A DNA virus is a virus that has a genome made of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) that is replicated by a DNA polymerase. They can be divided between those that have two strands of DNA in their genome, called double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) viruses, and those that have one strand of DNA in their genome, called single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) viruses. dsDNA viruses primarily belong to two realms: Duplodnaviria and Varidnaviria, and ssDNA viruses are almost exclusively assigned to the realm Monodnaviria, which also includes dsDNA viruses. Additionally, many DNA viruses are unassigned to higher taxa. Viruses that have a DNA genome that is replicated through an RNA intermediate by a reverse transcriptase are separately considered reverse transcribing viruses and are assigned to the kingdom Pararnavirae in the realm Riboviria.
A provirus is a virus genome that is integrated into the DNA of a host cell. In the case of bacterial viruses (bacteriophages), proviruses are often referred to as prophages. However, it is important to note that proviruses are distinctly different from prophages and these terms should not be used interchangeably. Unlike prophages, proviruses do not excise themselves from the host genome when the host cell is stressed.
Viroids are small infectious pathogens. They are composed solely of a short strand of circular, single-stranded RNA. Unlike viruses, they have no protein coating. All known viroids are inhabitants of angiosperms, and most cause diseases, whose respective economic importance to humans varies widely.

The Epstein–Barr virus (EBV), formally called Human gammaherpesvirus 4, is one of the nine known human herpesvirus types in the herpes family, and is one of the most common viruses in humans. EBV is a double-stranded DNA virus.
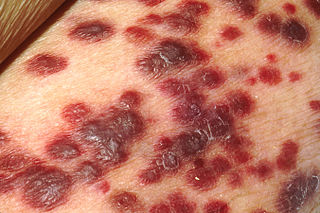
Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) is the ninth known human herpesvirus; its formal name according to the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV) is Human gammaherpesvirus 8, or HHV-8 in short. Like other herpesviruses, its informal names are used interchangeably with its formal ICTV name. This virus causes Kaposi's sarcoma, a cancer commonly occurring in AIDS patients, as well as primary effusion lymphoma, HHV-8-associated multicentric Castleman's disease and KSHV inflammatory cytokine syndrome. It is one of seven currently known human cancer viruses, or oncoviruses. Even after so many years of discovery of KSHV/HHV8, there is no known cure for KSHV associated tumorigenesis.
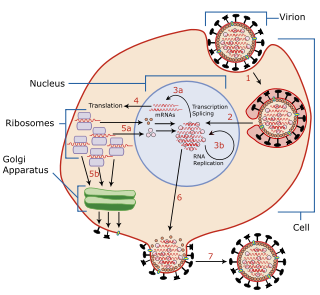
Virus latency is the ability of a pathogenic virus to lie dormant within a cell, denoted as the lysogenic part of the viral life cycle. A latent viral infection is a type of persistent viral infection which is distinguished from a chronic viral infection. Latency is the phase in certain viruses' life cycles in which, after initial infection, proliferation of virus particles ceases. However, the viral genome is not eradicated. The virus can reactivate and begin producing large amounts of viral progeny without the host becoming reinfected by new outside virus, and stays within the host indefinitely.

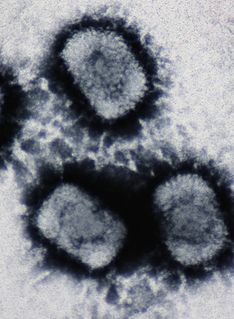
Herpesviridae is a large family of DNA viruses that cause infections and certain diseases in animals, including humans. The members of this family are also known as herpesviruses. The family name is derived from the Greek word herpein 'to creep', referring to spreading cutaneous lesions, usually involving blisters, seen in flares of herpes simplex 1, herpes simplex 2 and herpes zoster (shingles). In 1971, the International Committee on the Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV) established Herpesvirus as a genus with 23 viruses among four groups. As of 2020, 115 species are recognized, all but one of which are in one of the three subfamilies. Herpesviruses can cause both latent and lytic infections.

Herpes simplex virus1 and 2, also known by their taxonomical names Human alphaherpesvirus 1 and Human alphaherpesvirus 2, are two members of the human Herpesviridae family, a set of new viruses that produce viral infections in the majority of humans. Both HSV-1 and HSV-2 are common and contagious. They can be spread when an infected person begins shedding the virus.

Gammaherpesvirinae is a subfamily of viruses in the order Herpesvirales and in the family Herpesviridae. Viruses in Gammaherpesvirinae are distinguished by reproducing at a more variable rate than other subfamilies of Herpesviridae. Mammals serve as natural hosts. There are 43 species in this subfamily, divided among 7 genera with three species unassigned to a genus. Diseases associated with this subfamily include: HHV-4: infectious mononucleosis. HHV-8: Kaposi's sarcoma.
Nepovirus is a genus of viruses in the order Picornavirales, in the family Secoviridae, in the subfamily Comovirinae. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are 40 species in this genus. Nepoviruses, unlike the other two genera in the subfamily Comovirinae, are transmitted by nematodes.
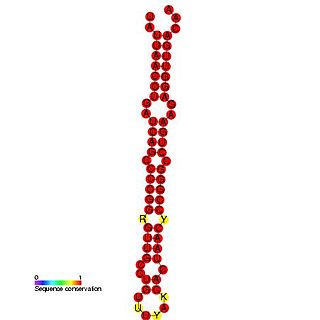
The mir-BHRF1-1 microRNA precursor found in Human herpesvirus 4 and Cercopithicine herpesvirus 15. In Epstein–Barr virus, mir-BHRF1-1 is found in the 5' UTR of the BHRF1 gene, which is known to encode a distant Bcl-2 homolog. The mature sequence is excised from the 5' arm of the hairpin. Two other miRNA precursors were found in this reading frame, namely Mir-BHRF1-2 and Mir-BHRF1-3.

The mir-BHRF1-2 microRNA precursor found in human herpesvirus 4, cercopithicine herpesvirus 15 and herpesvirus papio. In Epstein-Barr virus, mir-BHRF1-2 is found in the 3' UTR of the BHRF1 gene, which is known to encode a distant Bcl-2 homolog. The mature sequence is excised from the 3' arm of the hairpin. Two other miRNA precursors were found in this reading frame, namely Mir-BHRF1-1 and Mir-BHRF1-3.

The mir-BHRF1-3 microRNA precursor found in Human herpesvirus 4. In Epstein-Barr virus, mir-BHRF1-3 is found in the 3' UTR of the BHRF1 gene, which is known to encode a distant Bcl-2 homolog. The mature sequence is excised from the 5' arm of the hairpin. Two other miRNA precursors were found in this reading frame, namely Mir-BHRF1-1 and Mir-BHRF1-2.
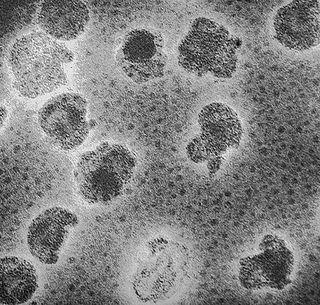
Plasmaviridae is a family of bacteria-infecting viruses. Acholeplasma species serve as natural hosts. There is one genus in the family, Plasmavirus, which contains one species: Acholeplasma virus L2. All viruses known in this family have been isolated from species in the class Mollicutes.

Carlavirus, formerly known as the "Carnation latent virus group", is a genus of viruses in the order Tymovirales, in the family Betaflexiviridae. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are 53 species in this genus. Diseases associated with this genus include: mosaic and ringspot symptoms.

A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea. Since Dmitri Ivanovsky's 1892 article describing a non-bacterial pathogen infecting tobacco plants and the discovery of the tobacco mosaic virus by Martinus Beijerinck in 1898, more than 9,000 virus species have been described in detail of the millions of types of viruses in the environment. Viruses are found in almost every ecosystem on Earth and are the most numerous type of biological entity. The study of viruses is known as virology, a subspeciality of microbiology.
Epstein–Barr virus (EBV) latent membrane protein 2 (LMP2) are two viral proteins of the Epstein–Barr virus. LMP2A/LMP2B are transmembrane proteins that act to block tyrosine kinase signaling. LMP2A is a transmembrane protein that inhibits normal B-cell signal transduction by mimicking an activated B-cell receptor (BCR). The N-terminus domain of LMP2A is tyrosine phosphorylated and associates with Src family protein tyrosine kinases (PTKs) as well as spleen tyrosine kinase (Syk). PTKs and Syk are associated with BCR signal transduction.
Amalgaviridae is a family of double-stranded RNA viruses. Member viruses infect plants and are transmitted vertically via seeds. The name derives from amalgam which refers to amalgaviruses possessing characteristics of both partitiviruses and totiviruses. There are ten species in the family.
Lolavirus is a genus of viruses in the order Tymovirales, in the family Alphaflexiviridae. Plants, specifically ryegrass, serve as natural hosts. There is only one species in this genus: Lolium latent virus.
Human Herpes Viruses, also known as HHVs, are part of a family of DNA viruses that cause several diseases in humans. One of the most notable functions of this virus family is their ability to enter a latent phase and lay dormant within animals for extended periods of time. The mechanism that controls this is very complex because expression of viral proteins during latency is decreased a great deal, meaning that the virus must have transcription of its genes repressed. There are many factors and mechanisms that control this process and epigenetics is one way this is accomplished. Epigenetics refers to persistent changes in expression patterns that are not caused by changes to the DNA sequence. This happens through mechanisms such as methylation and acetylation of histones, DNA methylation, and non-coding RNAs (ncRNA). Altering the acetylation of histones creates changes in expression by changing the binding affinity of histones to DNA, making it harder or easier for transcription machinery to access the DNA. Methyl and acetyl groups can also act as binding sites for transcription factors and enzymes that further modify histones or alter the DNA itself.













