
The Republic of Colombia is situated largely in the north-west of South America, with some territories falling within the boundaries of Central America. It is bordered to the north-west by Panama; to the east by Brazil and Venezuela; to the south by Ecuador and Peru; and it shares maritime limits with Costa Rica, Nicaragua, Honduras, Jamaica, the Dominican Republic, and Haiti.

The Caribbean Sea is a sea of the North Atlantic Ocean in the tropics of the Western Hemisphere, located south of the Gulf of Mexico and southwest of the Sargasso Sea. It is bounded by the Greater Antilles to the north from Cuba to Puerto Rico, the Lesser Antilles to the east from the Virgin Islands to Trinidad and Tobago, South America to the south from the Venezuelan coastline to the Colombian coastline, and Central America and the Yucatán Peninsula to the west from Panama to Mexico. The geopolitical region centered around the Caribbean Sea, including the numerous islands of the West Indies and adjacent coastal areas in the mainland of the Americas, is known as the Caribbean.

Guinea is a country on the coast of West Africa and is bordered by Guinea-Bissau, Senegal, Mali, Ivory Coast, Liberia, and Sierra Leone.

The geography of Guinea-Bissau is that of low coastal plains bordering the Atlantic Ocean. The country borders Senegal in the north and Guinea in the southeast.

Morocco is the northwesternmost country which spans from the Mediterranean Sea and Atlantic Ocean on the north and the west respectively, into large mountainous areas in the interior, to the Sahara desert in the far south. Morocco is a Northern African country, located in the extreme northwest of Africa on the edge of continental Europe. The Strait of Gibraltar separates Spain from Morocco with a 13 kilometres (8.1 mi) span of water. Morocco borders the North Atlantic Ocean to the west, and the western Mediterranean Sea to the north, and has borders with Algeria and disputed Western Sahara.

Spain is a country located in southwestern Europe occupying most of the Iberian Peninsula. It also includes a small exclave inside France called Llívia, as well as the Balearic Islands in the Mediterranean, the Canary Islands in the Atlantic Ocean 108 km (67 mi) off northwest Africa, and five places of sovereignty on and off the coast of North Africa: Ceuta, Melilla, Islas Chafarinas, Peñón de Alhucemas, and Peñón de Vélez de la Gomera.

The term "United States," when used in the geographic sense, refers to the contiguous United States, Alaska, Hawaii, the five insular territories of Puerto Rico, Northern Mariana Islands, U.S. Virgin Islands, Guam, American Samoa, and minor outlying possessions. The United States shares land borders with Canada and Mexico and maritime borders with Russia, Cuba, the Bahamas, and many other countries, mainly in the Caribbeanin addition to Canada and Mexico. The northern border of the United States with Canada is the world's longest bi-national land border.
The Geography of Guyana comprises the physical characteristics of the country in Northern South America and part of Caribbean South America, bordering the North Atlantic Ocean, between Suriname and Venezuela, with a land area of approximately 214,969 square km. The country is situated between 1 and 9 north latitude and between 56 and 62 west longitude. With a 459 km (285 mi)-long Atlantic coastline on the northeast, Guyana is bounded by Venezuela on the west, Brazil on the west and south, and Suriname on the east.

The Wadden Sea is an intertidal zone in the southeastern part of the North Sea. It lies between the coast of northwestern continental Europe and the range of low-lying Frisian Islands, forming a shallow body of water with tidal flats and wetlands. It has a high biological diversity and is an important area for both breeding and migrating birds. In 2009, the Dutch and German parts of the Wadden Sea were inscribed on UNESCO's World Heritage List and the Danish part was added in June 2014.

England comprises most of the central and southern two-thirds of the island of Great Britain, in addition to a number of small islands of which the largest is the Isle of Wight. England is bordered to the north by Scotland and to the west by Wales. It is closer to continental Europe than any other part of mainland Britain, divided from France only by a 33 km (21 mi) sea gap, the English Channel. The 50 km (31 mi) Channel Tunnel, near Folkestone, directly links England to mainland Europe. The English/French border is halfway along the tunnel.
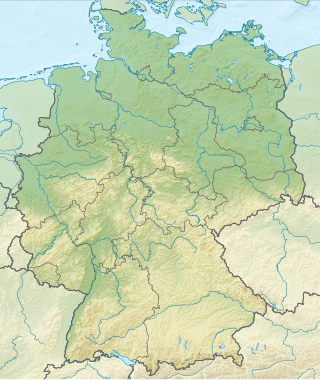
Germany is a country in Central and Western Europe that stretches from the Alps, across the North European Plain to the North Sea and the Baltic Sea. It is the second-most populous country in Europe after Russia, and is seventh-largest country by area in the continent. The area of Germany ranked 63rd and covers 357,600 km2 (138,070 sq mi), consisting of 349,250 km2 (134,846 sq mi) of land and 8,350 km2 (3,224 sq mi) of waters, smaller than Japan but larger than Republic of the Congo.

The Mediterranean Biogeographic Region is the biogeographic region around and including the Mediterranean Sea. The term is defined by the European Environment Agency as applying to the land areas of Europe that border on the Mediterranean Sea, and the corresponding territorial waters. The region is rich in biodiversity and has many endemic species. The term may also be used in the broader sense of all the lands of the Mediterranean Basin, or in the narrow sense of just the Mediterranean Sea.

The European Arctic Biogeographic Region is the biogeographic region of Europe around and in the Arctic Ocean.

The Boreal Biogeographic Region is the biogeographic region of Northern Europe that consists primarily of coniferous forests and wetlands.

The biogeographic regions of Europe are biogeographic regions defined by the European Environment Agency. They were initially limited to the European Union member states, but later extended to cover all of Europe west of the Urals, including all of Turkey. The map of biogeographic regions is deliberately simplified and ignores local anomalies. It is intended primarily as a framework for coordinating and reporting overall results of conservation efforts.

The Continental Biogeographic Region is a biogeographic region of Europe that extends in a broad band from east to west through the center of the continent.

The Black Sea Biogeographic Region is a biogeographic region of land bordering the west and south of the Black Sea, as defined by the European Environment Agency.

The Alpine Biogeographic Region is a biogeographic region, as defined by the European Environment Agency, that covers the mountainous regions of Europe.

The Pannonian Biogeographic Region is a biogeographic region, as defined by the European Environment Agency. It covers the lowlands of the Pannonian Basin centered on Hungary.

The Steppic Biogeographic Region is a biogeographic region of Europe, as defined by the European Environment Agency.




















