
Aristotle was an Ancient Greek philosopher and polymath. His writings cover a broad range of subjects spanning the natural sciences, philosophy, linguistics, economics, politics, psychology and the arts. As the founder of the Peripatetic school of philosophy in the Lyceum in Athens, he began the wider Aristotelian tradition that followed, which set the groundwork for the development of modern science.

Heraclitus was an ancient Greek pre-Socratic philosopher from the city of Ephesus, which was then part of the Persian Empire.

Metaphysics is the branch of philosophy that studies the fundamental nature of reality. This includes the first principles of: being or existence, identity, change, space and time, cause and effect, necessity, actuality, and possibility.

Mortimer Jerome Adler was an American philosopher, educator, encyclopedist, and popular author. As a philosopher he worked within the Aristotelian and Thomistic traditions. He taught at Columbia University and the University of Chicago, served as chairman of the Encyclopædia Britannica board of editors, and founded the Institute for Philosophical Research.
Reason is the capacity of applying logic consciously by drawing conclusions from new or existing information, with the aim of seeking the truth. It is closely associated with such characteristically human activities as philosophy, science, language, mathematics, and art, and is normally considered to be a distinguishing ability possessed by humans. Reason is sometimes referred to as rationality.
In philosophy, rationalism is the epistemological view that "regards reason as the chief source and test of knowledge" or "any view appealing to reason as a source of knowledge or justification", often in contrast to other possible sources of knowledge such as faith, tradition, or sensory experience. More formally, rationalism is defined as a methodology or a theory "in which the criterion of truth is not sensory but intellectual and deductive".

Aristotelianism is a philosophical tradition inspired by the work of Aristotle, usually characterized by deductive logic and an analytic inductive method in the study of natural philosophy and metaphysics. It covers the treatment of the social sciences under a system of natural law. It answers why-questions by a scheme of four causes, including purpose or teleology, and emphasizes virtue ethics. Aristotle and his school wrote tractates on physics, biology, metaphysics, logic, ethics, aesthetics, poetry, theatre, music, rhetoric, psychology, linguistics, economics, politics, and government. Any school of thought that takes one of Aristotle's distinctive positions as its starting point can be considered "Aristotelian" in the widest sense. This means that different Aristotelian theories may not have much in common as far as their actual content is concerned besides their shared reference to Aristotle.

Natural philosophy or philosophy of nature is the philosophical study of physics, that is, nature and the physical universe. It was dominant before the development of modern science.

Thomism is the philosophical and theological school which arose as a legacy of the work and thought of Thomas Aquinas (1225–1274), the Dominican philosopher, theologian, and Doctor of the Church.

Great Books of the Western World is a series of books originally published in the United States in 1952, by Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc., to present the great books in 54 volumes.
Philosophical theology is both a branch and form of theology in which philosophical methods are used in developing or analyzing theological concepts. It therefore includes natural theology as well as philosophical treatments of orthodox and heterodox theology. Philosophical theology is also closely related to the philosophy of religion.
Aristotle first used the term ethics to name a field of study developed by his predecessors Socrates and Plato. In philosophy, ethics is the attempt to offer a rational response to the question of how humans should best live. Aristotle regarded ethics and politics as two related but separate fields of study, since ethics examines the good of the individual, while politics examines the good of the City-State, which he considered to be the best type of community.
The unmoved mover or prime mover is a concept advanced by Aristotle as a primary cause or "mover" of all the motion in the universe. As is implicit in the name, the unmoved mover moves other things, but is not itself moved by any prior action. In Book 12 of his Metaphysics, Aristotle describes the unmoved mover as being perfectly beautiful, indivisible, and contemplating only the perfect contemplation: self-contemplation. He equates this concept also with the active intellect. This Aristotelian concept had its roots in cosmological speculations of the earliest Greek pre-Socratic philosophers and became highly influential and widely drawn upon in medieval philosophy and theology. St. Thomas Aquinas, for example, elaborated on the unmoved mover in the Quinque viae.
Nous, or Greek νοῦς, sometimes equated to intellect or intelligence, is a concept from classical philosophy for the faculty of the human mind necessary for understanding what is true or real.

The four causes or four explanations are, in Aristotelian thought, four fundamental types of answer to the question "why?", in analysis of change or movement in nature: the material, the formal, the efficient, and the final. Aristotle wrote that "we do not have knowledge of a thing until we have grasped its why, that is to say, its cause." While there are cases in which classifying a "cause" is difficult, or in which "causes" might merge, Aristotle held that his four "causes" provided an analytical scheme of general applicability.

Alfred Edward Taylor, usually cited as A. E. Taylor, was a British idealist philosopher most famous for his contributions to the philosophy of idealism in his writings on metaphysics, the philosophy of religion, moral philosophy, and the scholarship of Plato. He was a fellow of the British Academy (1911) and president of the Aristotelian Society from 1928 to 1929. At Oxford he was made an honorary fellow of New College in 1931. In an age of universal upheaval and strife, he was a notable defender of Idealism in the Anglophone world.
Romanian philosophy is a name covering either:
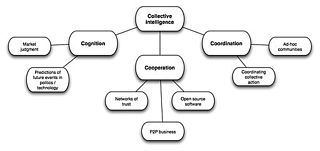
Common sense is sound, practical judgement concerning everyday matters, or a basic ability to perceive, understand, and judge in a manner that is shared by nearly all people.
The Conditions of Philosophy: Its Checkered Past, Its Present Disorder, and Its Future Promise is a 1965 book by the philosopher Mortimer Adler. The book is a reflexive account of philosophy's current status, and its future promise. Its main thesis is that philosophy can recover from its present state by meeting six conditions. Then he tackles related problems of methodology, the "Is-Ought" test, the "Mixed Question" test, as well as including incidental examinations of Popper, Heisenberg, James, etc., and reserving three chapters for the glories and fallacies of Ancient, Medieval and post-Cartesian philosophy.
This is a list of philosophical literature articles.












