
The Alps are the highest and most extensive mountain range system that lies entirely in Europe, and stretch approximately 1,200 kilometres (750 mi) across eight Alpine countries : France, Switzerland, Monaco, Italy, Liechtenstein, Austria, Germany, and Slovenia. The Alpine arch generally extends from Nice on the western Mediterranean to Trieste on the Adriatic and Vienna at the beginning of the Pannonian basin. The mountains were formed over tens of millions of years as the African and Eurasian tectonic plates collided. Extreme shortening caused by the event resulted in marine sedimentary rocks rising by thrusting and folding into high mountain peaks such as Mont Blanc and the Matterhorn. Mont Blanc spans the French–Italian border, and at 4,809 m (15,778 ft) is the highest mountain in the Alps. The Alpine region area contains about a hundred peaks higher than 4,000 metres (13,000 ft).

The Alpine region of Switzerland, conventionally referred to as the Swiss Alps, represents a major natural feature of the country and is, along with the Swiss Plateau and the Swiss portion of the Jura Mountains, one of its three main physiographic regions. The Swiss Alps extend over both the Western Alps and the Eastern Alps, encompassing an area sometimes called Central Alps. While the northern ranges from the Bernese Alps to the Appenzell Alps are entirely in Switzerland, the southern ranges from the Mont Blanc massif to the Bernina massif are shared with other countries such as France, Italy, Austria and Liechtenstein.
![Afrotropical realm One of the Earths eight [[biogeographic realm]]s](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/8/8d/Ecozone_Afrotropic.svg/320px-Ecozone_Afrotropic.svg.png)
The Afrotropical realm is one of the Earth's eight biogeographic realms. It includes Africa south of the Sahara Desert, the majority of the Arabian Peninsula, the island of Madagascar, southern Iran and extreme southwestern Pakistan, and the islands of the western Indian Ocean. It was formerly known as the Ethiopian Zone or Ethiopian Region.

Alpine tundra is a type of natural region or biome that does not contain trees because it is at high elevation. As the latitude of a location approaches the poles, the threshold elevation for alpine tundra gets lower until it reaches sea level, and alpine tundra merges with polar tundra.

The Mont Blanc massif is a mountain range in the Alps, located mostly in France and Italy, but also straddling Switzerland at its northeastern end. It contains eleven major independent summits, each over 4,000 metres (13,123 ft) in height. It is named after Mont Blanc, the highest point in western Europe and the European Union. Because of its considerable overall altitude, a large proportion of the massif is covered by glaciers, which include the Mer de Glace and the Miage Glacier – the longest glaciers in France and Italy, respectively.

Gran Paradiso National Park, is an Italian national park in the Graian Alps, between the Aosta Valley and Piedmont regions. The park is named after Gran Paradiso mountain, which is located in the park, and is contiguous with the French Vanoise national park. The land the park encompasses was initially protected in order to protect the Alpine ibex from poachers, as it was a personal hunting ground for king Victor Emmanuel II, but now also protects other species.
Altitudinal zonation in mountainous regions describes the natural layering of ecosystems that occurs at distinct elevations due to varying environmental conditions. Temperature, humidity, soil composition, and solar radiation are important factors in determining altitudinal zones, which consequently support different vegetation and animal species. Altitudinal zonation was first hypothesized by geographer Alexander von Humboldt who noticed that temperature drops with increasing elevation. Zonation also occurs in intertidal and marine environments, as well as on shorelines and in wetlands. Scientist C. Hart Merriam observed that changes in vegetation and animals in altitudinal zones map onto changes expected with increased latitude in his concept of life zones. Today, altitudinal zonation represents a core concept in mountain research.

Dendrosenecio is a genus of flowering plants in the sunflower family. It is a segregate of Senecio, in which it formed the subgenus Dendrosenecio. Its members, the giant groundsels, are native to the higher altitude zones of ten mountain groups in equatorial East Africa, where they form a conspicuous element of the flora.

The flora of Italy was traditionally estimated to comprise about 5,500 vascular plant species. However, as of 2019, 7,672 species are recorded in the second edition of the flora of Italy and in its digital archives Digital flora of Italy. In particular, 7031 are autochtonous and 641 are non native species widely naturalized since more than three decades. Additionally, further 468 exotic species have been recorded as adventitious or naturalized in more recent times. Geobotanically, the Italian flora is shared between the Circumboreal Region and Mediterranean Region. According to the index compiled by the Italian Ministry for the Environment in 2001, 274 vascular plant species were protected.

The Jungfrau-Aletsch protected area is located in south-western Switzerland between the cantons of Berne and Valais. It is a mountainous region in the easternmost side of the Bernese Alps, containing the northern wall of Jungfrau and Eiger, and the largest glaciated area in western Eurasia, comprising the Aletsch Glacier. The Jungfrau-Aletsch protected area is the first World Natural Heritage site in the Alps; it was inscribed in 2001.

Montane ecosystems are found on the slopes of mountains. The alpine climate in these regions strongly affect the ecosystem because temperatures fall as elevation increases, causing the ecosystem to stratify. Dense montane forests are common at moderate elevations, due to moderate temperatures and high rainfall. At higher elevations, the climate is harsher, with lower temperatures and higher winds, preventing the growth of trees and causing the plant community to transition to montane grasslands, shrublands or alpine tundra.
Biogeographic classification of India is the division of India according to biogeographic characteristics. Biogeography is the study of the distribution of species (biology), organisms, and ecosystems in geographic space and through geological time. India has a rich heritage of natural diversity. India ranks fourth in Asia and tenth in the world amongst the top 17 mega-diverse countries in the world. India harbours nearly 11% of the world’s floral diversity comprising over 17500 documented flowering plants, 6200 endemic species, 7500 medicinal plants and 246 globally threatened species in only 2.4% of world’s land area. India is also home to four biodiversity hotspots—Andaman & Nicobar Islands, Eastern Himalaya, Indo-Burma region, and the Western Ghats. Hence the importance of biogeographical study of India's natural heritage.

The Ruwenzori-Virunga montane moorlands is a montane grasslands and shrublands ecoregion of central Africa.
Alpine vegetation refers to the zone of vegetation between the altitudinal limit for tree growth and the nival zone. Alpine zones in Tasmania can be difficult to classify owing to Tasmania's maritime climate limiting snow lie to short periods and the presence of a tree line that is not clearly defined.

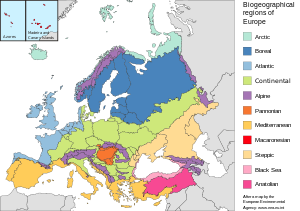
The Mediterranean Biogeographic Region is the biogeographic region around and including the Mediterranean Sea. The term is defined by the European Environment Agency as applying to the land areas of Europe that border on the Mediterranean Sea, and the corresponding territorial waters. The region is rich in biodiversity and has many endemic species. The term may also be used in the broader sense of all the lands of the Mediterranean Basin, or in the narrow sense of just the Mediterranean Sea.

The biogeographic regions of Europe are biogeographic regions defined by the European Environment Agency. They were initially limited to the European Union member states, but later extended to cover all of Europe west of the Urals, including all of Turkey. The map of biogeographic regions is deliberately simplified and ignores local anomalies. It is intended primarily as a framework for coordinating and reporting overall results of conservation efforts.

The Atlantic Biogeographic Region is the biogeographic region of Europe bordering the Atlantic Ocean and North Sea.

The Continental Biogeographic Region is a biogeographic region of Europe that extend in a broad band from east to west through the center of the continent.

The Pannonian Biogeographic Region is a biogeographic region, as defined by the European Environment Agency. It covers the lowlands of the Pannonian Basin centered on Hungary.



![Afrotropical realm One of the Earths eight [[biogeographic realm]]s](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/8/8d/Ecozone_Afrotropic.svg/320px-Ecozone_Afrotropic.svg.png)













