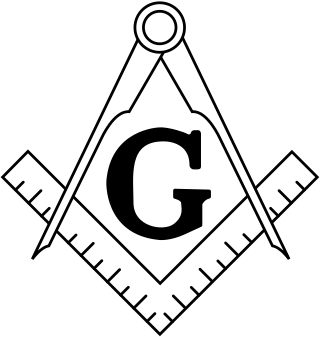
Freemasonry or Masonry refers to fraternal organisations that trace their origins to the local guilds of stonemasons that, from the end of the 14th century, regulated the qualifications of stonemasons and their interaction with authorities and clients. Modern Freemasonry broadly consists of two main recognition groups: Regular Freemasonry, which insists that a volume of scripture be open in a working lodge, that every member professes belief in a Supreme Being, that no women be admitted, and that the discussion of religion and politics do not take place within the lodge; and Continental Freemasonry, which consists of the jurisdictions that have removed some, or all, of these restrictions.
In Anglo-American Freemasonry, York Rite, sometimes referred to as the American Rite, is one of several Rites of Freemasonry. It is named for York, of Yorkshire, England; where in the legend of the Rite, it was first practiced.
The Knights of the Golden Eagle was a fraternal organization founded in Baltimore in 1872.
Fraternal Order of Eagles (F.O.E.) is a fraternal organization that was founded on February 6, 1898, in Seattle, Washington, by a group of six theater-owners including John Cort, brothers John W. and Tim J. Considine, Harry (H.L.) Leavitt, Mose Goldsmith and Arthur Williams. Originally made up of those engaged in one way or another in the performing arts, the Eagles grew and claimed credit for establishing the Mother's Day holiday in the United States as well as the "impetus for Social Security" in the United States. Their lodges are known as "aeries".
The Swedish Rite is a variation or Rite of Freemasonry that is common in Scandinavian countries and to a limited extent in Germany. It is different from other branches of Freemasonry in that, rather than having the three self-contained foundation degrees and seemingly-endless side degrees and appendant bodies, it has an integrated system with ten degrees. It is also different in that, rather than moving through the offices or 'chairs', progress in the Swedish Rite is based on moving through the ten degrees. A fundamental difference is the Swedish Rite's position on religious affiliation: Anglo/American 'Regular' Masonry requires a belief in any theistic religion and Continental 'Liberal' Masonry does not require belief in any religion, whereas Swedish Masonry is specifically Christian, and requires a Christian trinitarian belief in all its members. Nonetheless, the main Swedish Rite constitutions are all recognised as regular by the United Grand Lodge of England, and stand in full amity.
Fraternal Order Orioles is a social and charitable organization that was founded in August 1910. The organization currently consists of about 54 local Nests and affiliated Auxiliaries located in 9 states in the eastern United States.
While many Christian denominations either allow or take no stance on their members joining Freemasonry, others discourage or prohibit their members from joining the fraternity.

The Knights Templar, full name The United Religious, Military and Masonic Orders of the Temple and of St John of Jerusalem, Palestine, Rhodes and Malta, is a fraternal order affiliated with Freemasonry. Unlike the initial degrees conferred in a regular Masonic Lodge, which only require a belief in a Supreme Being regardless of religious affiliation, the Knights Templar is one of several additional Masonic Orders in which membership is open only to Freemasons who profess a belief in Christianity. One of the obligations entrants to the order are required to declare is to protect and defend the Christian faith. The word "United" in its full title indicates that more than one historical tradition and more than one actual order are jointly controlled within this system. The individual orders 'united' within this system are principally the Knights of the Temple, the Knights of Malta, the Knights of St Paul, and only within the York Rite, the Knights of the Red Cross.
Freemasonry in Sweden was introduced by the Swedish Order of Freemasons, founded in 1735 as the oldest still active Swedish fraternal order, working the Swedish Rite of Freemasonry. It is under royal patronage of the King of Sweden and closely associated with the Lutheran Church of Sweden. It is a jurisdiction that admits Christian men only, and is recognised by the United Grand Lodge of England as a Regular Masonic jurisdiction. Its total membership is about 16,500.
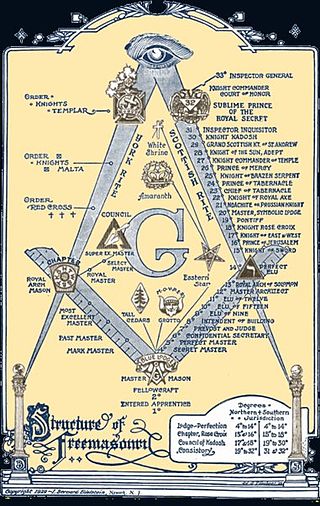
There are many organisations and orders which form part of the widespread fraternity of Freemasonry, each having its own structure and terminology. Collectively these may be referred to as Masonic bodies, Masonic orders, Concordant bodies or appendant bodies of Freemasonry.

The Rectified Scottish Rite (RER), also known as the Rectified Rite or RSR, is a Christian Masonic rite with a long and complex history. It was founded in 1778 at the Convent of Lyon in France under the leadership of Jean-Baptiste Willermoz, who served as the primary architect and driving force behind its formation. It emerged as a reform and restructuring of the earlier Templar Strict Observance system that had spread in Germany and France in the mid-18th century.
The history of Freemasonry in Mexico can be traced to at least 1806 when the first Masonic lodge was formally established in the nation.

The Red Cross of Constantine, or more formally the Masonic and Military Order of the Red Cross of Constantine and the Appendant Orders of the Holy Sepulchre and of St John the Evangelist, is a Christian fraternal order of Freemasonry. Candidates for the order must already be members of Craft Freemasonry (lodge) and Royal Arch Freemasonry (chapter); they must also be members of the Christian religion, and proclaim their belief in the Christian doctrine of the Holy Trinity.

The Degree of Honor Protective Association is a fraternal benefit society. It was originally organized as a female auxiliary to the Ancient Order of United Workmen, but split off in 1910 to become its own independent group. It merged with Catholic Financial Life in 2017.
The Knights and Ladies of Honor was a highly successful and popular American fraternal benefit organization in the late 19th and early twentieth century. It is perhaps the first major fraternal benefit organization to adopt the idea of diversity allowing non-white persons and racial groups to be recognized and establish lodges.