
Vostok was a family of rockets derived from the Soviet R-7 Semyorka ICBM and was designed for the human spaceflight programme. This family of rockets launched the first artificial satellite and the first crewed spacecraft (Vostok) in human history. It was a subset of the R-7 family of rockets.
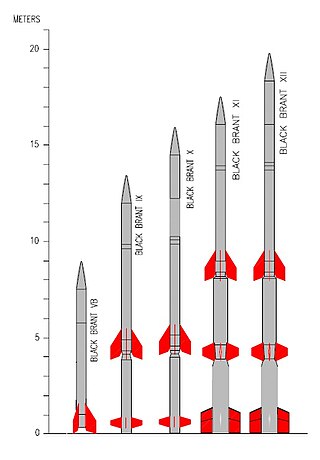
The Black Brant is a family of Canadian-designed sounding rockets originally built by Bristol Aerospace, since absorbed by Magellan Aerospace in Winnipeg, Manitoba. Over 800 Black Brants of various versions have been launched since they were first produced in 1961, and the type remains one of the most popular sounding rockets. They have been repeatedly used by the Canadian Space Agency and NASA.

The RL10 is a liquid-fuel cryogenic rocket engine built in the United States by Aerojet Rocketdyne that burns cryogenic liquid hydrogen and liquid oxygen propellants. Modern versions produce up to 110 kN (24,729 lbf) of thrust per engine in vacuum. RL10 versions were produced for the Centaur upper stage of the Atlas V and the DCSS of the Delta IV. More versions are in development or in use for the Exploration Upper Stage of the Space Launch System and the Centaur V of the Vulcan rocket.

Titan IIIB was the collective name for a number of derivatives of the Titan II ICBM and Titan III launch vehicle, modified by the addition of an Agena upper stage. It consisted of five separate rockets. The Titan-3B Agena-D was a basic Titan IIIA with an Agena D upper stage. The Titan 23B was a basic Titan II with an Agena upper stage, and the Titan 24B was the same concept, but using the slightly enlarged Titan IIIM rocket as the base. The Titan 33B was a Titan 23B with the Agena enclosed in an enlarged fairing, in order to allow larger payloads to be launched. The final member of the Titan IIIB family was the Titan 34B which was a Titan 24B with the larger fairing used on the Titan 33B.

The Scout family of rockets were American launch vehicles designed to place small satellites into orbit around the Earth. The Scout multistage rocket was the first orbital launch vehicle to be entirely composed of solid fuel stages. It was also the only vehicle of that type until the successful launch of the Japanese Lambda 4S in 1970.

Bélier is the designation of a French sounding rocket family. Three versions of the Bélier were launched between 1961 and 1970 at the CIEES launch facility at Hammaguir, the Salto di Quirra and Ile du Levant missile ranges, and Kourou Space Center.

Orion is the designation of a small American sounding rocket. The Orion has a length of 5.60 meters, a diameter of 0.35 m, a launch weight of 400 kg, a launch thrust of 7 kN and a ceiling of 85 kilometers. The Orion, built by NASA Goddard Space Flight Center's Wallops Flight Facility, is also used as an upper stage of sounding rockets, usually paired with a Terrier missile as the first stage, although Nike, Taurus and VS-30 rockets are also used.

The Dragon is a two-stage French solid propellant sounding rocket used for high altitude research between 1962 and 1973. It belonged thereby to a family of solid-propellant rockets derived from the Bélier, including the Centaure, the Dauphin and the Éridan.

The Dauphin is a French sounding rocket, flown six times between 1967 and 1979. It consists of a modification of the first stage of the Dragon with a larger payload nosecone.
Cora was a French experimental rocket. It was the largest rocket ever launched in Western Europe. It was primarily used for testing the second (Coralie) and third stages (Astris) of the multinational Europa Rocket, which was developed and produced by the European Launcher Development Organisation, the predecessor to the present day European Space Agency.

Centaure was a two-stage French sounding rocket consisting of a Venus first stage and a Belier second stage. It belongs to a family of solid-propellant rockets consisting of the Belier, Centaure, Dragon, Dauphin, and Eridan.

Kappa was a family of solid-fuel Japanese sounding rockets, which were built starting from 1956.

Nike Asp was an American sounding rocket. The Nike Asp has a ceiling of 220 km, a takeoff thrust of 217 kN, a takeoff weight of 700 kg, a diameter of 0.42 m and a length of 7.90 m.

Arcas was the designation of an American sounding rocket, developed by the Atlantic Research Corp., Alexandria, Va.
The Keldysh bomber was a Soviet design for a rocket-powered sub-orbital bomber spaceplane, which drew heavily upon work carried out by Eugen Sänger and Irene Bredt for the German Silbervogel project.

Waxwing was a British solid rocket motor used for apogee kick as the 3rd (upper) stage of the Black Arrow satellite launch vehicles. It was also known as Black Arrow-3. Waxwing was used to successfully place the Prospero X-3 satellite into low Earth orbit on 28 October 1971, Britain's only satellite launched on an indigenously developed launch vehicle. Before being separated from the Black Arrow launch vehicle, it would be spun on a turntable using six radial 'Imp' solid rocket motors to spin stabilise the satellite. This means that any discrepancy in thrust in any direction would be cancelled out. The Waxwing motor is now out of production.
The Nike stage or Nike booster, a solid fuel rocket motor, was developed by Hercules Aerospace for use as the first stage of the Nike Ajax and Nike Hercules missiles as part of Project Nike.

The Algol family of solid-fuel rocket stages and boosters is built by Aerojet and used on a variety of launch vehicles. It was developed by Aerojet from the earlier Jupiter Senior and the Navy Polaris programs. Upgrades to the Algol motor occurred from 1960 until the retirement of the Scout launch vehicle in 1994.

The Astris was an upper stage developed by ERNO Raumfahrttechnik GmbH and MBB as the third stage of the Europa 1 launch vehicle. It was the German contribution to the project and only flew activated four times. The high failure rate of the three and four stage rocket meant that the project was cancelled.

The Able rocket stage was a rocket stage manufactured in the United States by Aerojet as the second of three stages of the Vanguard rocket used in the Vanguard project from 1957 to 1959. The rocket engine used nitric acid and UDMH as rocket propellants. The Able rocket stage was discontinued in 1960. The improved Ablestar version was used as the upper stage of the Thor-Ablestar two stage launcher. The Ablestar second stage was an enlarged version of the Able rocket stage, which gave the Thor-Ablestar a greater payload capacity compared to the earlier Thor-Able. It also incorporated restart capabilities, allowing a multiple-burn trajectory to be flown, further increasing payload, or allowing the rocket to reach different orbits. It was the first rocket to be developed with such a capability and development of the stage took a mere eight months.




















