
Antrodia albida is a species of fungus in the genus Antrodia that grows on the dead wood of deciduous trees. A widely distributed species, it is found in Africa, Asia, Europe, Oceania, North America, and South America. The fungus was first described under the name Daedalea albida by Elias Magnus Fries in his 1815 work Observationes mycologicae. Marinus Anton Donk transferred it to Antrodia in 1960.

The Fomitopsidaceae are a family of fungi in the order Polyporales. Most species are parasitic on woody plants, and tend to cause brown rots. The name comes from Fomitopsis + -aceae.

Fomitopsis is a genus of more than 40 species of bracket fungi in the family Fomitopsidaceae.

Antrodia is a genus of fungi in the family Fomitopsidaceae. Antrodia species have fruit bodies that typically resupinate, with the hymenium exposed to the outside; the edges may be turned so as to form narrow brackets. Most species are found in temperate and boreal forests, and cause brown rot.
Gelatoporia is a fungal genus in the family Gelatoporiaceae. This is a monotypic genus, containing the single widely distributed species Gelatoporia subvermispora. The genus was circumscribed in 1985 by Finnish mycologist Tuomo Niemelä to contain poroid crust fungi with a monomitic hyphal structure, clamped hyphae, and producing white rot.
3-Methyl-3-octanol (systematically named 3-methyloctan-3-ol) is an organic compound with the chemical formula CH3(CH2)4C(CH3)(CH2CH3)OH (also written as C
9H
20O). This simple tertiary alcohol is a clear colourless liquid under standard conditions, and is tasteless.

Fibroporia vaillantii, also known as mine fungus, white pore fungus, Antrodia vaillantii, Polyporus vaillantii, and various other names is a wood-decaying fungus which can occur on timber in humid conditions. The fungus causes brown rot of pine wood, in which cellulose and hemicellulose are broken down, leading to brown discoloration and shrinkage of wood.

Taiwanofungus camphoratus, also known as stout camphor fungus, is a species of fungus that is endemic to Taiwan, where it grows only on the endemic tree Cinnamomum kanehirae, causing a brown heart rot. Synonyms include Antrodia camphorata and Ganoderma camphoratum.
Antrodia serialiformis is a species of polypore fungus in the family Fomitopsidaceae. The fungus is resupinate, consisting of a fertile spore-bearing pore surface lying flat on the underside of decaying wood, although one or more fan-shaped overlapping caps may also be formed. Although quite common in the eastern United States, it was not recognized as a distinct species until 2009, owing to its resemblance to the closely related Antrodia serialis. Differences in ecology, spore size, and DNA sequences distinguish the two lookalikes.

Antrodia serialis is a species of polypore fungus in the genus Antrodia. Originally named Polyporus serialis by Elias Fries in 1821, it was given its current name by Marinus Anton Donk in 1966. A widespread species, A. serialis causes heart rot in living trees. In North America, it is often confused with the morphologically similar Antrodia serialiformis, which grows on oak.

Antrodia cinnamomea is a fungus species described as new to science in 1995. It causes brown heart rot of the aromatic tree Cinnamomum kanehirae. It is used in Taiwanese traditional medicine as a supposed remedy for cancer, hypertension, and hangover. The annual market is worth over $100 million (US) in Taiwan alone. The 32.15 Mb genome containing 9,254 genes has been sequenced.
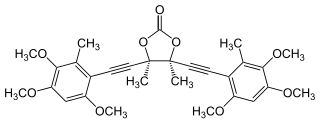
Antrodioxolanone is an anti-inflammatory isolated from Antrodia camphorata.

Antrocamphin B is a bioactive isolate of Taiwanofungus camphoratus. Antrocamphin B is a congener of antrocamphin A.

Fibroporia is a genus of ten species of poroid crust fungi in the family Fomitopsidaceae. The genus contains species similar to those in genus Antrodia, but they are phylogenetically distinct.

In Finland, Kotiranta and Niemelä introduced a widely used method for comparing the conservation values of different forest areas, based on the observation that certain wood-rotting fungi are very sensitive to the impact of human activities on forest ecosystems. Such species are slow to return to areas from where they have disappeared, so their presence is evidence of a long continuity in forest ecosystems.
Amyloporia is a genus of five species of crust fungi in the family Polyporaceae. Its main distinguishing characteristic is the amyloid reaction of the skeletal hyphae, although some authors do not consider this to be sufficient to distinguish Amyloporia from the related genus Antrodia.
Cerarioporia is a fungal genus in the family Polyporaceae. It is a monotypic genus, containing the single species Cerarioporia cystidiata, a wood-decaying poroid crust fungus found in tropical China. Cerarioporia resembles fungi placed in the genus Antrodia, but can be distinguished by its waxy to resinous fruit bodies, and microscopically by the thick-walled, encrusted cystidia. Additionally, Cerarioporia causes a white rot, while Antrodia are brown-rot fungi.

Anthoporia is a fungal genus in the family Meripilaceae. It is a monotypic genus, circumscribed in 2016 to contain the single species Anthoporia albobrunnea.

Cerrena zonata is a species of poroid fungus in the genus Cerrena.
Neoantrodia primaeva is a species of fungus belonging to the family Fomitopsidaceae.











