
Aristolochic acids are a family of carcinogenic, mutagenic, and nephrotoxic phytochemicals commonly found in the flowering plant family Aristolochiaceae (birthworts). Aristolochic acid (AA) I is the most abundant one. The family Aristolochiaceae includes the genera Aristolochia and Asarum, which are commonly used in Chinese herbal medicine. Although these compounds are widely associated with kidney problems, liver and urothelial cancers, the use of AA-containing plants for medicinal purposes has a long history. The FDA has issued warnings regarding consumption of AA-containing supplements.

Soursop is the fruit of Annona muricata, a broadleaf, flowering, evergreen tree. It is native to the tropical regions of the Americas and the Caribbean and is widely propagated. It is in the same genus, Annona, as cherimoya and is in the Annonaceae family.

The Annonaceae are a family of flowering plants consisting of trees, shrubs, or rarely lianas commonly known as the custard apple family or soursop family. With 108 accepted genera and about 2400 known species, it is the largest family in the Magnoliales. Several genera produce edible fruit, most notably Annona, Anonidium, Asimina, Rollinia, and Uvaria. Its type genus is Annona. The family is concentrated in the tropics, with few species found in temperate regions. About 900 species are Neotropical, 450 are Afrotropical, and the remaining are Indomalayan.

Annona is a genus of flowering plants in the pawpaw/sugar apple family, Annonaceae. It is the second largest genus in the family after Guatteria, containing approximately 166 species of mostly Neotropical and Afrotropical trees and shrubs.

Annona squamosa is a small, well-branched tree or shrub from the family Annonaceae that bears edible fruits called sugar apples or sweetsops. It tolerates a tropical lowland climate better than its relatives Annona reticulata and Annona cherimola helping make it the most widely cultivated of these species. Annona squamosa is a small, semi-(or late) deciduous, much-branched shrub or small tree 3 to 8 metres tall similar to soursop. It is a native of tropical climate in the Americas and West Indies, and Spanish traders aboard the Manila galleons docking in the Philippines brought it to Asia.
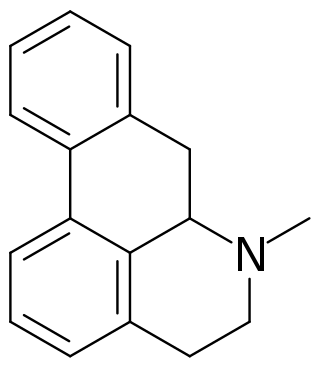
Aporphine is an alkaloid with the chemical formula C17H17N. It is the core chemical substructure of the aporphine alkaloids, a subclass of quinoline alkaloids. It can exist in either of two enantiomeric forms, (R)-aporphine and (S)-aporphine.

Akuammine (vincamajoridine) is an indole alkaloid. It is the most abundant alkaloid found in the seeds from the tree Picralima nitida, commonly known as akuamma, comprising 0.56% of the dried powder. It has also been isolated from Vinca major. Akuammine is structurally related to yohimbine, mitragynine and more distantly Voacangine, all of which are alkaloid plant products with pharmacological properties.

Annonacin is a chemical compound with toxic effects, especially in the nervous system, found in some fruits such as the paw paw, custard apples, soursop, and others from the family Annonaceae. It is a member of the class of compounds known as acetogenins. Annonacin-containing fruit products are regularly consumed throughout the West Indies for their traditional medicine uses.

Acetogenins are a class of polyketide natural products found in plants of the family Annonaceae. They are characterized by linear 32- or 34-carbon chains containing oxygenated functional groups including hydroxyls, ketones, epoxides, tetrahydrofurans and tetrahydropyrans. They are often terminated with a lactone or butenolide. Over 400 members of this family of compounds have been isolated from 51 different species of plants. Many acetogenins are characterized by neurotoxicity.

N-n-Propylnorapomorphine (NPA) is an aporphine derivative dopamine agonist closely related to apomorphine. In rodents it has been shown to produce hyperactivity, stereotypy, hypothermia, antinociception, and penile erection, among other effects. Notably, its effects on locomotion are biphasic, with low doses producing inhibition and catalepsy and high doses resulting in enhancement of activity. This is likely due to preferential activation of D2/D3 autoreceptors versus postsynaptic receptors, the latter of which overcomes the former to increase postsynaptic dopaminergic signaling only with high doses.

Glaucine(1,2,9,10-TetraMethoxyAporphine, Bromcholitin, Glauvent, Tusidil, Tussiglaucin) is an aporphine alkaloid found in several different plant species in the family Papaveraceae such as Glaucium flavum, Glaucium oxylobum and Corydalis yanhusuo, and in other plants like Croton lechleri in the family Euphorbiaceae.

Higenamine (norcoclaurine) is a chemical compound found in a variety of plants including Nandina domestica (fruit), Aconitum carmichaelii (root), Asarum heterotropioides, Galium divaricatum, Annona squamosa, and Nelumbo nucifera.

A phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitor, commonly referred to as a PDE4 inhibitor, is a drug used to block the degradative action of phosphodiesterase 4 (PDE4) on cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP). It is a member of the larger family of PDE inhibitors. The PDE4 family of enzymes are the most prevalent PDE in immune cells. They are predominantly responsible for hydrolyzing cAMP within both immune cells and cells in the central nervous system.

(S)-Magnoflorine is a quaternary benzylisoquinoline alkaloid (BIA) of the aporphine structural subgroup which has been isolated from various species of the family Menispermaceae, such as Pachygone ovata,Sinomenium acutum, and Cissampelos pareira.

Anonaine is a bioactive benzylisoquinoline alkaloid, present in members of the plant families Magnoliaceae and Annonaceae It is named after the plant it was first extracted from, Annona reticulata, which is commonly known as Anona.

Liriodenine is a bio-active isolate of the Chinese medicinal herb Zanthoxylum nitidum. It was isolated for the first time, at least with the name liriodenine, from the heartwood of Liriodendron tulipifera, the common yellow poplar of the south-eastern USA. It is found in very many other plants, notably in Annona cherimolia and Annona muricata, widely cultivated for their edible fruit.

Domesticine is an α1D-adrenergic receptor antagonist. The compound belongs to the group of Aporphine alkaloids.

Aporphine alkaloids are naturally occurring chemical compounds from the group of alkaloids. After the benzylisoquinoline alkaloids they are the second largest group of isoquinoline alkaloids.
(S)-corytuberine synthase is a cytochrome P450 enzyme purified from the plant Coptis japonica, with EC number EC 1.14.19.51 and CYP Symbol CYP80G2, and catalyses an intramolecular C-C phenol coupling of (S)-reticuline in magnoflorine biosynthesis.
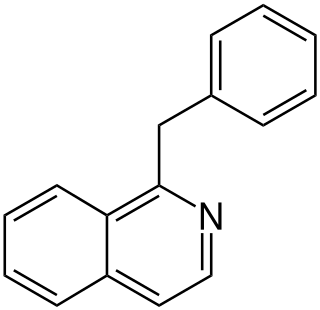
The benzylisoquinoline alkaloids are natural products that can be classified as isoquinoline alkaloids and are derived from benzylisoquinoline. They also include the benzyl(tetrahydro)isoquinoline alkaloids.

















