
A boiler is a closed vessel in which fluid is heated. The fluid does not necessarily boil. The heated or vaporized fluid exits the boiler for use in various processes or heating applications, including water heating, central heating, boiler-based power generation, cooking, and sanitation.
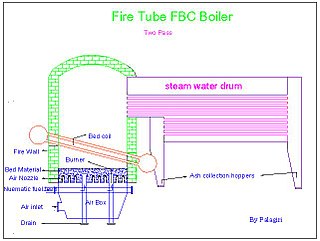
Fluidized bed combustion (FBC) is a combustion technology used to burn solid fuels.

A fire-tube boiler is a type of boiler invented in 1828 by Mark Seguin, in which hot gases pass from a fire through one or more tubes running through a sealed container of water. The heat of the gases is transferred through the walls of the tubes by thermal conduction, heating the water and ultimately creating steam.

A high pressure watertube boiler is a type of boiler in which water circulates in tubes heated externally by fire. Fuel is burned inside the furnace, creating hot gas which boils water in the steam-generating tubes. In smaller boilers, additional generating tubes are separate in the furnace, while larger utility boilers rely on the water-filled tubes that make up the walls of the furnace to generate steam.
A superheater is a device used to convert saturated steam or wet steam into superheated steam or dry steam. Superheated steam is used in steam turbines for electricity generation, in some steam engines, and in processes such as steam reforming. There are three types of superheaters: radiant, convection, and separately fired. A superheater can vary in size from a few tens of feet to several hundred feet.
A magnetohydrodynamic generator is a magnetohydrodynamic converter that transforms thermal energy and kinetic energy directly into electricity. An MHD generator, like a conventional generator, relies on moving a conductor through a magnetic field to generate electric current. The MHD generator uses hot conductive ionized gas as the moving conductor. The mechanical dynamo, in contrast, uses the motion of mechanical devices to accomplish this.

A heat recovery steam generator (HRSG) is an energy recovery heat exchanger that recovers heat from a hot gas stream, such as a combustion turbine or other waste gas stream. It produces steam that can be used in a process (cogeneration) or used to drive a steam turbine.
A cyclone furnace is a type of coal combustor commonly used in large industrial boilers.

A thermal power station, also known as a thermal power plant, is a type of power station in which the heat energy generated from various fuel sources is converted to electrical energy. The heat from the source is converted into mechanical energy using a thermodynamic power cycle. The most common cycle involves a working fluid heated and boiled under high pressure in a pressure vessel to produce high-pressure steam. This high pressure-steam is then directed to a turbine, where it rotates the turbine's blades. The rotating turbine is mechanically connected to an electric generator which converts rotary motion into electricity. Fuels such as natural gas or oil can also be burnt directly in gas turbines, skipping the steam generation step. These plants can be of the open cycle or the more efficient combined cycle type.
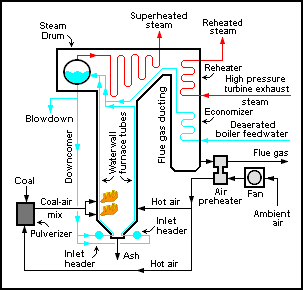
An air preheater is any device designed to heat air before another process, with the primary objective of increasing the thermal efficiency of the process. They may be used alone or to replace a recuperative heat system or to replace a steam coil.
A pulverized coal-fired boiler is an industrial or utility boiler that generates thermal energy by burning pulverized coal that is blown into the firebox.
Economizers, or economisers (UK), are mechanical devices intended to reduce energy consumption, or to perform useful function such as preheating a fluid. The term economizer is used for other purposes as well. Boiler, power plant, heating, refrigeration, ventilating, and air conditioning (HVAC) may all use economizers. In simple terms, an economizer is a heat exchanger.
A pulverizer or grinder or flour mill is a mechanical device for the grinding of many different types of materials. For example, a pulverizer mill is used to pulverize coal for combustion in the steam-generating furnaces of coal power plants.

A flue-gas stack, also known as a smoke stack, chimney stack or simply as a stack, is a type of chimney, a vertical pipe, channel or similar structure through which combustion product gases called flue gases are exhausted to the outside air. Flue gases are produced when coal, oil, natural gas, wood or any other fuel is combusted in an industrial furnace, a power plant's steam-generating boiler, or other large combustion device. Flue gas is usually composed of carbon dioxide (CO2) and water vapor, as well as nitrogen and excess oxygen remaining from the intake combustion air. It also contains a small percentage of pollutants such as particulate matter, carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides and sulfur oxides. The flue gas stacks are often quite tall, up to 420 metres (1,380 ft), to increase the stack effect and dispersion of pollutants.

Recovery boiler is the part of kraft process of pulping where chemicals for white liquor are recovered and reformed from black liquor, which contains lignin from previously processed wood. The black liquor is burned, generating heat, which is usually used in the process of making electricity, much as in a conventional steam power plant. The invention of the recovery boiler by G.H. Tomlinson in the early 1930s was a milestone in the advancement of the kraft process.

A boiler or steam generator is a device used to create steam by applying heat energy to water. Although the definitions are somewhat flexible, it can be said that older steam generators were commonly termed boilers and worked at low to medium pressure but, at pressures above this, it is more usual to speak of a steam generator.

Staged combustion is a method used to reduce the emission of nitrogen oxides (NOx) during combustion. There are two methods for staged combustion: air staged supply and fuel staged supply. Applications of staged combustion include boilers and rocket engines.

High Marnham Power Station was a coal fuelled power station in Nottinghamshire, to the west of the River Trent, approximately 0.5 miles (0.8 km) north of the village of High Marnham. Construction site clearance began in November 1955, No. 1 Unit power generation commenced in October 1959, and the station became fully operational in June 1962. The plant operated until 2003 when it was decommissioned, though the cooling towers weren't demolished until 2012.

Three-drum boilers are a class of water-tube boiler used to generate steam, typically to power ships. They are compact and of high evaporative power, factors that encourage this use. Other boiler designs may be more efficient, although bulkier, and so the three-drum pattern was rare as a land-based stationary boiler.

A package boiler is a factory-made boiler. Package boilers are available in a range of standard designs. Package boilers are used for heating and act as a steam generator for small power purposes such as self-powered industrial plants. Package boilers are low pressure designs. A low pressure means low temperature water in the heat exchanger. The large difference between the flame temperature and the heat exchanger discards most of the available entropy. Discarding most of the entropy caps the thermodynamic efficiency below the range needed to make a low pressure boiler suitable for a co-generation plants even when the available capacity is adequate for the application. Advantages of package boilers are that they can be delivered and installed as a complete insulated assembly that doesn’t require a large exclusion zone around itself. The required steam, water, fuel, and electrical connections can be made rapidly. These boilers are inexpensive to operate because their automatic burner management system doesn’t require continuous supervision and they have low scheduled maintenance costs.














