Arginine is the amino acid with the formula (H2N)(HN)CN(H)(CH2)3CH(NH2)CO2H. The molecule features a guanidino group appended to a standard amino acid framework. At physiological pH, the carboxylic acid is deprotonated (−CO2−) and both the amino and guanidino groups are protonated, resulting in a cation. Only the l-arginine (symbol Arg or R) enantiomer is found naturally. Arg residues are common components of proteins. It is encoded by the codons CGU, CGC, CGA, CGG, AGA, and AGG. The guanidine group in arginine is the precursor for the biosynthesis of nitric oxide. Like all amino acids, it is a white, water-soluble solid.
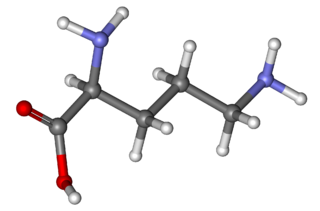
Ornithine is a non-proteinogenic amino acid that plays a role in the urea cycle. Ornithine is abnormally accumulated in the body in ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency. The radical is ornithyl.

Ornithine transcarbamylase (OTC) is an enzyme that catalyzes the reaction between carbamoyl phosphate (CP) and ornithine (Orn) to form citrulline (Cit) and phosphate (Pi). There are two classes of OTC: anabolic and catabolic. This article focuses on anabolic OTC. Anabolic OTC facilitates the sixth step in the biosynthesis of the amino acid arginine in prokaryotes. In contrast, mammalian OTC plays an essential role in the urea cycle, the purpose of which is to capture toxic ammonia and transform it into urea, a less toxic nitrogen source, for excretion.

N-Acetylglutamic acid (also referred to as N-acetylglutamate, abbreviated NAG, chemical formula C7H11NO5) is biosynthesized from glutamate and acetylornithine by ornithine acetyltransferase, and from glutamic acid and acetyl-CoA by the enzyme N-acetylglutamate synthase. The reverse reaction, hydrolysis of the acetyl group, is catalyzed by a specific hydrolase. It is the first intermediate involved in the biosynthesis of arginine in prokaryotes and simple eukaryotes and a regulator in the process known as the urea cycle that converts toxic ammonia to urea for excretion from the body in vertebrates.
N-Acetylglutamate synthase (NAGS) is an enzyme that catalyses the production of N-acetylglutamate (NAG) from glutamate and acetyl-CoA.

Aralkylamine N-acetyltransferase (AANAT), also known as arylalkylamine N-acetyltransferase or serotonin N-acetyltransferase (SNAT), is an enzyme that is involved in the day/night rhythmic production of melatonin, by modification of serotonin. It is in humans encoded by the ~2.5 kb AANAT gene containing four exons, located on chromosome 17q25. The gene is translated into a 23 kDa large enzyme. It is well conserved through evolution and the human form of the protein is 80 percent identical to sheep and rat AANAT. It is an acetyl-CoA-dependent enzyme of the GCN5-related family of N-acetyltransferases (GNATs). It may contribute to multifactorial genetic diseases such as altered behavior in sleep/wake cycle and research is on-going with the aim of developing drugs that regulate AANAT function.

L-Arginine:glycine amidinotransferase is the enzyme that catalyses the transfer of an amidino group from L-arginine to glycine. The products are L-ornithine and glycocyamine, also known as guanidinoacetate, the immediate precursor of creatine. Creatine and its phosphorylated form play a central role in the energy metabolism of muscle and nerve tissues. Creatine is in highest concentrations in the skeletal muscle, heart, spermatozoa and photoreceptor cells. Creatine helps buffer the rapid changes in ADP/ATP ratio in muscle and nerve cells during active periods. Creatine is also synthesized in other tissues, such as pancreas, kidneys, and liver, where amidinotransferase is located in the cytoplasm, including the intermembrane space of the mitochondria, of the cells that make up those tissues.
In enzymology, a N-succinylarginine dihydrolase (EC 3.5.3.23) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a [acyl-carrier-protein] S-acetyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the reversible chemical reaction
In enzymology, an arginine N-succinyltransferase (EC 2.3.1.109) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a glutamate N-acetyltransferase (EC 2.3.1.35) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an acetylornithine transaminase (EC 2.6.1.11) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a succinylornithine transaminase (EC 2.6.1.81) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
Delta-1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate synthetase (P5CS) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ALDH18A1 gene. This gene is a member of the aldehyde dehydrogenase family and encodes a bifunctional ATP- and NADPH-dependent mitochondrial enzyme with both gamma-glutamyl kinase and gamma-glutamyl phosphate reductase activities. The encoded protein catalyzes the reduction of glutamate to delta1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate, a critical step in the de novo biosynthesis of proline, ornithine and arginine. Mutations in this gene lead to hyperammonemia, hypoornithinemia, hypocitrullinemia, hypoargininemia and hypoprolinemia and may be associated with neurodegeneration, cataracts and connective tissue diseases. Alternatively spliced transcript variants, encoding different isoforms, have been described for this gene. As reported by Bruno Reversade and colleagues, ALDH18A1 deficiency or dominant-negative mutations in P5CS in humans causes a progeroid disease known as De Barsy Syndrome.
A ureohydrolase is a type of hydrolase enzyme. The ureohydrolase superfamily includes arginase, agmatinase, formiminoglutamase and proclavaminate amidinohydrolase. These enzymes share a 3-layer alpha-beta-alpha structure, and play important roles in arginine/agmatine metabolism, the urea cycle, histidine degradation, and other pathways.

In molecular biology, group IV pyridoxal-dependent decarboxylases are a family of enzymes comprising ornithine decarboxylase EC 4.1.1.17, lysine decarboxylase EC 4.1.1.18, arginine decarboxylase EC 4.1.1.19 and diaminopimelate decarboxylaseEC 4.1.1.20. It is also known as the Orn/Lys/Arg decarboxylase class-II family.
In molecular biology, the ATCase/OTCase family is a protein family which contains two related enzymes: aspartate carbamoyltransferase EC 2.1.3.2 and ornithine carbamoyltransferase EC 2.1.3.3. It has been shown that these enzymes are evolutionary related. The predicted secondary structure of both enzymes is similar and there are some regions of sequence similarities. One of these regions includes three residues which have been shown, by crystallographic studies to be implicated in binding the phosphoryl group of carbamoyl phosphate and may also play a role in trimerisation of the molecules. The N-terminal domain is the carbamoyl phosphate binding domain. The C-terminal domain is an aspartate/ornithine-binding domain.
N-succinylornithine carbamoyltransferase (EC 2.1.3.11, succinylornithine transcarbamylase, N-succinyl-L-ornithine transcarbamylase, SOTCase) is an enzyme with systematic name carbamoyl phosphate:N2-succinyl-L-ornithine carbamoyltransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Gingipain R is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction:

L-ornithine N5 monooxygenase (EC 1.14.13.195 or EC 1.14.13.196) is an enzyme which catalyzes one of the following chemical reactions:
L-ornithine + NADPH + O2 N(5)-hydroxy-L-ornithine + NADP+ + H2O L-ornithine + NAD(P)H + O2 N(5)-hydroxy-L-ornithine + NAD(P)+ + H2O