
Mohave County is in the northwestern corner of the U.S. state of Arizona. As of the 2020 census, its population was 213,267. The county seat is Kingman, and the largest city is Lake Havasu City. It is the fifth largest county in the United States.
North Central Arizona is a geographical region of Arizona. It is in the Transition Zone between the Basin and Range Province and the Colorado Plateau, and has some of the most rugged and scenic landscapes in Arizona.

Wire Pass Trailhead is a recreation access point in Kane County, Utah that features several trails leading to natural points of interest.

The Arizona Strip is the part of Arizona lying north of the Colorado River. Despite being larger in area than several U.S. states, the entire region has a population of fewer than 10,000 people. Consisting of northeastern Mohave County and northwestern Coconino County, the largest settlements in the Strip are Colorado City, Fredonia, and Beaver Dam, with smaller communities of Scenic, Littlefield and Desert Springs. The Kaibab Indian Reservation lies within the region. Lying along the North Rim of the Grand Canyon creates physical barriers to the rest of Arizona. Only three major roads traverse the region, I-15 crosses the northwestern corner while Arizona State Route 389 and U.S. Route 89A crosses the northeastern part of the strip, US 89A crosses the Colorado River via the Navajo Bridge, providing the only direct road connection between the strip and the rest of the state. The nearest metropolitan area is the St. George, Utah metro area, to which the region is more connected than to the rest of Arizona.

The Sierra Ancha is a mountain range in Gila County, in central Arizona. It lies between Roosevelt Lake to the south, the Tonto Basin to the west, Cherry Creek to the east, and Pleasant Valley to the north. The range is one of several, including the Bradshaw Mountains, Mingus Mountain of the Black Hills, and the Mazatzal Mountains, which form a transitional zone between the lowland deserts of southern Arizona and the Colorado Plateau of northeastern Arizona. The highest point in the range is Aztec Peak, at an elevation of 2345 m (7694 ft).

Kanab Creek is one of the many tributaries of the Colorado River. It begins in Kane County, Utah, just south of the watershed to the Great Basin and flows 125 miles (201 km) south to the Colorado River.

The Black Mountains of northwest Arizona are an extensive, mostly linear, north-south trending 75 miles (121 km) long mountain range. It forms the north-south border of southwest Mohave County as it borders the eastern shore of the south-flowing Colorado River from Hoover Dam.
The San Cristobal Wash is an ephemeral wash and watercourse of the San Cristobal Valley, flowing north into the Gila River Valley of the southwestern desert region of Arizona. Besides Death Valley, the Chihuahuan Desert area, and regions of Baja Peninsula North America, the southeast California deserts along the Lower Colorado River Valley, this drainage region is in the harshest desert regions of North America.
Tenmile Wash is an ephemeral wash and watercourse about 85 miles (137 km) long in the northern Sonoran Desert of south-central Arizona. It forms the eastern drainage of a two drainage system of dry washes into the Gila River Valley; both flow northwesterly, and the western drainage is the San Cristobal Wash Drainage of approximately the same length.
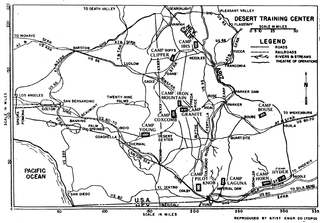
The Desert Training Center (DTC), also known as California–Arizona Maneuver Area (CAMA), was a World War II training facility established in the Mojave Desert and Sonoran Desert, largely in Southern California and Western Arizona in 1942.
The Harcuvar Mountains are a narrow mountain range in western-central Arizona, United States. The range lies just east of the north-south Colorado River, and south of the east-west, west-flowing Bill Williams River, from Alamo Lake.
The Park Valley of Arizona is a small, northwest by southeast trending valley centered on the Gila River in central-east Yuma County. The southeast border of the valley is the northern Sentinel Plain of Maricopa County which drains northwestwards toward the Gila River Valley.
Dutch Flat of Arizona is a valley south of the Sacramento Valley and Interstate 40 in southern Mohave County.
The Belmont Mountains are a 25 mi (40 km) long, arid, low elevation mountain range about 50 mi west of Phoenix, Arizona in the northern Sonoran Desert, north of the Gila River. The range is in the south of a region of two parallel washes; the Bouse Wash flows northwest to the Colorado River, and the Centennial Wash flows southeast to meet the Gila River.
The Chino Valley of Arizona is a large, 70-mi (113 km) long valley, centered on Seligman, Arizona in northwest Yavapai County and southwest Coconino County. The valley is located at the southwest of the Coconino Plateau and lies in the extreme northwest of Arizona's transition zone.
The Hualapai War, or Walapai War, was an armed conflict fought from 1865 to 1870 between the Hualapai native Americans and the United States in Arizona Territory. The Yavapai also participated on the side of the Hualapai and Mohave scouts were employed by the United States Army. Following the death of the prominent Yavapai leader Anasa in April 1865, the natives began raiding American settlements which provoked a response by the United States Army forces stationed in the area. By the spring of 1869 disease forced the majority of the Hualapais to surrender though some skirmishing continued for almost two more years.

Deer Valley or Deer Valley Village is one of the 15 urban villages that make up Phoenix, Arizona, United States. As of 2010, the population was 165,656, 25% of whom were under 18 years of age. The origin of the name is unclear; it first appeared on a 1921 General Land Office map of the area describing the valley created by Skunk Creek.
Hualapai Valley is a valley in Mohave County, Arizona.

Walnut Creek is an urban stream in the San Gabriel Valley of Southern California, and is a tributary of the San Gabriel River. The creek begins at the Puddingstone Dam of Puddingstone Reservoir in Frank G. Bonelli Regional Park and flows westward for about 13 miles (21 km), through San Dimas, Covina, West Covina and Baldwin Park, to join the San Gabriel River in El Monte.
Granite Wash Pass is a gap between the Granite Wash Mountains and the Little Harquahala Mountains, in La Paz County, Arizona. Granite Wash Pass is located at the southwest end of the Granite Wash Mountains and the northwest end of the Little Harquahala Mountains. The apex of the pass is at an elevation of 1,834 feet/559 meters.
!["Aztec Pass," Western Arizona, 1,330 miles from Missouri River, [ca. 1867-1868]. Photographs of the American West, Boston Public Library 'Aztec Pass,' Western Arizona, 1,330 miles from Missouri River. (Boston Public Library) (cropped).jpg](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/7/7f/%27Aztec_Pass%2C%27_Western_Arizona%2C_1%2C330_miles_from_Missouri_River._%28Boston_Public_Library%29_%28cropped%29.jpg/220px-%27Aztec_Pass%2C%27_Western_Arizona%2C_1%2C330_miles_from_Missouri_River._%28Boston_Public_Library%29_%28cropped%29.jpg)









