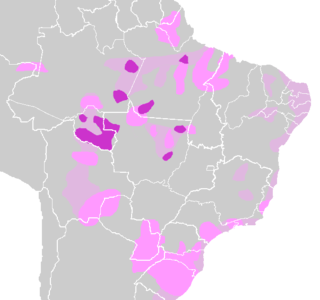
The Tupi or Tupian language family comprises some 70 languages spoken in South America, of which the best known are Tupi proper and Guarani.

The Chapacuran languages are a nearly extinct Native American language family of South America. Almost all Chapacuran languages are extinct, and the four that are extant are moribund. They are spoken in Rondônia in the southern Amazon Basin of Brazil and in northern Bolivia.

Munichi is a recently extinct language which was spoken in the village of Munichis, about 10 miles (16 km) west of Yurimaguas, Loreto Region, Peru. In 1988, there were two mother-tongue speakers, but they had not met since the 1970s. The last known fluent speaker, Victoria Huancho Icahuate, died in the late 1990s. As of 2009 there were several semi-speakers who retained significant lexical, and partial grammatical, knowledge of the language.
The Cahuapanan languages are a language family spoken in the Amazon basin of northern Peru. They include two languages, Chayahuita and Jebero, which are spoken by more than 11,300 people. Chayahuita is spoken by most of that number, but Jebero is almost extinct.
Arikapú or Maxubí is an endangered Yabutian language.
Katukinan (Catuquinan) is a language family consisting of two languages in Brazil, Katukina-Kanamarí and the perhaps moribund Katawixi. It is often not clear which names in the literature, which are generally tribal names and often correspond to dialects, refer to distinct languages. Indeed, they're close enough that some consider them all to be dialects of a single language, Kanamari.
Andaqui is an extinct language from the southern highlands of Colombia. It has been linked to the Paezan or Barbacoan languages, but no connections have been demonstrated. It was spoken by the Andaqui people of Colombia.
Aikanã is an endangered language isolate spoken by about 200 Aikanã people in Rondônia, Brazil. It is morphologically complex and has SOV word order. Aikanã uses the Latin script. The people live with speakers of Koaia (Kwaza).

The Yabutian or Jabutian languages are two similar moribund languages of southern Rondônia, Brazil, namely Arikapú (Maxubí) and Djeoromitxi (Yabutí/Jabotí). They are members of the Macro-Je language family.

The Nambikwaran languages are a language family of half a dozen languages, all spoken in the state of Mato Grosso in Brazil. They have traditionally been considered dialects of a single language, but at least three of them are mutually unintelligible.
The Tuparí languages of Brazil form a branch of the Tupian language family.
The Monde languages of Brazil form a branch of the Tupian language family.

The Ramarama languages of Rondônia, Brazil form a branch of the Tupian language family. They are Karo, or Ramarama, with 150 speakers, and the extinct Urumi.
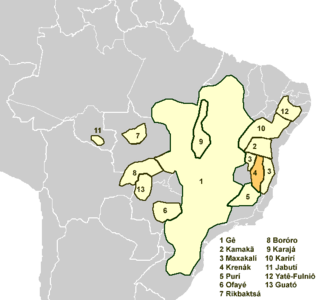
The Aimoré, Botocudoan or Borum languages, now sometimes known as Krenakan after the last one remaining, are a branch of the Macro-Jê languages – spoken mainly in Brazil – including moribund Krenak and extinct languages such as Guerén and Nakrehé. Loukotka (1968) considered them dialects of a single language, but more recent treatments describe at least some of them as separate languages.

The Kamakã languages are a small family of extinct Macro-Jê languages of Bahía, northeastern Brazil. The attested Kamakã languages are:
The Puruborá language of Brazil is one of the Tupian languages. It is also known as: Aurã, Cujubim, Burubora, Kuyubi, Migueleno, Miguelenho or Pumbora. Specifically it is spoken in the Brazilian state of Rondônia, in Costa Marques and around the headwaters of the Rio São Miguel tributary of the right bank of the Guaporé. It is nearly extinct, with only two native speakers reported in 2002.
Cañari and Puruhá are two poorly-attested extinct languages of the Marañón River basin in Ecuador that are difficult to classify. Puruhá is scarcely attested, and Cañari is known primarily from placenames. Loukotka (1968) suggests they may have been related instead to Mochica (Yunga) in a family called Chimuan, but Adelaar (2004:397) thinks it is more likely that they were Barbacoan languages.

Guamo is an extinct language of Venezuela. Kaufman (1990) finds a connection with the Chapacuran languages convincing.
The Yuruna languages of Brazil form a branch of the Tupian language family.








