
Alkaloids are a class of basic, naturally occurring organic compounds that contain at least one nitrogen atom. This group also includes some related compounds with neutral and even weakly acidic properties. Some synthetic compounds of similar structure may also be termed alkaloids. In addition to carbon, hydrogen and nitrogen, alkaloids may also contain oxygen, sulfur and, more rarely, other elements such as chlorine, bromine, and phosphorus.

Sodium is a chemical element with the symbol Na and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal. Sodium is an alkali metal, being in group 1 of the periodic table. Its only stable isotope is 23Na. The free metal does not occur in nature, and must be prepared from compounds. Sodium is the sixth most abundant element in the Earth's crust and exists in numerous minerals such as feldspars, sodalite, and halite (NaCl). Many salts of sodium are highly water-soluble: sodium ions have been leached by the action of water from the Earth's minerals over eons, and thus sodium and chlorine are the most common dissolved elements by weight in the oceans.

Resorcinol (or resorcin) is an organic compound with the formula C6H4(OH)2. It is one of three isomeric benzenediols, the 1,3-isomer (or meta-isomer). Resorcinol crystallizes from benzene as colorless needles that are readily soluble in water, alcohol, and ether, but insoluble in chloroform and carbon disulfide.

A natural product is a chemical compound or substance produced by a living organism—that is, found in nature. In the broadest sense, natural products include any substance produced by life. Natural products can also be prepared by chemical synthesis and have played a central role in the development of the field of organic chemistry by providing challenging synthetic targets. The term natural product has also been extended for commercial purposes to refer to cosmetics, dietary supplements, and foods produced from natural sources without added artificial ingredients.
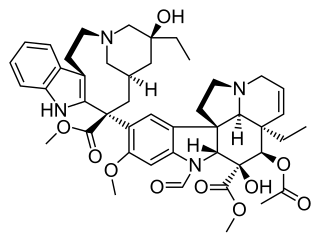
Vinca alkaloids are a set of anti-mitotic and anti-microtubule alkaloid agents originally derived from the periwinkle plant Catharanthus roseus and other vinca plants. They block beta-tubulin polymerization in a dividing cell.

Butriptyline, sold under the brand name Evadyne among others, is a tricyclic antidepressant (TCA) that has been used in the United Kingdom and several other European countries for the treatment of depression but appears to no longer be marketed. Along with trimipramine, iprindole, and amoxapine, it has been described as an "atypical" or "second-generation" TCA due to its relatively late introduction and atypical pharmacology. It was very little-used compared to other TCAs, with the number of prescriptions dispensed only in the thousands.
Reaxys is a web-based tool for the retrieval of chemistry information and data from published literature, including journals and patents. The information includes chemical compounds, chemical reactions, chemical properties, related bibliographic data, substance data with synthesis planning information, as well as experimental procedures from selected journals and patents. It is licensed by Elsevier.

Spirolactones are a class of functional group in organic chemistry featuring a cyclic ester attached spiro to another ring system. The name is also used to refer to a class of synthetic steroids, called steroid-17α-spirolactones, 17α-spirolactosteroids, or simply 17α-spirolactones, which feature their spirolactone group at the C17α position. They are antimineralocorticoids, or antagonists of the mineralocorticoid receptor, and have been employed clinically as potassium-sparing diuretics. Some also possess progestogenic and/or antiandrogen properties, which have both contributed to side effects and been utilized for medical indications. The spirolactones were developed by G. D. Searle & Company in the 1950s and thereafter and were denoted as "SC" compounds.

Penmesterol (INN), or penmestrol, also known as 17α-methyltestosterone 3-cyclopentyl enol ether, is a synthetic, orally active anabolic-androgenic steroid (AAS) that was developed in the early 1960s. It is the 3-cyclopentyl enol ether of methyltestosterone.
Streptomyces chartreusis is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from soil in Africa. Streptomyces chartreusis produces N-deacyltunicamycin, elsamicin A, aminoacylase and chartreusin.
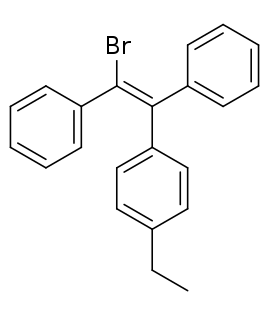
Broparestrol (INN), also known as α-bromo-α,β-diphenyl-β-p-ethylphenylethylene (BDPE), is a synthetic, nonsteroidal selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM) of the triphenylethylene group that has been used in Europe as a dermatological agent and for the treatment of breast cancer. The drug is described as slightly estrogenic and potently antiestrogenic, and inhibits mammary gland development and suppresses prolactin levels in animals. It is structurally related to clomifene and diethylstilbestrol. Broparestrol is a mixture of E- and Z- isomers, both of which are active and are similarly antiestrogenic but, unlike broparestrol, were never marketed.

Doisynolic acid is a synthetic, nonsteroidal, orally active estrogen that was never marketed. The reaction of estradiol or estrone with potassium hydroxide, a strong base, results in doisynolic acid as a degradation product, which retains high estrogenic activity, and this reaction was how the drug was discovered, in the late 1930s. The drug is a highly active and potent estrogen by the oral or subcutaneous route. The reaction of equilenin or dihydroequilenin with potassium hydroxide was also found to produce bisdehydrodoisynolic acid, the levorotatory isomer of which is an estrogen with an "astonishingly" high degree of potency, while the dextrorotatory isomer is inactive. Doisynolic acid was named after Edward Adelbert Doisy, a pioneer in the field of estrogen research and one of the discoverers of estrone.

LM22A-4 is a synthetic, selective small-molecule partial agonist of TrkB (EC50 for TrkB activation = 200–500 pM; IC50 for inhibition of BDNF binding to TrkB = 47 nM; IA = ~85%), the main receptor of brain-derived neurotrophic factor. It has been found to possess poor blood-brain-barrier penetration when administered systemically, so LM22A-4 has been given to animals instead via intranasal administration, with central nervous system TrkB activation observed. The compound produces neurogenic and neuroprotective effects in animals, and shows beneficial effects on respiration in animal models of Rett syndrome.
Streptomyces nitrosporeus is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from garden soil in Japan. Streptomyces nitrosporeus produces Benzastatin E, Benzastatin F, Benzastatin G Nitrosporeusine A and Nitrosporeusine B and the antibiotics nitrosporin and virantomycin and the inhibitor of angiotensin-converting enzyme foroxymithine. Streptomyces nitrosporeus can degrade cellulose.

Dianethole is a naturally occurring organic compound that is found in anise and fennel. It is a dimeric polymer of anethole. It has estrogenic activity, and along with anethole and photoanethole, may be responsible for the estrogenic effects of anise and fennel. These compounds bear resemblance to the estrogens stilbene and diethylstilbestrol, which may explain their estrogenic activity. In fact, it is said that diethylstilbestrol and related drugs were originally modeled after dianethole and photoanethole.

Allenolic acid, or allenoic acid, is a synthetic, nonsteroidal estrogen discovered in 1947 or 1948 that, although studied clinically, was never marketed. It is an open-ring or seco-analogue of steroidal estrogens like estrone and equilenin. The compound was named after Edgar Allen, one of the pioneers in estrogen research. Although described as an estrogen, allenolic acid probably is totally inactive at the receptor, whereas a derivative, allenestrol, is reported to be a potent estrogen. Another derivative of allenolic acid, methallenestril, is also a potent estrogen and, in contrast to allenolic acid and allenestrol, has been marketed.
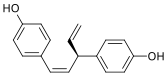
Nyasol, also known as cis-hinokiresinol or as (Z)-hinokiresinol, is a lignan that is found in Anemarrhena asphodeloides. It has estrogenic activity, acting as a selective agonist of the ERβ, and hence is a phytoestrogen. In addition, (-)-nyasol has been found to inhibit the production of eicosanoids and nitric oxide in vitro and shows anti-inflammatory effects.

Apparicine is a monoterpenoid indole alkaloid. It is named after Apparicio Duarte, a Brazilian botanist who studied the Aspidosperma species from which apparicine was first isolated. It was the first member of the vallesamine group of alkaloids to be isolated and have its structure established, which was first published in 1965. It has also been known by the synonyms gomezine, pericalline, and tabernoschizine.

Photoanethole is a naturally occurring organic compound that is found in anise and fennel. It has estrogenic activity, and along with anethole and dianethole, may be responsible for the estrogenic effects of anise and fennel. These compounds bear resemblance to the estrogens stilbene and diethylstilbestrol, which may explain their estrogenic activity. In fact, it is said that diethylstilbestrol and related drugs were originally modeled after photoanethole and dianethole.
Cerium(IV) perchlorate is an inorganic compound composed of cerium and perchloric acid. It has the chemical formula of Ce(ClO4)4.
















