Related Research Articles
Educational software is a term used for any computer software which is made for an educational purpose. It encompasses different ranges from language learning software to classroom management software to reference software. The purpose of all this software is to make some part of education more effective and efficient.

In contemporary education, mathematics education is the practice of teaching and learning mathematics, along with the associated scholarly research.
Electronic assessment, also known as digital assessment, e-assessment, online assessment or computer-based assessment, is the use of information technology in assessment such as educational assessment, health assessment, psychiatric assessment, and psychological assessment. This covers a wide range of activity ranging from the use of a word processor for assignments to on-screen testing. Specific types of e-assessment include multiple choice, online/electronic submission, computerized adaptive testing such as the Frankfurt Adaptive Concentration Test, and computerized classification testing.

CELTA is an initial teacher training qualification for teaching English as a second or foreign language. It is provided by Cambridge Assessment English through authorised Cambridge English Teaching Qualification centres and can be taken either full-time or part-time. CELTA was developed to be suitable both for those interested in Teaching English as a Foreign Language (TEFL) and for Teaching English to the Speakers of Other Languages (TESOL).. The full name of the course was originally the Certificate in English Language Teaching to Adults and is still referred to in this way by some course providers. However, in 2011 the qualification title was amended on the Ofqual register to the Cambridge English Level 5 Certificate In Teaching English to Speakers of Other Languages (CELTA) in order to reflect that the wider range of students that teachers might have, including younger learners.

The Mata Amritanandamayi Math (MAM) is an international charitable organization aimed at the spiritual and material upliftment of humankind. It was founded by Hindu spiritual leader and humanitarian Mata Amritanandamayi in 1981, with its headquarters in Paryakadavu, Alappad Panchayat, Kollam district, Kerala. Along with its sister organization, the Mata Amritanandamayi Mission Trust, MAM conducts charitable work including disaster relief, healthcare for the poor, environmental programs, fighting hunger and scholarships for impoverished students, amongst others. It also runs the seven-campus university known as Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham, 55 campus English medium CBSE schools known as Amrita Vidyalayam, and classes in yoga, meditation and Sanskrit.
A learning management system (LMS) is a software application for the administration, documentation, tracking, reporting, automation, and delivery of educational courses, training programs, or learning and development programs. The learning management system concept emerged directly from e-Learning. Learning management systems make up the largest segment of the learning system market. The first introduction of the LMS was in the late 1990s. Learning management systems have faced a massive growth in usage due to the emphasis on remote learning during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Educational technology is the combined use of computer hardware, software, and educational theory and practice to facilitate learning. When referred to with its abbreviation, edtech, it is often referring to the industry of companies that create educational technology.
Technology integration is the use of technology tools in general content areas in education in order to allow students to apply computer and technology skills to learning and problem-solving. Generally speaking, the curriculum drives the use of technology and not vice versa. Technology integration is defined as the use of technology to enhance and support the educational environment. Technology integration in the classroom can also support classroom instruction by creating opportunities for students to complete assignments on the computer rather than with normal pencil and paper. In a larger sense, technology integration can also refer to the use of an integration platform and APIs in the management of a school, to integrate disparate SaaS applications, databases, and programs used by an educational institution so that their data can be shared in real-time across all systems on campus, thus supporting students' education by improving data quality and access for faculty and staff.
"Curriculum integration with the use of technology involves the infusion of technology as a tool to enhance the learning in a content area or multidisciplinary setting... Effective integration of technology is achieved when students are able to select technology tools to help them obtain information in a timely manner, analyze and synthesize the information, and present it professionally to an authentic audience. The technology should become an integral part of how the classroom functions—as accessible as all other classroom tools. The focus in each lesson or unit is the curriculum outcome, not the technology."
Technological literacy is the ability to use, manage, understand, and assess technology. Technological literacy is related to digital literacy in that when an individual is proficient in using computers and other digital devices to access the Internet, digital literacy gives them the ability to use the Internet to discover, review, evaluate, create, and use information via various digital platforms, such as web browsers, databases, online journals, magazines, newspapers, blogs, and social media sites.
Doon Public School is a co-educational private secondary school, in Paschim Vihar, Delhi, India. The school uses English as the medium for instruction. The school is housed in an imposing red brick structure and is over forty years old. Apart from being rated amongst the Top 10 Best Public Schools in Delhi/ NCR, the school also prides in the distinction of being awarded the Best E School in Delhi/NCR.

The National Council of Educational Research and Training (NCERT) is an autonomous organisation of the Government of India which was established in 1961 as a literary, scientific and charitable Society under the Societies' Registration Act. Its headquarters are located at Sri Aurbindo Marg in New Delhi. Dr. Dinesh Prasad Saklani is Director of the council since 2022.
Formative assessment, formative evaluation, formative feedback, or assessment for learning, including diagnostic testing, is a range of formal and informal assessment procedures conducted by teachers during the learning process in order to modify teaching and learning activities to improve student attainment. The goal of a formative assessment is to monitor student learning to provide ongoing feedback that can help students identify their strengths and weaknesses and target areas that need work. It also helps faculty recognize where students are struggling and address problems immediately. It typically involves qualitative feedback for both student and teacher that focuses on the details of content and performance. It is commonly contrasted with summative assessment, which seeks to monitor educational outcomes, often for purposes of external accountability.
ALEKS is an online tutoring and assessment program that includes course material in mathematics, chemistry, introductory statistics, and business.

Continuous and Comprehensive Evaluation (CCE) was a process of assessment, mandated by the Right to Education Act, of India in 2009. This approach to assessment was introduced by state governments in India, as well as by the Central Board of Secondary Education in India, for students of sixth to tenth grades and twelfth in some schools. From this the smaller classes student would have a practice to face the exam of board in younger age. The Karnataka government introduced CCE for grades 1 through 9 later it was also introduced for 12th grades students. The main aim of CCE was to evaluate every aspect of the child during their presence at the school. This was believed to help reduce the pressure on the child during/before examinations as the student will have to sit for multiple tests throughout the year, of which no test or the syllabus covered will be repeated at the end of the year, whatsoever. The CCE method was claimed to bring enormous changes from the traditional chalk and talk method of teaching, provided it is implemented accurately.
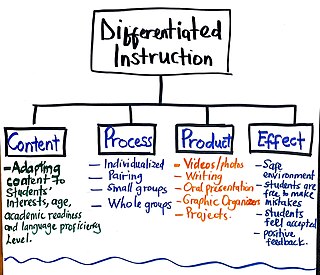
Differentiated instruction and assessment, also known as differentiated learning or, in education, simply, differentiation, is a framework or philosophy for effective teaching that involves providing all students within their diverse classroom community of learners a range of different avenues for understanding new information in terms of: acquiring content; processing, constructing, or making sense of ideas; and developing teaching materials and assessment measures so that all students within a classroom can learn effectively, regardless of differences in their ability. Differentiated instruction, according to Carol Ann Tomlinson, is the process of "ensuring that what a student learns, how he or she learns it, and how the student demonstrates what he or she has learned is a match for that student's readiness level, interests, and preferred mode of learning." According to Boelens et al. (2018), differentiation can be on two different levels: the administration level and the classroom level. The administration level takes the socioeconomic status and gender of students into consideration. At the classroom level, differentiation revolves around content, processing, product, and effects. On the content level, teachers adapt what they are teaching to meet the needs of students. This can mean making content more challenging or simplified for students based on their levels. The process of learning can be differentiated as well. Teachers may choose to teach individually at a time, assign problems to small groups, partners or the whole group depending on the needs of the students. By differentiating product, teachers decide how students will present what they have learnt. This may take the form of videos, graphic organizers, photo presentations, writing, and oral presentations. All these take place in a safe classroom environment where students feel respected and valued—effects.

Delhi Private School, Sharjah is a KG1–12 private school in Sharjah, United Arab Emirates. It is affiliated with the Central Board of Secondary Education. It is the first school in the United Arab Emirates to have branched out from its parent institute, Delhi Public School.

A flipped classroom is an instructional strategy and a type of blended learning, which aims to increase student engagement and learning by having pupils complete readings at home and work on live problem-solving during class time. This pedagogical style moves activities, including those that may have traditionally been considered homework, into the classroom. With a flipped classroom, students watch online lectures, collaborate in online discussions, or carry out research at home, while actively engaging concepts in the classroom, with a mentor's guidance.
CLT India is an Indian non-profit, non-government organisation based in Jakkur, Bengaluru. It was founded in 1997 by Bhagya Rangarchar. It aims to provide education using technology to the under-served communities and its solutions serve the base of the pyramid.

Kerala Infrastructure and Technology for Education (KITE) is a state owned special purpose company under education department of the Government of Kerala. It was developed to support ICT enabled education for schools in Kerala. The erstwhile IT@School Project was transformed into KITE for extending its scope of operations in August 2017. KITE was the first SPV company to get funded by KIIFB.

Extramarks Education is an education technology company, that provides online and offline schooling and curricula. It was founded in 2007, and headquartered in Noida, India.
References
- 1 2 Menon, Anasuya (2007-06-26). "Computers to Foster Enlightenment". The Hindu . Archived from the original on 2007-06-29.
- 1 2 3 4 5 "BSNL Plans To Launch Triple-player Services". Business Line, The Hindu. 2007-08-27.
- ↑ "News from world of education - February 3, 2022". The Hindu. 2022-02-03. ISSN 0971-751X . Retrieved 2022-02-11.
- 1 2 3 "Kalam Launches School Network". Amritapuri.org. 2008-02-04.
- ↑ "Kalam's Charter for Doctors". The Hindu . 2008-02-05. Archived from the original on 2008-02-09.