The United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) established an international environmental treaty to combat "dangerous human interference with the climate system", in part by stabilizing greenhouse gas concentrations in the atmosphere. It was signed by 154 states at the United Nations Conference on Environment and Development (UNCED), informally known as the Earth Summit, held in Rio de Janeiro from 3 to 14 June 1992. Its original secretariat was in Geneva but relocated to Bonn in 1996. It entered into force on 21 March 1994.

Alliance of Small Island States (AOSIS) is an intergovernmental organization of low-lying coastal and small island countries. AOSIS was established in 1990, ahead of the Second World Climate Conference. The main purpose of the alliance is to consolidate the voices of Small Island Developing States (SIDS) to address global warming.
Post-Kyoto negotiations refers to high level talks attempting to address global warming by limiting greenhouse gas emissions. Generally part of the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC), these talks concern the period after the first "commitment period" of the Kyoto Protocol, which expired at the end of 2012. Negotiations have been mandated by the adoption of the Bali Road Map and Decision 1/CP.13.

The 2009 United Nations Climate Change Conference, commonly known as the Copenhagen Summit, was held at the Bella Center in Copenhagen, Denmark, between 7 and 18 December. The conference included the 15th session of the Conference of the Parties to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) and the 5th session of the Conference of the Parties serving as the meeting of the Parties to the Kyoto Protocol. According to the Bali Road Map, a framework for climate change mitigation beyond 2012 was to be agreed there.

Brian Christopher Deese is an American economic and political advisor who was the 13th Director of the National Economic Council, serving under President Joe Biden.

Karen Christiana Figueres Olsen is a Costa Rican diplomat who has led national, international and multilateral policy negotiations. She was appointed Executive Secretary of the UN Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) in July 2010, six months after the failed COP15 in Copenhagen. During the next six years she worked to rebuild the global climate change negotiating process, leading to the 2015 Paris Agreement, widely recognized as a historic achievement.
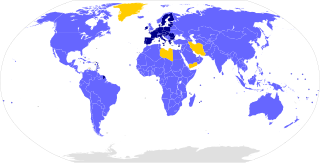
The Paris Agreement, often referred to as the Paris Accords or the Paris Climate Accords, is an international treaty on climate change. Adopted in 2015, the agreement covers climate change mitigation, adaptation, and finance. The Paris Agreement was negotiated by 196 parties at the 2015 United Nations Climate Change Conference near Paris, France. As of February 2023, 195 members of the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) are parties to the agreement. Of the three UNFCCC member states which have not ratified the agreement, the only major emitter is Iran. The United States withdrew from the agreement in 2020, but rejoined in 2021.

The United Nations Climate Change Conference, COP19 or CMP9 was held in Warsaw, Poland from 11 to 23 November 2013. This is the 19th yearly session of the Conference of the Parties to the 1992 United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) and the 9th session of the Meeting of the Parties to the 1997 Kyoto Protocol. The conference delegates continue the negotiations towards a global climate agreement. UNFCCC's Executive Secretary Christiana Figueres and Poland's Minister of the Environment Marcin Korolec led the negotiations.

The United Nations Climate Change Conferences are yearly conferences held in the framework of the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC). They serve as the formal meeting of the UNFCCC parties to assess progress in dealing with climate change, and beginning in the mid-1990s, to negotiate the Kyoto Protocol to establish legally binding obligations for developed countries to reduce their greenhouse gas emissions. Starting in 2005 the conferences have also served as the "Conference of the Parties Serving as the Meeting of Parties to the Kyoto Protocol" (CMP); also parties to the convention that are not parties to the protocol can participate in protocol-related meetings as observers. From 2011 to 2015 the meetings were used to negotiate the Paris Agreement as part of the Durban platform, which created a general path towards climate action. Any final text of a COP must be agreed by consensus.

The 2016 United Nations Climate Change Conference was an international meeting of political leaders and activists to discuss environmental issues. It was held in Marrakech, Morocco, on 7–18 November 2016. The conference incorporated the twenty-second Conference of the Parties (COP22), the twelfth meeting of the parties to the Kyoto Protocol (CMP12), and the first meeting of the parties to the Paris Agreement (CMA1). The purpose of the conference was to discuss and implement plans about combatting climate change and to "[demonstrate] to the world that the implementation of the Paris Agreement is underway". Participants work together to come up with global solutions to climate change.

Hakima El Haite is a Moroccan climate scientist, entrepreneur and politician. In 1994 she founded EauGlobe, the first environmental engineering firm in the MENA region. She served as Minister Delegate in Charge of the Environment for the Kingdom of Morocco from 2013 to 2017. In 2015, she was elected Vice President of United National International Climate Conference (COP21). She was appointed Special Envoy for Climate Change of the Kingdom of Morocco from 2015 to 2017 and the High Level Climate Champion of the United Nations International Climate Conference (COP22) in 2016 – 2017.

Robert K. Dixon is an energy, environment, and economic expert at the Office of International Affairs, US Department of Energy headquarters in Washington, DC, USA.
Article 6 of the Paris Agreement on climate change enables Parties to cooperate in implementing their nationally determined contributions (NDCs). Among other things, this means that emission reductions can be transferred between countries and counted towards NDCs. Agreement on the provisions of Article 6 was reached after intensive negotiations lasting several years.

Lavanya Rajamani is an Indian lawyer, author and professor whose area of expertise is international climate change law, environmental law, and policy. She is currently a professor of International Environmental Law at the Faculty of Law, University of Oxford, a Yamani Fellow in Public International Law at St Peter's College, Oxford, and a visiting professor at the Centre for Policy Research.
The Climate Law and Governance Initiative is an international consortium of partners in the climate law community working to build capacity and knowledge relating to law and governance approaches to address climate change. Ongoing research projects carried out by its partner institutions support the hosting of events and specialized capacity-building workshops in parallel with the annual climate negotiations under the UNFCCC. The initiative's focus is the effective implementation of SDG 13 on Climate Change. Its events are officially endorsed by the UNFCCC.
The history of climate change policy and politics refers to the continuing history of political actions, policies, trends, controversies and activist efforts as they pertain to the issue of global warming and other environmental anomalies. Dryzek, Norgaard, and Schlosberg suggest that critical reflection on the history of climate policy is necessary because it provides 'ways to think about one of the most difficult issues we human beings have brought upon ourselves in our short life on the planet’.
Cherkaoui is a surname. Notable people with this surname include:

Hatim Aznague is a climate justice advocate and activist from Morocco. He is known for mobilizing youth. and encouraging the government to engage and involve youth in the process of decision making related to sustainable development and climate change.
Joshua Amponsem is a Ghanaian climate advocate and a co-founder of Green Africa Youth Organization (GAYO). He is the climate specialist at the Office of the UN Secretary General's Envoy on Youth. He is the Lead Author of Adapt for Our Future, the first-ever research paper on the role of youth in advancing climate adaptation. His career has been more focused on grassroots climate and waste management solutions while advancing youth engagement in resilience building, disaster risk reduction, and climate change adaptation at the international level.

Elise Breyton Buckle is a French environmental policy expert and lecturer. She is the co-president of Climate & Sustainability, co-founder of SHE Changes Climate and board member of the Climate Action Accelerator. Buckle is a professor at the Graduate Institute of International and Development Studies for the Executive Programme Graduate Institute of Geneva. She also teaches Sustainability, Innovation and Entrepreneurship at the Glion Institute of Business Education. She was a local appointee in the municipal government of Nyon, Switzerland.













