Related Research Articles

A tunicate is a marine invertebrate animal, a member of the subphylum Tunicata. It is part of the Chordata, a phylum which includes all animals with dorsal nerve cords and notochords. The subphylum was at one time called Urochordata, and the term urochordates is still sometimes used for these animals. They are the only chordates that have lost their myomeric segmentation, with the possible exception of the 'seriation of the gill slits'. However, doliolids still display segmentation of the muscle bands.

Ascidiacea, commonly known as the ascidians or sea squirts, is a paraphyletic class in the subphylum Tunicata of sac-like marine invertebrate filter feeders. Ascidians are characterized by a tough outer "tunic" made of a polysaccharide.

Salinas is a municipality in the northeast of the Brazilian state of Minas Gerais.

Ciona intestinalis is an ascidian, a tunicate with very soft tunic. Its Latin name literally means "pillar of intestines", referring to the fact that its body is a soft, translucent column-like structure, resembling a mass of intestines sprouting from a rock. It is a globally distributed cosmopolitan species. Since Linnaeus described the species, Ciona intestinalis has been used as a model invertebrate chordate in developmental biology and genomics. Studies conducted between 2005 and 2010 have shown that there are at least two, possibly four, sister species. More recently it has been shown that one of these species has already been described as Ciona robusta. By anthropogenic means, the species has invaded various parts of the world and is known as an invasive species.
Pseudomonas xanthomarina is a bacterium found in marine ascidians. Unlike many other members of the genus Pseudomonas, it is not fluorescent.
Taiobeiras is a municipality in the north of the state of Minas Gerais in Brazil. As of 2020 the population was 34,397 in an area of 1,194 km2. The elevation of the municipal seat is 821 meters. It became a municipality in 1953. The postal code (CEP) is 39550-000 and it belongs to the statistical microregion of Salinas

Rio Pardo de Minas is a municipality in the northeast of the Brazilian state of Minas Gerais. Its population in 2020 was 31,045 inhabitants in a total area of 3,117 square kilometres (1,203 sq mi).

Berizal is a Brazilian municipality located in the northeast of the state of Minas Gerais. As of 2020 the population was 4,764 in a total area of 493 km².
Mina is a town and municipality located in the Northwestern part of the northeastern Mexican state of Nuevo León. The population was 4,309 at the 2005 census. Its name honors Spaniard insurgent general Francisco Javier Mina, who fought for the Mexican side in the independence movement from Spain. Located at the northwestern part of the state of Nuevo León. Mina is a renowned tourist destination, for its mysticism and legends in the state of Nuevo León.

Pyura stolonifera, commonly known in South Africa as "red bait", is a sessile ascidian, or sea squirt, that lives in coastal waters attached to rocks or artificial structures. Sea squirts are named for their habit of squirting a stream of water from their exhalant siphons when touched at low tide.
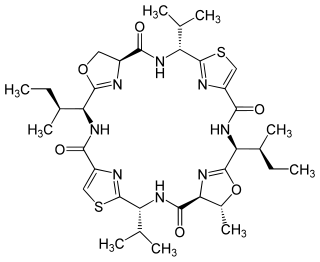
Patellamide A is a peptide natural product produced by Prochloron didemni, a cyanobacterial symbiont of Lissoclinum patella, and was first isolated in 1981. Patellamide A is one of many didemnid peptides. Other closely related peptides include patellamides B, C, and D and trunkamide. The patellamides and trunkamide show moderate cytotoxicity and activity against multidrug resistant cancer cell lines.
A meroterpene is a chemical compound having a partial terpenoid structure.
Cardiosporidium is a genus of parasitic alveolates in the phylum Apicomplexa. It infects the ascidian Ciona intestinalis.
Spermosin is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction

Halocyamines are antibiotic peptides isolated from the ascidian Halocynthia roretzi.
Merogregarina is a genus of parasitic alveolate in the phylum Apicomplexa. Species in this genus infect marine invertebrates.

Eudistoma is a genus of sea squirts belonging to the class Ascidiacea. It was first described in 1909 by Maurice Caullery. Originally it was thought to be a subgenus of Distoma. Eudistoma is the most species-rich genus in the family Polycitoridae, with 124 valid species as of 2014. They are found in tropical and temperate waters; some species are also found in the Antarctic and subtropical area.

Pleurobranchus areolatus is a species of pleurobranchid sea slug, a type of marine gastropod mollusc, commonly found in the Caribbean Sea. It is up to 15 cm long and it feeds on ascidians.
Nephromyces is a genus of apicomplexans that are symbionts of the ascidian genus Molgula.
Aureisphaera is a genus of bacteria from the family of Flavobacteriaceae.
References
- 1 2 "Species: Aureisphaera salina". lpsn.dsmz.de.
- 1 2 Yoon, Jaewoo; Adachi, Kyoko; Kasai, Hiroaki (1 August 2016). "Aureisphaera salina sp. nov., a member of the family Flavobacteriaceae isolated from an ascidian". International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology. 66 (8): 2999–3004. doi: 10.1099/ijsem.0.001132 .