
Datura is a genus of nine species of highly poisonous, vespertine-flowering plants belonging to the nightshade family Solanaceae. They are commonly known as thornapples or jimsonweeds, but are also known as devil's trumpets. Other English common names include moonflower, devil's weed, and hell's bells. All species of Datura are very poisonous and potentially psychoactive, especially their seeds and flowers, which can cause respiratory depression, arrhythmias, fever, delirium, hallucinations, anticholinergic syndrome, psychosis, and even death if taken internally. Due to their effects and symptoms, they have occasionally been used not only as poisons, but also as hallucinogens by various groups throughout history. Traditionally, psychoactive administration of Datura species has often been associated with witchcraft and sorcery or similar practices in many cultures, including the Western world. Certain common Datura species have also been used ritualistically as entheogens by some Native American groups. Nonpsychoactive use of the plant is usually done for medicinal purposes, and the alkaloids present in plants of the Datura genus have long been considered traditional medicines in both the New and Old Worlds due to the presence of the alkaloids scopolamine and atropine, which are also produced by Old World plants such as Hyoscyamus niger, Atropa belladonna, and Mandragora officinarum.

Datura stramonium, known by the common names thorn apple, jimsonweed, devil's snare, or devil's trumpet, is a species of flowering plant in the nightshade family Solanaceae. Its likely origin was in Central America, and it has been introduced in many world regions. It is an aggressive invasive weed in temperate climates across the world. D. stramonium has frequently been employed in traditional medicine to treat a variety of ailments. It has also been used as a hallucinogen, taken entheogenically to cause intense, sacred or occult visions. It is unlikely ever to become a major drug of abuse owing to effects upon both mind and body frequently perceived subjectively as being highly unpleasant, giving rise to a state of profound and long-lasting disorientation or delirium with a potentially fatal outcome. It contains tropane alkaloids which are responsible for the psychoactive effects, and may be severely toxic.

Hyoscyamine is a naturally occurring tropane alkaloid and plant toxin. It is a secondary metabolite found in certain plants of the family Solanaceae, including henbane, mandrake, angel's trumpets, jimsonweed, tomato, the sorcerers' tree, and deadly nightshade. It is the levorotary isomer of atropine and thus sometimes known as levo-atropine.

Datura wrightii, commonly known as sacred datura, is a poisonous perennial plant species and ornamental flower of the family Solanaceae native to the Southwestern United States and northwestern Mexico. It is sometimes used as a hallucinogen due to its psychoactive alkaloids. D. wrightii is classified as an anticholinergic deliriant.

Brugmansia is a genus of seven species of flowering plants in the nightshade family Solanaceae. They are woody trees or shrubs, with pendulous flowers, and have no spines on their fruit. Their large, fragrant flowers give them their common name of angel's trumpets, a name sometimes used for the closely related genus Datura.

Deliriants are a class of hallucinogen. The term was coined in the early 1980s to distinguish these drugs from psychedelics and dissociatives such as LSD and ketamine, due to their primary effect of causing delirium, as opposed to the more lucid and less disturbed states produced by other types of hallucinogens. The term generally refers to anticholinergic drugs, which are substances that inhibit the function of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine. Common examples of deliriants include plants of the genera Datura and Brugmansia as well as higher than recommended dosages of diphenhydramine (Benadryl). A number of plant deliriants such as that of the Solanaceae family, particularly in the Americas have been used by some indigenous cultures to reach delirious and altered states for traditions or rituals, such as rites of passage, divination or communicating with the ancestors. Despite their long history of use, deliriants are the least-studied class of hallucinogens in terms of their behavioral and neurological effects.
Tropane is a nitrogenous bicyclic organic compound. It is mainly known for the other alkaloids derived from it, which include atropine and cocaine, among others. Tropane alkaloids occur in plants of the families Erythroxylaceae and Solanaceae.

Datura metel is a shrub-like annual or short-lived, shrubby perennial, commonly known in Europe as Indian thornapple, Hindu Datura, or metel and in the United States as devil's trumpet or angel's trumpet. Datura metel is naturalised in all the warmer countries of the world. It is found notably in India, where it is known by the ancient, Sanskrit-derived, Hindi name dhatūra (धतूरा), from which the genus name Datura is derived.

Datura innoxia, known as pricklyburr, recurved thorn-apple, downy thorn-apple, Indian-apple, lovache, moonflower, nacazcul, toloatzin, toloaxihuitl, tolguache or toloache, is a species of flowering plant in the family Solanaceae. It is more rarely called sacred datura, a common name which is applied more often to the closely related Datura wrightii. It is native to the Southwestern United States, Central and South America, and introduced in Africa, Asia, Australia and Europe. The scientific name is often cited as D. innoxia. When English botanist Philip Miller first described the species in 1768, he misspelled the Latin word innoxia (inoffensive) when naming it D. inoxia. The name Datura meteloides was for some time erroneously applied to some members of the species, but that name has now been abandoned.

Datura ferox, commonly known as long spined thorn apple and fierce thornapple, as well as Angel's-trumpets, is a species of Datura. Like all such species, every part of the plant contains deadly toxins that can kill animals that ingest it. Its fruit, red-brown when ripe, has unusually long thorns or spikes.
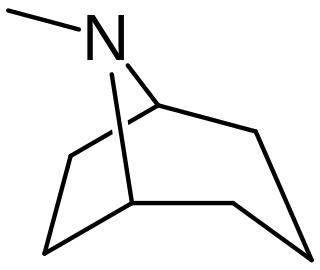
Tropane alkaloids are a class of bicyclic [3.2.1] alkaloids and secondary metabolites that contain a tropane ring in their chemical structure. Tropane alkaloids occur naturally in many members of the plant family Solanaceae. Certain tropane alkaloids such as cocaine and scopolamine are notorious for their psychoactive effects, related usage and cultural associations. Particular tropane alkaloids such as these have pharmacological properties and can act as anticholinergics or stimulants.

Anisodamine, also known as 7β-hydroxyhyoscyamine, is an anticholinergic and α1 adrenergic receptor antagonist used in the treatment of acute circulatory shock in China. It is given orally or by injection, as a racemic mixture (racanisodamine) or as a hydrobromide salt. Eye drops at 0.5% concentration for slowing the progression of myopia is also available in China.

The biosynthesis of cocaine has long attracted the attention of biochemists and organic chemists. This interest is partly motivated by the strong physiological effects of cocaine, but a further incentive was the unusual bicyclic structure of the molecule. The biosynthesis can be viewed as occurring in two phases, one phase leading to the N-methylpyrrolinium ring, which is preserved in the final product. The second phase incorporates a C4 unit with formation of the bicyclic tropane core.
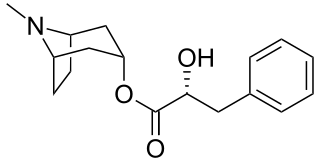
Littorine is a tropane alkaloid found in a variety of plants including Datura and Atropa belladonna. It is closely related in chemical structure to atropine, hyoscyamine, and scopolamine, which all share a common biosynthetic pathway.
Pseudotropine acyltransferase is an enzyme with systematic name acyl-CoA:pseudotropine O-acyltransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction

Meteloidine is an alkaloid found in some Brugmansia and Datura species. Its also found in Erythroxylum australe and is said to be cocaine-like alkaloid.

The Solanaceae, or nightshades, are a family of flowering plants that ranges from annual and perennial herbs to vines, lianas, epiphytes, shrubs, and trees, and includes a number of agricultural crops, medicinal plants, spices, weeds, and ornamentals. Many members of the family contain potent alkaloids, and some are highly toxic, but many—including tomatoes, potatoes, eggplant, bell and chili peppers—are used as food. The family belongs to the order Solanales, in the asterid group and class Magnoliopsida (dicotyledons). The Solanaceae consists of about 98 genera and some 2,700 species, with a great diversity of habitats, morphology and ecology.

An O-acylpseudotropine is any derivative of pseudotropine in which the alcohol group is substituted with an acyl group.

Methylecgonine is a prominent tropane alkaloid found in coca leaves. It is metabolite of cocaine, and maybe is used as precursor for it. It also occurs as minor alkaloid in roots of many Datura species such as Datura stramonium and Datura innoxia.

Datumetine is a tropane alkaloid found in leaves of Datura metel. It is said to modulate NMDA receptor and thus causes memory loss. It also causes epileptic seizures in mice. Docking studies suggest that it fits on both allosteric and orthosteric sites of NMDA receptor. It acts together with other anticholinergic tropane alkaloids of datura to cause amnesia.


















