitmarvirus, which contains a single species, Nitmarvirus NSV1.

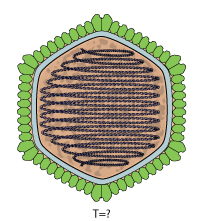
Adnaviria is a realm of viruses that includes archaeal viruses that have a filamentous virion and a linear, double-stranded DNA genome. The genome exists in A-form (A-DNA) and encodes a dimeric major capsid protein (MCP) that contains the SIRV2 fold, a type of alpha-helix bundle containing four helices. The virion consists of the genome encased in capsid proteins to form a helical nucleoprotein complex. For some viruses, this helix is surrounded by a lipid membrane called an envelope. Some contain an additional protein layer between the nucleoprotein helix and the envelope. Complete virions are long and thin and may be flexible or a stiff like a rod.
Haloarculaceae is a family of halophilic and mostly chemoorganotrophic archaea within the order Halobacteriales. The type genus of this family is Haloarcula. Its biochemical characteristics are the same as the order Halobacteriales.







