Related Research Articles

Neuroscience is the scientific study of the nervous system, its functions and disorders. It is a multidisciplinary science that combines physiology, anatomy, molecular biology, developmental biology, cytology, psychology, physics, computer science, chemistry, medicine, statistics, and mathematical modeling to understand the fundamental and emergent properties of neurons, glia and neural circuits. The understanding of the biological basis of learning, memory, behavior, perception, and consciousness has been described by Eric Kandel as the "epic challenge" of the biological sciences.
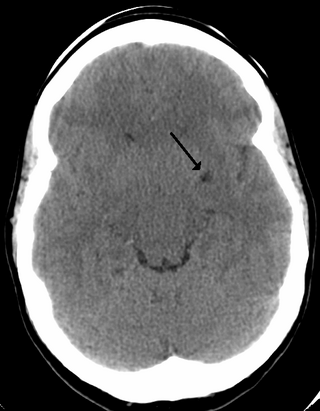
Vascular dementia is dementia caused by a series of strokes. Restricted blood flow due to strokes reduces oxygen and glucose delivery to the brain, causing cell injury and neurological deficits in the affected region. Subtypes of vascular dementia include subcortical vascular dementia, multi-infarct dementia, stroke-related dementia, and mixed dementia.

The National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS) is a part of the U.S. National Institutes of Health (NIH). It conducts and funds research on brain and nervous system disorders and has a budget of just over US$2.03 billion. The mission of NINDS is "to reduce the burden of neurological disease—a burden borne by every age group, every segment of society, and people all over the world". NINDS has established two major branches for research: an extramural branch that funds studies outside the NIH, and an intramural branch that funds research inside the NIH. Most of NINDS' budget goes to fund extramural research. NINDS' basic science research focuses on studies of the fundamental biology of the brain and nervous system, genetics, neurodegeneration, learning and memory, motor control, brain repair, and synapses. NINDS also funds clinical research related to diseases and disorders of the brain and nervous system, e.g. AIDS, Alzheimer's disease, epilepsy, muscular dystrophy, multiple sclerosis, Parkinson's disease, spinal cord injury, stroke, and traumatic brain injury.

Cerebrovascular disease includes a variety of medical conditions that affect the blood vessels of the brain and the cerebral circulation. Arteries supplying oxygen and nutrients to the brain are often damaged or deformed in these disorders. The most common presentation of cerebrovascular disease is an ischemic stroke or mini-stroke and sometimes a hemorrhagic stroke. Hypertension is the most important contributing risk factor for stroke and cerebrovascular diseases as it can change the structure of blood vessels and result in atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis narrows blood vessels in the brain, resulting in decreased cerebral perfusion. Other risk factors that contribute to stroke include smoking and diabetes. Narrowed cerebral arteries can lead to ischemic stroke, but continually elevated blood pressure can also cause tearing of vessels, leading to a hemorrhagic stroke.

CADASIL or CADASIL syndrome, involving cerebral autosomal dominant arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leukoencephalopathy, is the most common form of hereditary stroke disorder, and is thought to be caused by mutations of the NOTCH3 gene on chromosome 19. The disease belongs to a family of disorders called the leukodystrophies. The most common clinical manifestations are migraine headaches and transient ischemic attacks or strokes, which usually occur between 40 and 50 years of age, although MRI is able to detect signs of the disease years prior to clinical manifestation of disease.
Cerebral softening, also known as encephalomalacia, is a localized softening of the substance of the brain, due to bleeding or inflammation. Three varieties, distinguished by their color and representing different stages of the disease progress, are known respectively as red, yellow, and white softening.
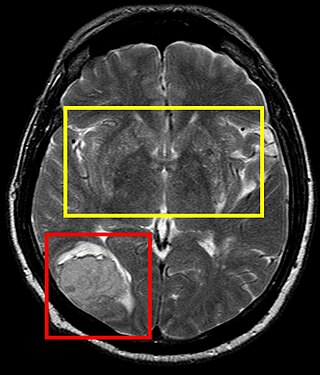
A perivascular space, also known as a Virchow–Robin space, is a fluid-filled space surrounding certain blood vessels in several organs, including the brain, potentially having an immunological function, but more broadly a dispersive role for neural and blood-derived messengers. The brain pia mater is reflected from the surface of the brain onto the surface of blood vessels in the subarachnoid space. In the brain, perivascular cuffs are regions of leukocyte aggregation in the perivascular spaces, usually found in patients with viral encephalitis.
Familial hemiplegic migraine (FHM) is an autosomal dominant type of hemiplegic migraine that typically includes weakness of half the body which can last for hours, days, or weeks. It can be accompanied by other symptoms, such as ataxia, coma, and paralysis. Migraine attacks may be provoked by minor head trauma. Some cases of minor head trauma in patients with hemiplegic migraine can develop into delayed cerebral edema, a life-threatening medical emergency. Clinical overlap occurs in some FHM patients with episodic ataxia type 2 and spinocerebellar ataxia type 6, benign familial infantile epilepsy, and alternating hemiplegia of childhood.
Nancy Coover Andreasen is an American neuroscientist and neuropsychiatrist. She currently holds the Andrew H. Woods Chair of Psychiatry at the Roy J. and Lucille A. Carver College of Medicine at the University of Iowa.

Neurogenic locus notch homolog protein 3(Notch 3) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NOTCH3 gene.

Patricia Goldman-Rakic was an American professor of neuroscience, neurology, psychiatry and psychology at Yale University School of Medicine. She pioneered multidisciplinary research of the prefrontal cortex and working memory.

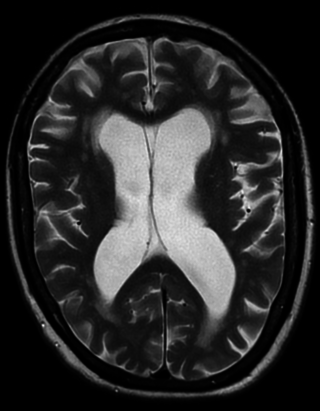
A hyperintensity or T2 hyperintensity is an area of high intensity on types of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans of the brain of a human or of another mammal that reflect lesions produced largely by demyelination and axonal loss. These small regions of high intensity are observed on T2 weighted MRI images within cerebral white matter or subcortical gray matter. The volume and frequency is strongly associated with increasing age. They are also seen in a number of neurological disorders and psychiatric illnesses. For example, deep white matter hyperintensities are 2.5 to 3 times more likely to occur in bipolar disorder and major depressive disorder than control subjects. WMH volume, calculated as a potential diagnostic measure, has been shown to correlate to certain cognitive factors. Hyperintensities appear as "bright signals" on an MRI image and the term "bright signal" is occasionally used as a synonym for a hyperintensity.

Cerebral autosomal recessive arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leukoencephalopathy (CARASIL) is disease of the arteries in the brain, which causes tissue loss in the subcortical region of the brain and the destruction of myelin in the CNS. CARASIL is characterized by symptoms such as gait disturbances, hair loss, low back pain, dementia, and stroke. CARASIL is a rare disease, having only been diagnosed in about 50 patients, of which ten have been genetically confirmed. Most cases have been reported in Japan, but Chinese and caucasian individuals have also been diagnosed with the disease. CARASIL is inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern. There is currently no cure for CARASIL. Other names for CARASIL include familial young-adult-onset arteriosclerotic leukoencephalopathy with alopecia and lumbago without arterial hypertension, Nemoto disease and Maeda syndrome.
Joanna Marguerite Wardlaw is a Scottish physician, radiologist, and academic specialising in neuroradiology and pathophysiology. Wardlaw worked as a junior doctor before specialising as a radiologist. She continues to practice medicine as an Honorary Consultant Neuroradiologist with NHS Lothian. She has spent her entire academic career at the University of Edinburgh.

The Sainte-Anne Hospital Center is a hospital located in the 14th arrondissement of Paris, specializing in psychiatry, neurology, neurosurgery, neuroimaging and addiction. With its creation dating to 1651, the organization remains, along with the Esquirol Hospital in Saint-Maurice, the symbol of psychiatric asylums in France.

Irene Mary Carmel Tracey is Vice-Chancellor of the University of Oxford and former Warden of Merton College, Oxford. She is also Professor of Anaesthetic Neuroscience in the Nuffield Department of Clinical Neurosciences and formerly Pro-Vice-Chancellor at the University of Oxford. She is a co-founder of the Oxford Centre for Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the Brain (FMRIB), now the Wellcome Centre for Integrative Neuroimaging. Her team’s research is focused on the neuroscience of pain, specifically pain perception and analgesia as well as how anaesthetics produce altered states of consciousness. Her team uses multidisciplinary approaches including neuroimaging.
Maria Natashini "Natasha" Rajah is a Canadian neuroscientist who is a Full Professor at the Department of Psychology, Toronto Metropolitan University. Prior to joining Toronto Metropolitan University in August 2023, she was Full Professor at the Department of Psychiatry at McGill University from 2005 to July 2023, and was the inaugural Scientific Director of the Cerebral Imaging Center (CIC) at the Douglas Research Centre from 2011 to 2021. She is a cognitive neuroscientist who is interested in episodic memory, ageing and dementia. Her research uses functional magnetic resonance imaging to investigate how sex, gender, and social determinants of health interact with age and affect the neural networks responsible for episodic memory encoding and retrieval.
Marie-Germaine Bousser is a French neuroscientist. She won the Brain Prize in 2019 for her work on CADASIL.
Joana Palha is a neuroscientist and professor at the School of Medicine of the University of Minho, in Braga in the north of Portugal.
Élisabeth Tournier-Lasserve is a French neurologist, medical geneticist, university professor and hospital practitioner in genetics. Together with three colleagues, she was the co-recipient of the Brain Prize in 2019, the world's largest brain research prize.
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 "Anne Joutel". Lundbeckfonden. Retrieved 10 May 2021.
- 1 2 3 "Dr. Anne Joutel, M.D. Ph.D." Leducq Center Against Small Vessel Disease. Retrieved 10 May 2021.
- 1 2 "The Institute". Institute of Psychiatry and Neuroscience, Paris. Retrieved 10 May 2021.
- ↑ "Anne Joutel". SVD. Retrieved 10 May 2021.
- ↑ "French Neuroscientists Awarded 2019 Brain Prize for their Research into Small Vessel Strokes". British Neuroscience Association. Retrieved 10 May 2021.
- ↑ "The Brain Prize Winners". Lundbeckfonded. Retrieved 9 May 2021.
- ↑ "Joutel Anne". Google Scholar. Retrieved 10 May 2021.