
National Tsing Hua University (NTHU) is a public research university in Hsinchu, Taiwan. It was first founded in Beijing. After the Chinese Civil War, president Mei Yiqi and other academics fled with the retreating Nationalist government to Taiwan, where they founded National Tsing Hua University in 1956. The university remains independent and distinct from Tsinghua University in Beijing.
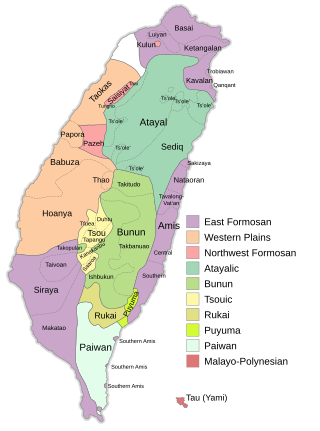
The Formosan languages are a geographic grouping comprising the languages of the indigenous peoples of Taiwan, all of which are Austronesian. They do not form a single subfamily of Austronesian but rather up to nine separate primary subfamilies. The Taiwanese indigenous peoples recognized by the government are about 2.3% of the island's population. However, only 35% speak their ancestral language, due to centuries of language shift. Of the approximately 26 languages of the Taiwanese indigenous peoples, at least ten are extinct, another four are moribund, and all others are to some degree endangered. They are national languages of Taiwan.
Academia Sinica is the national academy of the Republic of China (Taiwan). It is headquartered in Nangang, Taipei.
Ernest Julius Walter Simon, was a German sinologist and librarian.
Chih-Tang "Tom" Sah is a Chinese-American electronics engineer and condensed matter physicist. He is best known for inventing CMOS logic with Frank Wanlass at Fairchild Semiconductor in 1963. CMOS is used in nearly all modern very large-scale integration (VLSI) semiconductor devices.
David Der-wei Wang is a literary historian, critic, and the Edward C. Henderson Professor of Chinese Literature at Harvard University. He has written extensively on post-late Qing Chinese fiction, comparative literary theory, colonial and modern Taiwanese literature, diasporic literature, Chinese Malay literature, Sinophone literature, and Chinese intellectuals and artists in the 20th century. His notions such as "repressed modernities", "post-loyalism", and "modern lyrical tradition" are instrumental and widely discussed in the field of Chinese literary studies.

Der-Tsai Lee, also known as D. T. Lee, is a Taiwanese computer scientist, known for his work in computational geometry. For many years he was a professor at Northwestern University. He has been a distinguished research fellow of the Institute for Information Science at the Academia Sinica in Taipei, Taiwan since 1998. From 1998 to 2008, he was director of this institute. He had been the 14th President of National Chung Hsing University from August 1, 2011 to Jul 31, 2015. More than in academia, he had been an advisory committee member of National Security Council (Taiwan) from 2016 to 2020. Currently, he has been the chairman of Higher Education Evaluation and Accreditation Council of Taiwan since 2020.

Lo Tsung-lo was a Chinese botanist and plant physiologist. Lo was a main founder of modern plant physiology in China. He was the first President of National Taiwan University.
Gong Hwang-cherng (1934–2010) was a Taiwanese linguist who specialized in Sino-Tibetan comparative linguistics and the phonetic reconstruction of Tangut and Old Chinese.
Ping-ti Ho or Bingdi He, who also wrote under the name P.T. Ho, was a Chinese-American historian. He wrote widely on China's history, including works on demography, plant history, ancient archaeology, and contemporary events. He taught at University of Chicago for most of his career, and was president of the Association for Asian Studies in 1975, the first scholar of East Asian descent to have that honor.
Cho-yun Hsu is a Taiwanese historian.

Maw-Kuen Wu is a Taiwanese physicist specializing in superconductivity, low-temperature physics, and high-pressure physics. He was a professor of physics at University of Alabama in Huntsville, Columbia University, and National Tsing Hua University, the Director of the Institute of Physics at Academia Sinica, the President of National Dong Hwa University, and is currently a distinguished research fellow of the Institute of Physics, Academia Sinica, and international member of National Academy of Sciences.
Leroy L. Chang was a Taiwanese-American experimental physicist and solid state electronics researcher and engineer. Born in China, he studied in Taiwan and then the United States, obtaining his doctorate from Stanford University in 1963. As a research physicist he studied semiconductors for nearly 30 years at IBM's Thomas J. Watson Research Center, New York. This period included pioneering work on superlattice heterostructures with Nobel Prize-winning physicist Leo Esaki.

Zhu Jiahua or Chu Chia-hua was a Chinese scientist, geologist and Kuomintang politician in the Republic of China. In the early 1930s he served as Minister of Communications for the Nationalist Government in Nanjing. He was the Vice Premier in 1949–1950. Zhu became acting president of Academia Sinica upon the death of Cai Yuanpei in 1940, and was responsible for organizing the relocation of its institutes from China to Taiwan during the Chinese Civil War and a period of low monetary funds. Zhu repurposed funds originally set aside for Chinese students to study abroad. Although the Kuomintang government agreed with Zhu's actions when he first proposed them, Chiang Kai-shek later withdrew his approval and Zhu resigned as president of the Academia Sinica in 1957. Zhu was elected an academician of Academia Sinica in 1948. Following his death, Academia Sinica began hosting a lecture series in Zhu's honor.
Jing-shen Tao is professor emeritus of Chinese history at University of Arizona and Correspondence Research Fellow at Academia Sinica who specializes in medieval Chinese/Inner Asian history, particularly the Song dynasty, Liao dynasty, and Jin dynasty (1115–1234).
Chen Yung-fa is a Taiwanese historian.
Chang Yu-fa is a Chinese historian from Taiwan.
Liu Kwang-ching, who sometimes published under the name K.C. Liu, was a Chinese-born American historian of China. He taught at University of California-Davis from 1963 until his retirement in 1993. He is best known for his scholarship in late-Qing history, astute bibliographical work, and edited volumes, including co-editing Cambridge History of China volumes.
Ting Pang-hsin was a Chinese linguist, and an academician of the Academia Sinica.
Chang Hao was a Taiwanese historian and sinologist.





