Related Research Articles

Trilobites are extinct marine arthropods that form the class Trilobita. Trilobites form one of the earliest known groups of arthropods. The first appearance of trilobites in the fossil record defines the base of the Atdabanian stage of the Early Cambrian period and they flourished throughout the lower Paleozoic before slipping into a long decline, when, during the Devonian, all trilobite orders except the Proetida died out. The last trilobites disappeared in the mass extinction at the end of the Permian about 251.9 million years ago. Trilobites were among the most successful of all early animals, existing in oceans for almost 270 million years, with over 22,000 species having been described.
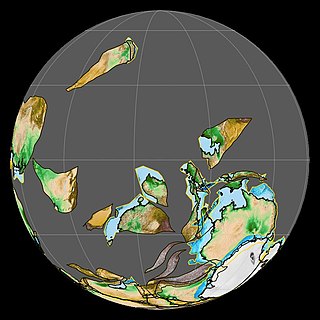
The Tournaisian is in the ICS geologic timescale the lowest stage or oldest age of the Mississippian, the oldest subsystem of the Carboniferous. The Tournaisian age lasted from 358.9 Ma to 346.7 Ma. It is preceded by the Famennian and is followed by the Viséan. In global stratigraphy, the Tournaisian contains two substages: the Hastarian and Ivorian. These two substages were originally designated as European regional stages.

Erbenochile is a genus of spinose phacopid trilobite, of the family Acastidae, found in Lower to Middle Devonian age rocks from Algeria and Morocco. Originally described from an isolated pygidium, the first complete articulated specimen of E. erbeni revealed the presence of extraordinarily tall eyes:
"Straight-sided towers of lenses... with [up to] 18 lenses in a vertical file"

Cyphaspis is a genus of small trilobite that lived from the Late Ordovician to the Late Devonian. Fossils have been found in marine strata in what is now Europe, Africa and North America. Various species had a compact body, and a large, bulbous glabellum. Many species had long spines arranged similarly to closely related genera, such as Otarian, Otarionella, Chamaeleoaspis, and Namuropyge.

Asteropyge is an extinct genus of trilobite. It lived from the end of the Lower Devonian into the Middle Devonian, in what are today France, Germany and Iran.
Boeckops is a genus of trilobites in the order Phacopida, which existed in what is now the Czech Republic. It was described by Chlupac in 1972, and the type species is Boeckops boecki, which was originally described as Phacops boecki by Hawle and Corda in 1847. Boeckops is also been discriped from the lower Devonian of Morocco and Algeria. The Genus Boeckops is interpreted as intermediate from between the traditional genus concept of Phacops and Reedops. The Genus Boeckops is regarded as problematic or difficult by McKellar et Chatterton 2009.
Tarijactinoides is a genus of trilobites in the order Phacopida, which existed in what is now Bolivia. It was described by Suárez Soruco in 1971, and the type species is Tarijactinoides jarcasensis.
Burmeisterella is a genus of trilobites in the order Phacopida. It was described by Reed in 1918.
Burmeisteria is a genus of trilobites in the order Phacopida that existed during the lower Devonian in what is now South Africa. It was described by Salter in 1865, and the type species is Burmeisteria herschelii, which was originally described under the genus Homalonotus by Murchison in 1839. It also contains the species B. accraensis, B. acuminata, and B. noticus. The type locality was the Bokkeveld Group.
Crotalocephalides is a genus of trilobites in the order Phacopida, that existed during the lower Devonian in what is now Germany. It was described by Alberti in 1967, and the type species is Crotalocephalides gaertneri, which the author had originally described under the genus Cheirurus in 1962. The type specimen was described from Ebersdorf, Upper Franconia.
Cryphaeoides is a genus of trilobites in the order Phacopida, that existed during the lower Devonian in what is now Bolivia. It was described by Delo in 1935, and the type species is Cryphaeoides rostratus, which originally described under the genus Cryphaeus by Kozlowski in 1923. It was described from the Sicasica Formation in Patacamaya.
Digonus is a genus of trilobites in the order Phacopida, that existed during the lower Devonian in what is now Germany. It was described by Gurich in 1909, and the type species is Digonus gigas, which was originally described under the genus Homalonotus by Roemer in 1843. It also contains the species Digonus accraensis and Digonus noticus, Digonus vialai, and Digonus zemmourensis. The type locality was in the Harz mountains.
Francovichia is a trilobite in the order Phacopida, that existed during the lower Devonian in what is now Bolivia. It was described by Branisa and Vanek in 1973, and the type species is Francovichia branisi, which was originally described under the genus Odontochile by Wolfart in 1968. It also contains the species, F. clarkei. The type locality was the Belén Formation.

Homalonotus is an extinct genus of trilobites in the order Phacopida. It contains several species, including H. armatus and H. roemeri. It is closely related to other trilobites such as Arduennella and Dipleura..

Kayserops is a trilobite in the order Phacopida, that existed during the lower Devonian in what is now Germany. It was described by Delo in 1935, and the type species is Kayserops kochi, which was originally described under the genus Cryphaeus by Kayser in 1883. The generic name is derived from the name of the species' author. The type locality was the Rhenish Massif.

The Devonian Jeffersonville Limestone is a mapped bedrock unit in Indiana and Kentucky. It is highly fossiliferous. The Vernon Fork Member contains Volcanic ash associated with the Tioga Bentonites.

Paleontology in Wisconsin refers to paleontological research occurring within or conducted by people from the U.S. state of Wisconsin. The state has fossils from the Precambrian, much of the Paleozoic, some a parts of the Mesozoic and the later part of the Cenozoic. Most of the Paleozoic rocks are marine in origin. Because of the thick blanket of Pleistocene glacial sediment that covers the rock strata in most of the state, Wisconsin’s fossil record is relatively sparse. In spite of this, certain Wisconsin paleontological occurrences provide exceptional insights concerning the history and diversity of life on Earth.
Bouleia is a genus of trilobites in the order Phacopida which existed during the lower Devonian in what is now Bolivia. It was described by Kozlowski in 1923, and the type species is B. dagincourti, which was originally described under the genus Phacops by Ulrich in 1892. It also contains the species B. sphaericeps, originally described by Kozlowski, also in 1923, as Dereimsia sphaericeps. The type locality was the Icla Formation in Padilla.

Gerastos is a genus of proetid trilobite in the family Proetidae that lived between the Pragian and Eifelian of the Lower-Middle Devonian, spanning approximately 21 million years.

The Vireux-Molhain national nature reserve (RNN104) is a national nature reserve of geological and paleontological interest. It is located in the Pointe de Givet, department of Ardennes, on the border between France and Belgium. It covers an area of 1.82 ha. The site is known as Customs Wall as it is near an old customs post. This outcrop of Middle Devonian shale is notable for the quantity and good state of preservation of its fossils. Trilobites are well-represented.
References
- ↑ Available Generic Names for Trilobites P.A. Jell and J.M. Adrain.
- ↑ Viersen, Allart P. VAN; Taghon, Peter (2020-01-30). "A poorly diversified trilobite association from the lower Emsian (Lower Devonian) in the Sankt Vith area (East Belgium)". Geologica Belgica. 23 (1–2): 19–28. doi: 10.20341/gb.2019.011 . ISSN 1374-8505.