Peptic ulcer disease is a break in the inner lining of the stomach, the first part of the small intestine, or sometimes the lower esophagus. An ulcer in the stomach is called a gastric ulcer, while one in the first part of the intestines is a duodenal ulcer. The most common symptoms of a duodenal ulcer are waking at night with upper abdominal pain, and upper abdominal pain that improves with eating. With a gastric ulcer, the pain may worsen with eating. The pain is often described as a burning or dull ache. Other symptoms include belching, vomiting, weight loss, or poor appetite. About a third of older people have no symptoms. Complications may include bleeding, perforation, and blockage of the stomach. Bleeding occurs in as many as 15% of cases.
In anatomy, a fistula is an abnormal connection joining two hollow spaces, such as blood vessels, intestines, or other hollow organs to each other, often resulting in an abnormal flow of fluid from one space to the other. An anal fistula connects the anal canal to the perianal skin. An anovaginal or rectovaginal fistula is a hole joining the anus or rectum to the vagina. A colovaginal fistula joins the space in the colon to that in the vagina. A urinary tract fistula is an abnormal opening in the urinary tract or an abnormal connection between the urinary tract and another organ. An abnormal communication between the bladder and the uterus is called a vesicouterine fistula, while if it is between the bladder and the vagina it is known as a vesicovaginal fistula, and if between the urethra and the vagina: a urethrovaginal fistula. When occurring between two parts of the intestine, it is known as an enteroenteral fistula, between the small intestine and the skin as an enterocutaneous fistula, and between the colon and the skin as a colocutaneous fistula.
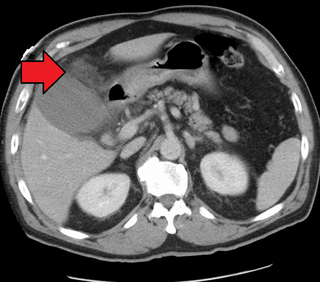
Cholecystitis is inflammation of the gallbladder. Symptoms include right upper abdominal pain, pain in the right shoulder, nausea, vomiting, and occasionally fever. Often gallbladder attacks precede acute cholecystitis. The pain lasts longer in cholecystitis than in a typical gallbladder attack. Without appropriate treatment, recurrent episodes of cholecystitis are common. Complications of acute cholecystitis include gallstone pancreatitis, common bile duct stones, or inflammation of the common bile duct.
Enteritis is inflammation of the small intestine. It is most commonly caused by food or drink contaminated with pathogenic microbes, such as Serratia, but may have other causes such as NSAIDs, radiation therapy as well as autoimmune conditions like Crohn's disease and celiac disease. Symptoms include abdominal pain, cramping, diarrhea, dehydration, and fever. Related diseases of the gastrointestinal system include inflammation of the stomach and large intestine.

Upper gastrointestinal bleeding is gastrointestinal bleeding (hemorrhage) in the upper gastrointestinal tract, commonly defined as bleeding arising from the esophagus, stomach, or duodenum. Blood may be observed in vomit or in altered form as black stool. Depending on the amount of the blood loss, symptoms may include shock.
Hematemesis is the vomiting of blood. It can be confused with hemoptysis or epistaxis (nosebleed), which are more common. The source is generally the upper gastrointestinal tract, typically above the suspensory muscle of duodenum. It may be caused by ulcers, tumors of the stomach or esophagus, varices, prolonged and vigorous retching, gastroenteritis, ingested blood, or certain drugs.

Gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs) are the most common mesenchymal neoplasms of the gastrointestinal tract. GISTs arise in the smooth muscle pacemaker interstitial cell of Cajal, or similar cells. They are defined as tumors whose behavior is driven by mutations in the KIT gene (85%), PDGFRA gene (10%), or BRAF kinase (rare). 95% of GISTs stain positively for KIT (CD117). Most (66%) occur in the stomach and gastric GISTs have a lower malignant potential than tumors found elsewhere in the GI tract.

An upper gastrointestinal series, also called a barium swallow, barium study, or barium meal, is a series of radiographs used to examine the gastrointestinal tract for abnormalities. A contrast medium, usually a radiocontrast agent such as barium sulfate mixed with water, is ingested or instilled into the gastrointestinal tract, and X-rays are used to create radiographs of the regions of interest. The barium enhances the visibility of the relevant parts of the gastrointestinal tract by coating the inside wall of the tract and appearing white on the film. This in combination with other plain radiographs allows for the imaging of parts of the upper gastrointestinal tract such as the pharynx, larynx, esophagus, stomach, and small intestine such that the inside wall lining, size, shape, contour, and patency are visible to the examiner. With fluoroscopy, it is also possible to visualize the functional movement of examined organs such as swallowing, peristalsis, or sphincter closure. Depending on the organs to be examined, barium radiographs can be classified into "barium swallow", "barium meal", "barium follow-through", and "enteroclysis". To further enhance the quality of images, air or gas is sometimes introduced into the gastrointestinal tract in addition to barium, and this procedure is called double-contrast imaging. In this case the gas is referred to as the negative contrast medium. Traditionally the images produced with barium contrast are made with plain-film radiography, but computed tomography is also used in combination with barium contrast, in which case the procedure is called "CT enterography".

In medicine (gastroenterology), angiodysplasia is a small vascular malformation of the gut. It is a common cause of otherwise unexplained gastrointestinal bleeding and anemia. Lesions are often multiple, and frequently involve the cecum or ascending colon, although they can occur at other places. Treatment may be with colonoscopic interventions, angiography and embolization, medication, or occasionally surgery.
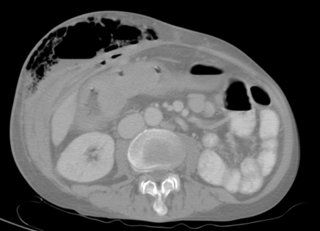
Diverticulitis, also called colonic diverticulitis, is a gastrointestinal disease characterized by inflammation of abnormal pouches—diverticula—that can develop in the wall of the large intestine. Symptoms typically include lower-abdominal pain of sudden onset, but the onset may also occur over a few days. There may also be nausea; and diarrhea or constipation. Fever or blood in the stool suggests a complication. Repeated attacks may occur.

Diverticulosis is the condition of having multiple pouches (diverticula) in the colon that are not inflamed. These are outpockets of the colonic mucosa and submucosa through weaknesses of muscle layers in the colon wall. Diverticula do not cause symptoms in most people. Diverticular disease occurs when diverticula become clinically inflamed, a condition known as diverticulitis.

A Meckel's diverticulum, a true congenital diverticulum, is a slight bulge in the small intestine present at birth and a vestigial remnant of the vitelline duct. It is the most common malformation of the gastrointestinal tract and is present in approximately 2% of the population, with males more frequently experiencing symptoms.
Gastrointestinal bleeding, also called gastrointestinal hemorrhage (GIB), is all forms of bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract, from the mouth to the rectum. When there is significant blood loss over a short time, symptoms may include vomiting red blood, vomiting black blood, bloody stool, or black stool. Small amounts of bleeding over a long time may cause iron-deficiency anemia resulting in feeling tired or heart-related chest pain. Other symptoms may include abdominal pain, shortness of breath, pale skin, or passing out. Sometimes in those with small amounts of bleeding no symptoms may be present.

A volvulus is when a loop of intestine twists around itself and the mesentery that supports it, resulting in a bowel obstruction. Symptoms include abdominal pain, abdominal bloating, vomiting, constipation, and bloody stool. Onset of symptoms may be rapid or more gradual. The mesentery may become so tightly twisted that blood flow to part of the intestine is cut off, resulting in ischemic bowel. In this situation there may be fever or significant pain when the abdomen is touched.

Blood in stool or rectal bleeding looks different depending on how early it enters the digestive tract—and thus how much digestive action it has been exposed to—and how much there is. The term can refer either to melena, with a black appearance, typically originating from upper gastrointestinal bleeding; or to hematochezia, with a red color, typically originating from lower gastrointestinal bleeding. Evaluation of the blood found in stool depends on its characteristics, in terms of color, quantity and other features, which can point to its source, however, more serious conditions can present with a mixed picture, or with the form of bleeding that is found in another section of the tract. The term "blood in stool" is usually only used to describe visible blood, and not fecal occult blood, which is found only after physical examination and chemical laboratory testing.

Lower gastrointestinal bleeding, commonly abbreviated LGIB, is any form of gastrointestinal bleeding in the lower gastrointestinal tract. LGIB is a common reason for seeking medical attention at a hospital's emergency department. LGIB accounts for 30–40% of all gastrointestinal bleeding and is less common than upper gastrointestinal bleeding (UGIB). It is estimated that UGIB accounts for 100–200 per 100,000 cases versus 20–27 per 100,000 cases for LGIB. Approximately 85% of lower gastrointestinal bleeding involves the colon, 10% are from bleeds that are actually upper gastrointestinal bleeds, and 3–5% involve the small intestine.

Double-balloon enteroscopy, also known as push-and-pull enteroscopy, is an endoscopic technique for visualization of the small bowel. It was developed by Hironori Yamamoto in 2001. It is novel in the field of diagnostic gastroenterology as it is the first endoscopic technique that allows for the entire gastrointestinal tract to be visualized in real time.

Capsule endoscopy is a medical procedure used to record internal images of the gastrointestinal tract for use in disease diagnosis. Newer developments are also able to take biopsies and release medication at specific locations of the entire gastrointestinal tract. Unlike the more widely used endoscope, capsule endoscopy provides the ability to see the middle portion of the small intestine. It can be applied to the detection of various gastrointestinal cancers, digestive diseases, ulcers, unexplained bleedings, and general abdominal pains. After a patient swallows the capsule, it passes along the gastrointestinal tract, taking a number of images per second which are transmitted wirelessly to an array of receivers connected to a portable recording device carried by the patient. General advantages of capsule endoscopy over standard endoscopy include the minimally invasive procedure setup, ability to visualize more of the gastrointestinal tract, and lower cost of the procedure.

Amoebiasis, or amoebic dysentery, is an infection of the intestines caused by a parasitic amoeba Entamoeba histolytica. Amoebiasis can be present with no, mild, or severe symptoms. Symptoms may include lethargy, loss of weight, colonic ulcerations, abdominal pain, diarrhea, or bloody diarrhea. Complications can include inflammation and ulceration of the colon with tissue death or perforation, which may result in peritonitis. Anemia may develop due to prolonged gastric bleeding.

Herpes esophagitis is a viral infection of the esophagus caused by Herpes simplex virus (HSV).
















