
Akhenaten, also spelled Akhenaton or Echnaton, was an ancient Egyptian pharaoh reigning c. 1353–1336 or 1351–1334 BC, the tenth ruler of the Eighteenth Dynasty. Before the fifth year of his reign, he was known as Amenhotep IV.

Nefertiti ) was a queen of the 18th Dynasty of Ancient Egypt, the great royal wife of Pharaoh Akhenaten. Nefertiti and her husband were known for their radical overhaul of state religious policy, in which they promoted the earliest known form of monotheism, Atenism, centered on the sun disc and its direct connection to the royal household. With her husband, she reigned at what was arguably the wealthiest period of ancient Egyptian history. Some scholars believe that Nefertiti ruled briefly as Neferneferuaten after her husband's death and before the ascension of Tutankhamun, although this identification is a matter of ongoing debate. If Nefertiti did rule as Pharaoh, her reign was marked by the fall of Amarna and relocation of the capital back to the traditional city of Thebes.

Kiya was one of the wives of the Egyptian Pharaoh Akhenaten. Little is known about her, and her actions and roles are poorly documented in the historical record, in contrast to those of Akhenaten's ‘Great royal wife’, Nefertiti. Her unusual name suggests that she may originally have been a Mitanni princess. Surviving evidence demonstrates that Kiya was an important figure at Akhenaten's court during the middle years of his reign, when she had a daughter with him. She disappears from history a few years before her royal husband's death. In previous years, she was thought to be mother of Tutankhamun, but recent DNA evidence suggests this is unlikely.

Meritaten, also spelled Merytaten, Meritaton or Meryetaten, was an ancient Egyptian royal woman of the Eighteenth Dynasty of Egypt. Her name means "She who is beloved of Aten"; Aten being the sun-deity whom her father, Pharaoh Akhenaten, worshipped. She held several titles, performing official roles for her father and becoming the Great Royal Wife to Pharaoh Smenkhkare, who may have been a brother or son of Akhenaten. Meritaten also may have served as pharaoh in her own right under the name Ankhkheperure Neferneferuaten.
Tey was the Great Royal Wife of Kheperkheprure Ay, who was the penultimate pharaoh of Ancient Egypt's Eighteenth Dynasty. She also had been the wet nurse of Nefertiti.

Ankhesenamun was a queen who lived during the 18th Dynasty of Egypt as the pharaoh Akhenaten's daughter and subsequently became the Great Royal Wife of pharaoh Tutankhamun. Born Ankhesenpaaten, she was the third of six known daughters of the Egyptian Pharaoh Akhenaten and his Great Royal Wife Nefertiti. She became the Great Royal Wife of Tutankhamun. The change in her name reflects the changes in ancient Egyptian religion during her lifetime after her father's death. Her youth is well documented in the ancient reliefs and paintings of the reign of her parents. The mummy of Tutankhamun's mother has been identified through DNA analysis as a full sister to his father, the unidentified mummy found in tomb KV55, and as a daughter of his grandfather, Amenhotep III. So far his mother's name is uncertain, but her mummy is known informally to scientists as the Younger Lady.

The Royal Tomb of Akhenaten, located in the Royal Wadi at Amarna, is the burial place of the Eighteenth Dynasty pharaoh Akhenaten.

Meketaten was the second daughter of six born to the Egyptian Pharaoh Akhenaten and his Great Royal Wife Nefertiti. She likely lived between Year 4 and Year 14 of Akhenaten's reign. Although little is known about her, she is frequently depicted with her sisters accompanying her royal parents in the first two-thirds of the Amarna Period.

Neferneferuaten Tasherit or Neferneferuaten the younger was an ancient Egyptian princess of the 18th Dynasty and the fourth daughter of Pharaoh Akhenaten and his Great Royal Wife Nefertiti.

Neferneferure was an ancient Egyptian princess of the 18th Dynasty. She was the fifth of six known daughters of Pharaoh Akhenaten and his Great Royal Wife Nefertiti.

Amarna Tomb 1 is a sepulchre near Amarna, Upper Egypt. It is the tomb of the ancient Egyptian noble Huya, which is located in the cluster of tombs known collectively as the Northern tombs.
Mahu was Chief of Police at Akhetaten.
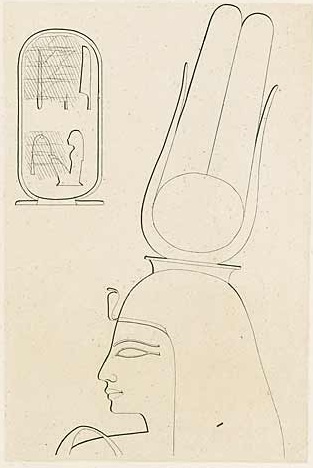
Setepenre or Sotepenre was an ancient Egyptian princess of the 18th Dynasty; sixth and last daughter of Pharaoh Akhenaten and his chief queen Nefertiti.
Mutbenret or Mutnodjmet was an Egyptian noblewoman, and said to be the sister of the King's Great Wife Nefertiti.

Amarna Tomb 5 is an ancient sepulchre in Amarna, Upper Egypt. It was built for the courtier Pentu, and is one of the six Northern tombs at Amarna. The burial is located to the south of the tomb of Meryra. It is very similar to the tomb of Ahmes. The sepulchre is T-shaped and its inner chamber would have served as the burial chamber.
The Amarna Era includes the reigns of Akhenaten, Smenkhkare, Tutankhamun and Ay. The period is named after the capital city established by Akhenaten, son of Amenhotep III. Akhenaten started his reign as Amenhotep IV, but changed his name when he discarded all other religions and declared the Aten or sun disc as the only god. He closed all the temples of the other Gods and removed their names from the monuments. Smenkhkare, then Tutankhamun, succeeded Akhenaten. Discarding Akhenten's religious beliefs, Tutankhamun returned to the traditional gods. He died young and was succeeded by Ay. Many kings did their best to remove all traces of the period from the records. The Amarna art is very distinctive: the royal family was portrayed with extended heads, long necks and narrow chests. They had skinny limbs, but heavy hips and thighs, with a marked stomach.

The Tomb of Panehsy is a sepulchre in Amarna, Upper Egypt. It was erected for the noble Panehsy who bore the titles the First servant of the Aten in the house of Aten in Akhet-Aten, Second prophet of the Lord of the Two Lands Neferkheprure-Waenre (Akhenaten), the sealbearer of the King of Lower Egypt, Overseer of the storehouse of the Aten in Akhetaten, Overseer of cattle of the Aten in Akhet-Aten.
The Anonymous Tombs in Amarna are ancient Tombs of Nobles at the Royal Wadi in Amarna, Upper Egypt. They consist of both sepulchres and burial pits in varying stages of construction.

Ipy, also transliterated as Apy, was a court official from the time of Amenhotep III and Akhenaten during the Egyptian 18th Dynasty. Ipy was High Steward of Memphis, and a royal scribe.


















